High-oleic acid peanut mutant gene AhFAD2B-814 and application thereof
An ahfad2b-814, mutated gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problem of peanut high oleic acid mutation gene that has not been published or published, and achieves increased genetic diversity and oleic acid content. , the effect of broadening the genetic basis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1: Screening and Purification of High Oleic Acid Peanut Mutant Individual Plants
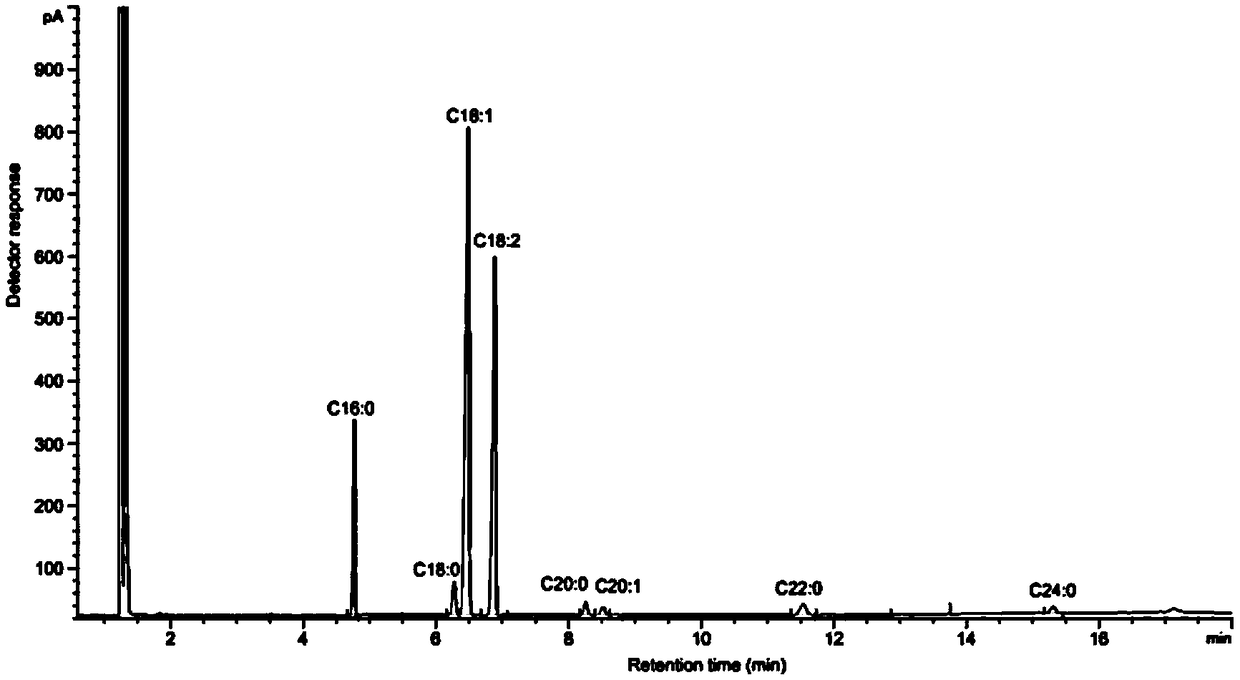
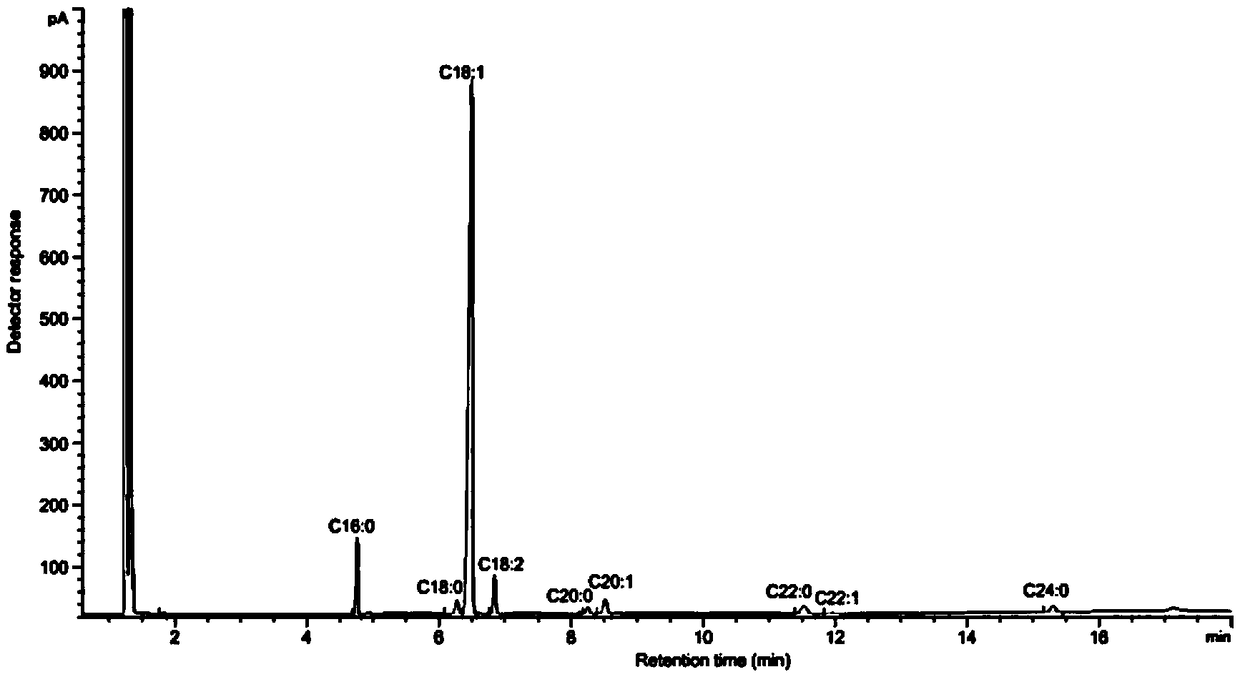
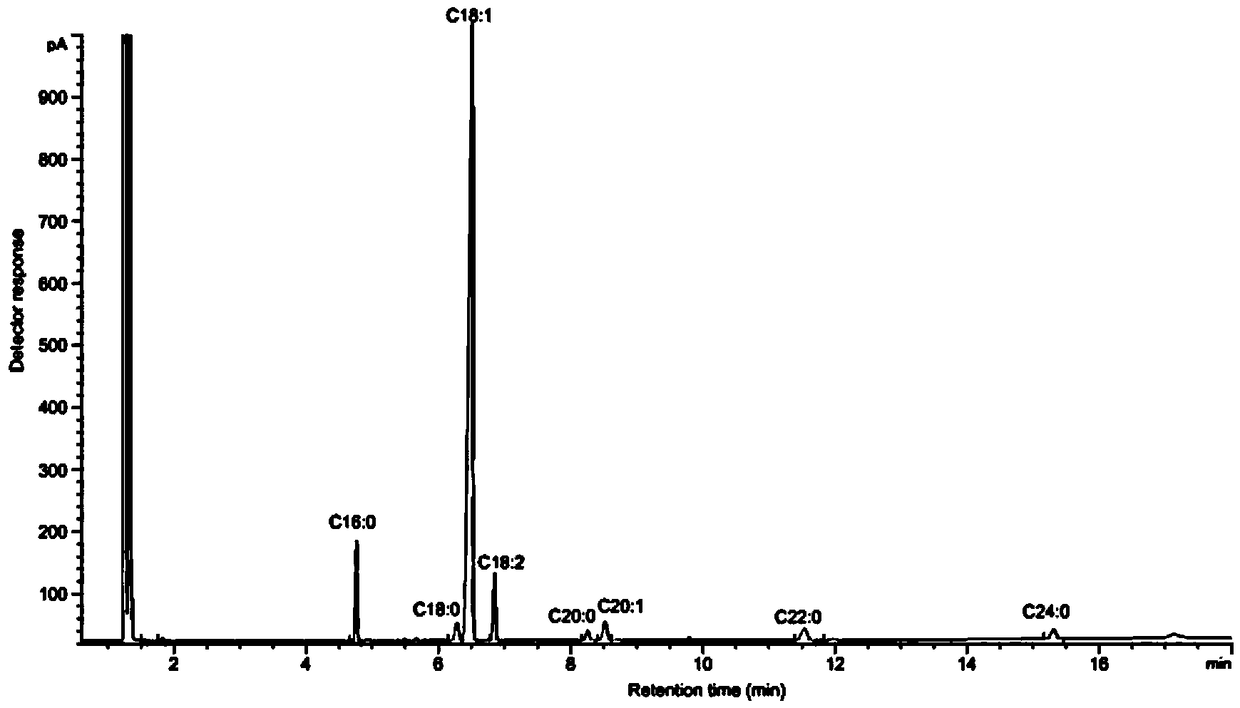
[0061] The collected 220 peanut germplasm resource materials and the created 150 germplasm were planted in the field, planted in rows according to the materials, sowed in a single seed, harvested after selfing, and harvested seeds in a single plant; in the second year, 3 seeds were selected for each material. A single plant was planted in a row in the field, and the self-inbred single plant was harvested as a single plant again, and the seeds were naturally air-dried and peeled off. Perten (Perten) DA7200 diode array near-infrared analyzer was used to detect the concentration of each individual plant seed. For the content of fatty acid, 9 rows with oleic acid content of each plant above 70% were screened out.
[0062] Utilize American Agilent 6890A gas chromatographic analyzer to further accurately detect the fatty acid composition and content of these strains, the steps are as fo...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2: Cloning and sequencing of mutant nucleic acid sequence of high oleic acid peanut oleic acid dehydrogenase gene
[0073] (1) Identify and obtain candidate genes for high oleic traits in peanuts.
[0074] The biological pathway of plant fatty acid synthesis has been relatively clear. Studies have confirmed that there are two pathways for the biosynthesis of oleic acid: one uses stearic acid as a substrate to generate oleic acid under the catalysis of stearyl-CoA desaturase (SAD), which is the main pathway for oleic acid synthesis. The second way is to use palmi-enoic acid as a substrate to further extend the carbon chain under the action of fatty acyl-CoA to generate oleic acid. Part of the synthesized oleic acid is bound to the carbon frame of triglyceride to become the final storage oil, part of it is dehydrogenated under the action of oleic acid dehydrogenase to further form linoleic acid with double unsaturated bonds, and a small part is in the Eicosenoic...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Example 3: Expression and functional analysis of a novel mutant gene of high oleic acid peanut AhFAD2B in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
[0094] The above-mentioned peanut AhFAD2 gene belongs to the endoplasmic reticulum oleate dehydrogenase, and the first choice for its functional analysis is yeast, because yeast contains the electron transfer system and suitable membrane environment required by this type of dehydrogenase, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Due to the lack of Δ12 (ω-6) and ω-3 fatty acid dehydrogenase, endogenous polyunsaturated fatty acids cannot be produced, and the intracellular fatty acid composition is simple, so it is the most ideal expression system for exogenous fatty acid dehydrogenase genes. INVScI / pYES2.0 is a commonly used Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression system for expressing exogenous fatty acid dehydrogenase.
[0095] According to the multiple cloning site of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector pYES2.0, the restriction sites of KpnI and Eco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com