Extraction-free direct amplification reagent for real-time fluorescent quantitation PCR and application thereof
A real-time fluorescence quantitative, extraction-free technology, applied in the biological field, can solve a large number of problems, complex operations, etc., to achieve high economic benefits, shorten the process, and improve efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
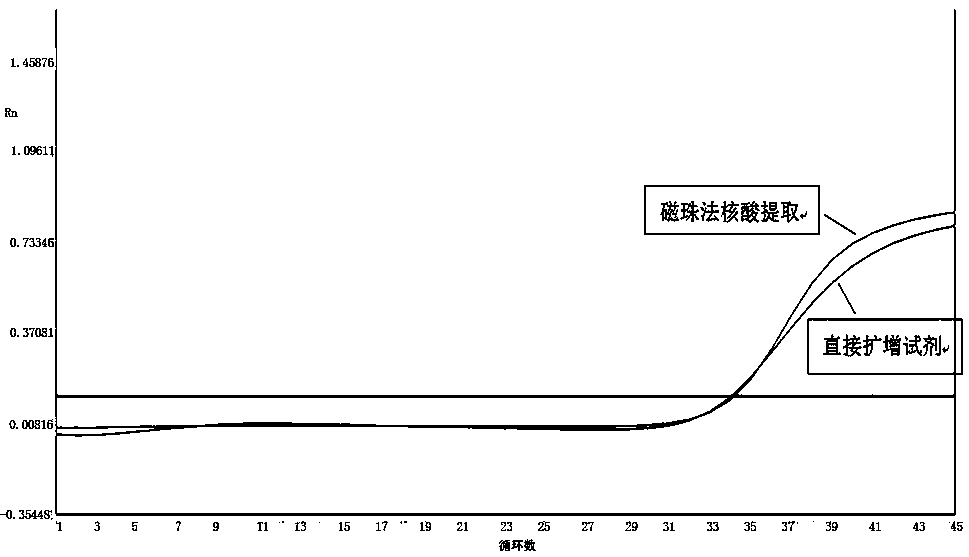
[0037] Example 1: Use of extraction-free direct amplification reagents for influenza A virus nucleic acid detection
[0038] Influenza viruses include Type A, Type B, and Type C. Type A is the most likely to cause an epidemic, followed by Type B, and Type C rarely causes an epidemic. According to the antigenicity of the outer membrane hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins of viral particles, influenza A viruses can be divided into 16 H subtypes (H1-H16) and 9 N subtypes ( N1-N9). There have been reports of human infections in subtypes such as H1, H2, H3, H5, H7 and H9. Because the nucleotide sequence encoding HA and (or) NA is prone to mutations, the epitopes of HA and (or) NA are changed. This antigenic change makes the population's original specific immunity ineffective, so Type influenza viruses often cause large-scale and even worldwide influenza epidemics. According to the characteristics of the epidemic, the influenza viruses that cause human influenza epidem...
Embodiment 2
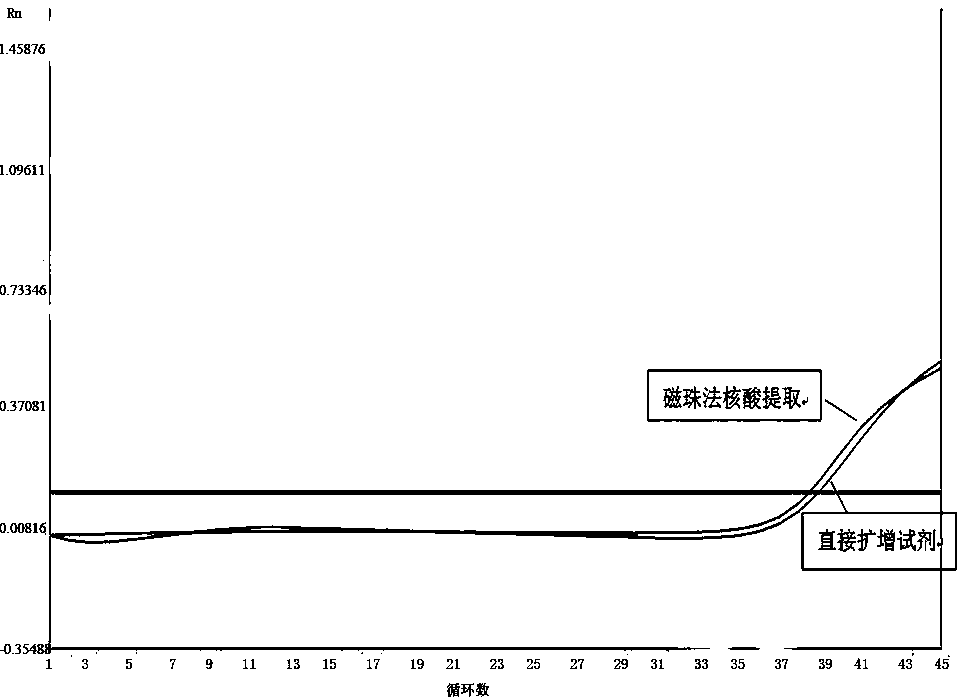
[0056] Example 2: Use of extraction-free direct amplification reagents for human papillomavirus nucleic acid typing detection
[0057] Human Papillomavirus (Human Papillomavirus, HPV) belongs to the papillomavirus family. It is a small molecule, non-enveloped 1, circular double-stranded DNA virus with a genome length of about 8000 base pairs (bp), divided into Three functional regions, namely the early transcribed region (E region), late transcribed region (L region) and non-transcribed region (long control region, LCR). HPV infects humans through direct or indirect contact with contaminated items or sexual transmission. The virus is not only host-specific, but also tissue-specific. It can only infect human skin and mucosal epithelial cells, causing various papillomas or warts on human skin and proliferative damage to the epithelium of the reproductive tract.
[0058] For many years, the internationally accepted diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer h...
Embodiment 3
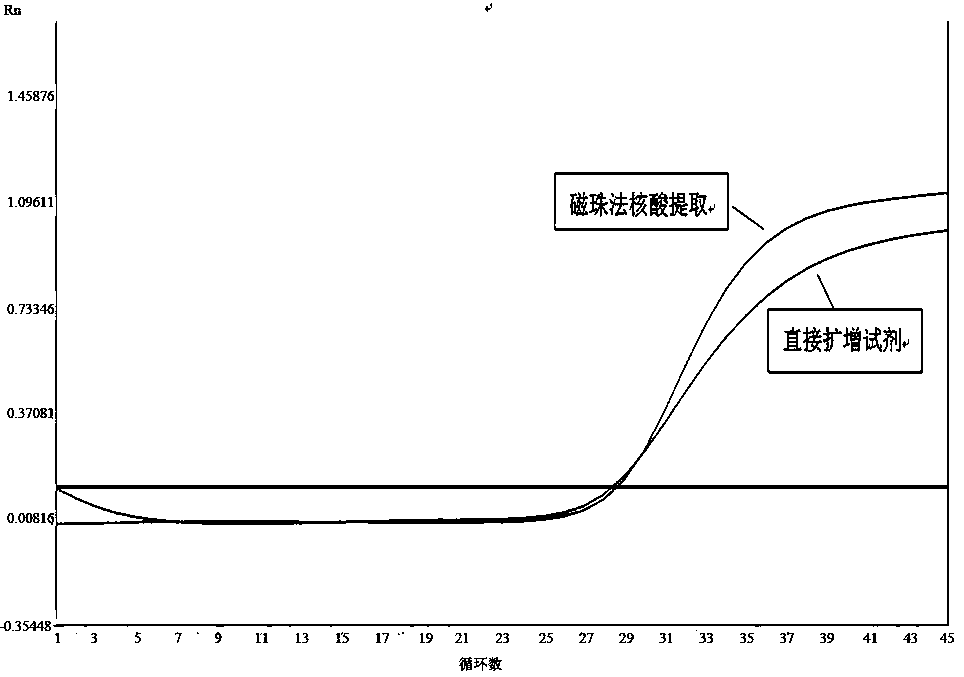
[0075] Example 3: Extraction-free direct amplification reagent combined with freeze-dried reagent for rapid detection of influenza A virus
[0076] Influenza viruses are mainly spread by air droplets, often causing fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and mild to moderate respiratory symptoms. In severe cases, they can cause pneumonia, myocarditis, and heart failure. Influenza virus nucleic acid detection reagents can be used for the auxiliary diagnosis of influenza. At this stage, the operation of influenza virus nucleic acid detection reagents is more complicated, and nucleic acid extraction---amplification reagent preparation---adding samples to the machine---PCR detection is required. process. During the testing period, a large number of professional laboratory equipment is required, and a strict laboratory environment is required to ensure that there is no cross-interference between different samples during the operation. The entire testing process takes 3.5 to 5 hours, which does...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com