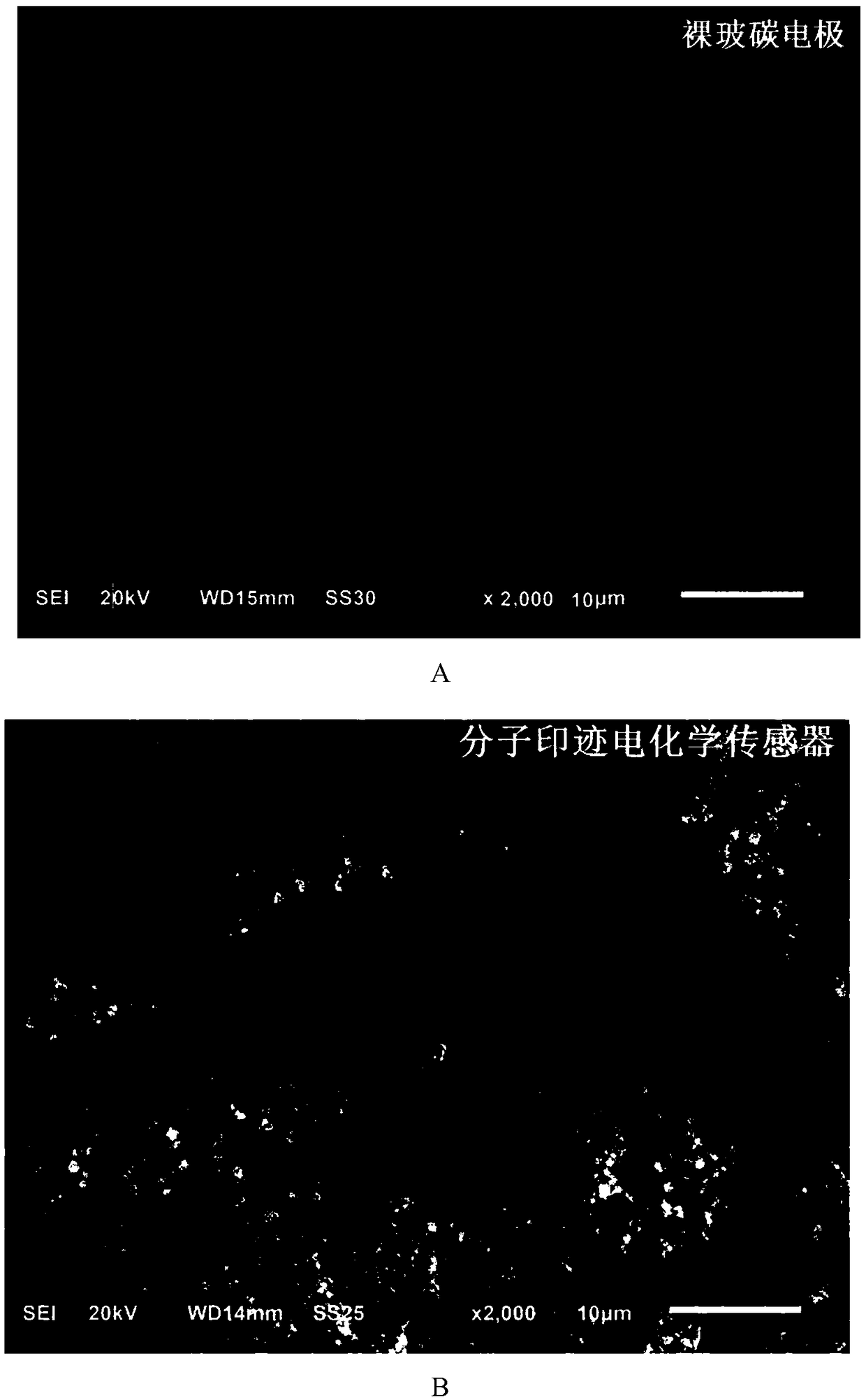
Molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor for selectively identifying chloramphenicol and fabrication method of molecular imprinting electrochemical sensor
A molecular imprinting and electrochemical technology, applied in the fields of electrochemical variables of materials, scientific instruments, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome method of grafting initiators on the membrane surface, affecting the conductivity and sensitivity of sensors, conductivity or sensitivity problems, etc. Achieve the effect of shortened preparation time, high selective recognition ability, guaranteed conductivity and sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Preparation of initiator graphene-hemin complex
[0037] Monolayer graphene oxide (0.83mmol, sheet diameter 50-200nm) and hemin (0.015mmol) were dissolved in 20ml of 50% ethanol solution, the pH was adjusted to 10.0 with 1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, and ultrasound was performed for 30 minutes Finally, reflux at 100 degrees for 1 hour, cool and store in the dark;
[0038] (2) Preparation of molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors
[0039] 2.1) Disperse the prepared graphene-hemin complex into dimethylformamide to make a 1 mg / mL solution, take 10 μL drop-coated on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, and dry it under an infrared lamp.
[0040] 2.2) Dissolve functional monomer methacrylic acid (4 mmol) and template molecule chloramphenicol (1 mmol) in 2.5 ml acetonitrile, sonicate for 10 minutes, and incubate at room temperature for 1 hour;
[0041] 2.3) Insert the graphene-hematin modified electrode prepared in step 2.1) into the crosslinker N,N-me...
Embodiment 2
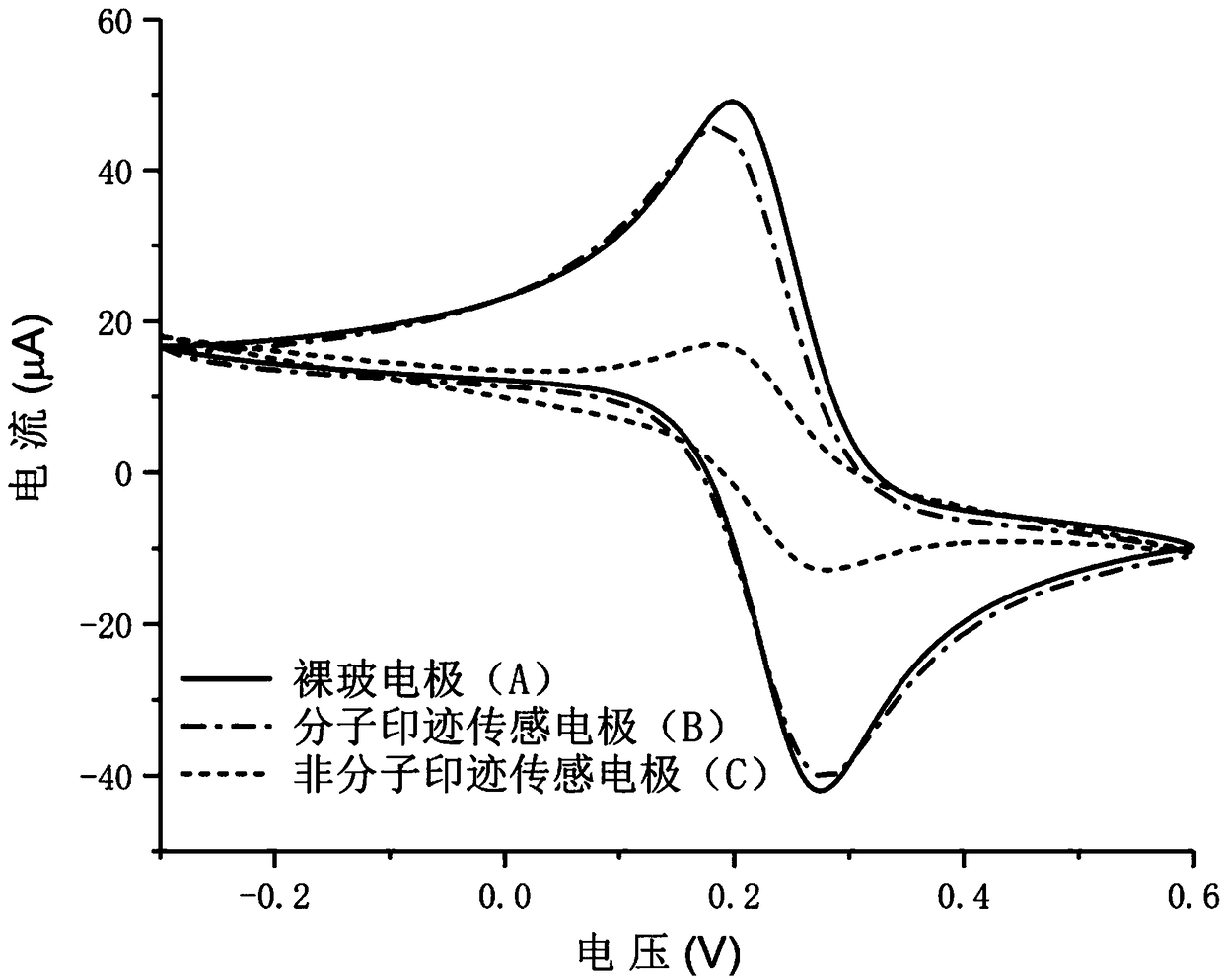
[0045] The molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing electrode, the non-molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing electrode and the bare glassy carbon electrode prepared in Example 1 were sequentially inserted into a three-electrode system consisting of a platinum counter electrode and a reference electrode in 10 ml 5 mmol L -1 K 3 Fe(CN) 6 In the aqueous solution, cyclic voltammetry scanning was carried out for 10 circles in the potential range of -0.3 ~ 0.6V, and the scanning speed was 50mV s -1 , to obtain the corresponding cyclic voltammetry curve. The result is as figure 2 As shown, after the surface of the glassy carbon electrode is modified with a molecularly imprinted polymer film, the current response becomes smaller, while the glassy carbon electrode modified with a non-molecularly imprinted polymer film has almost no current response. This is because the chloramphenicol molecularly imprinted film partially blocks the redox electrochemical behavior of the...
Embodiment 3
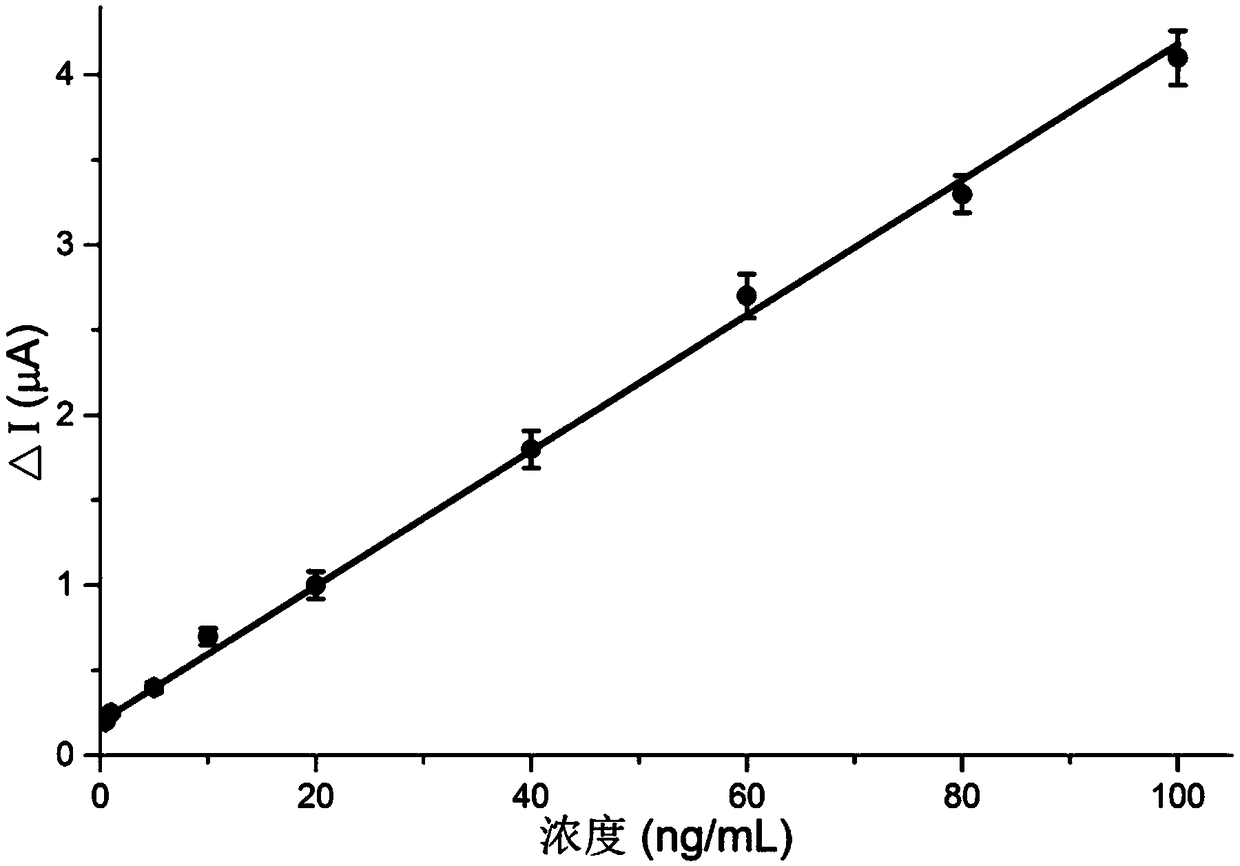
[0047] Insert the three-electrode system composed of the molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing electrode, platinum counter electrode and reference electrode prepared in Example 1 into 10 ml of chloramphenicol containing 5 mmol L -1 K 3 Fe(CN) 6 In the aqueous solution, the concentration of chloramphenicol is 0-100 μg / L respectively. After magnetic stirring for 10 minutes, cyclic voltammetry scanning was carried out in the potential range of -0.3 to 0.6V for 10 cycles, and the scanning speed was 50mV s -1 , to obtain the mean value of the peak current response difference with the bare glassy carbon electrode, and to obtain the relationship curve between the peak current difference and the concentration of the chloramphenicol standard solution. The result is as image 3 As shown, in the concentration range of 0.5-100ng / mL, the peak current response maintains good linearity with the concentration of chloramphenicol, and the detection limit is 0.1ng / mL, which can realiz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com