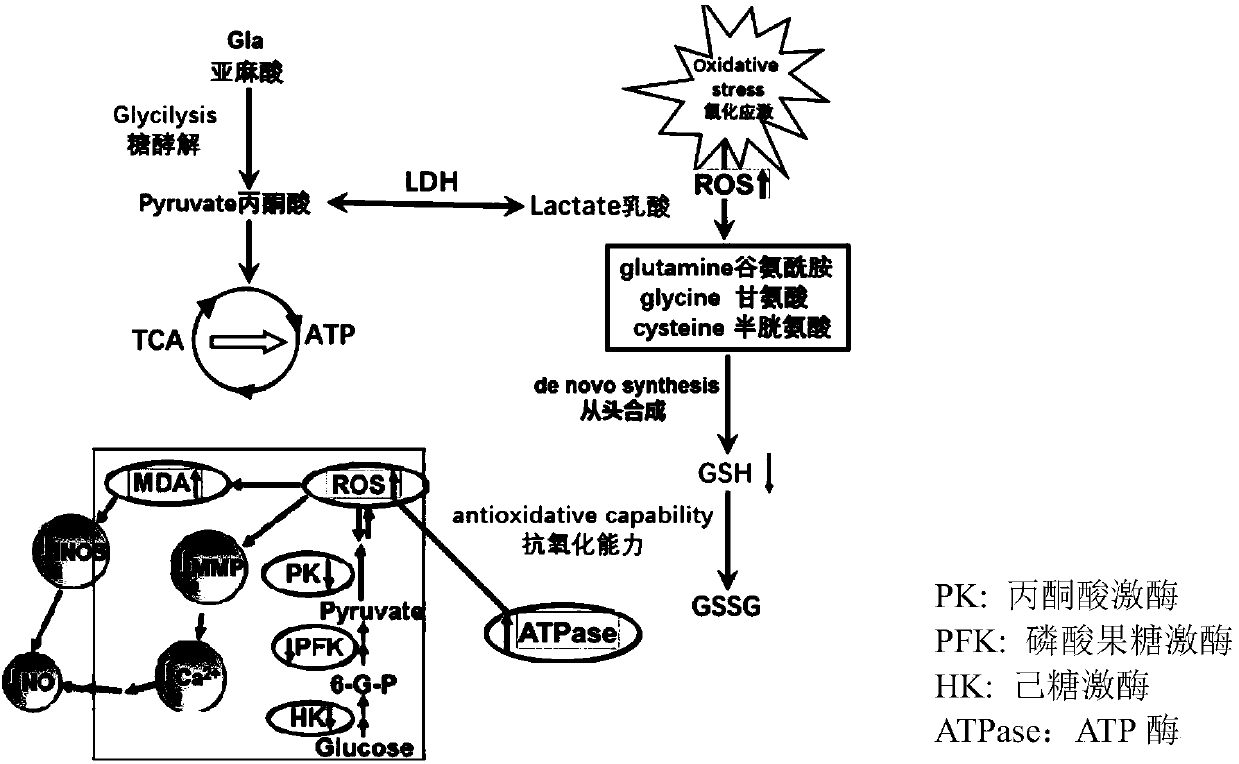
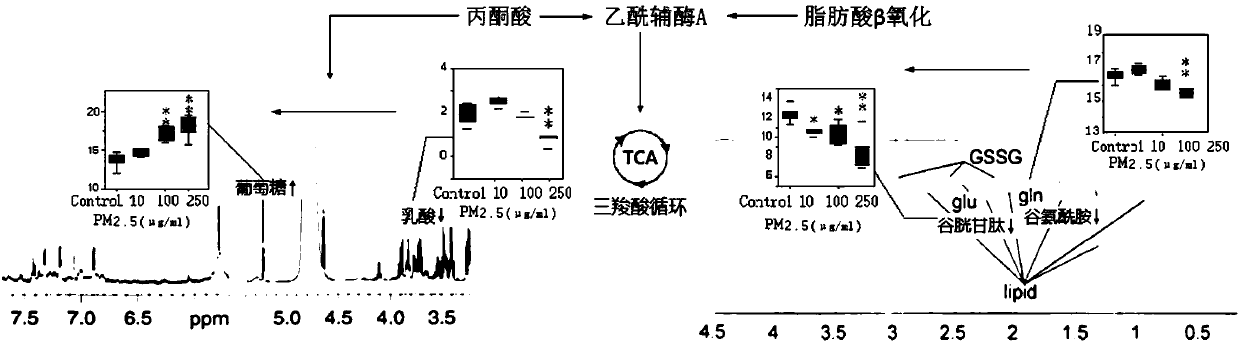
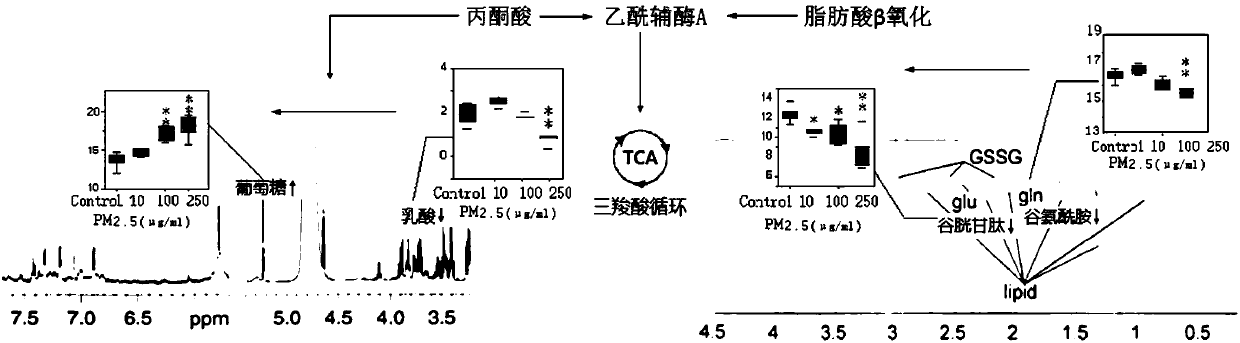
Method for evaluating effect of PM2.5 particles on free radical metabolic pathways in human lung cells
A technology based on free radicals and lung epithelial cells, applied in the field of evaluation based on molecular biology and analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of abnormal transcription, reduced activity, and reduced activity of antioxidant enzyme systems, achieving good specificity, small sample size, The effect of reducing the difference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The PM2.5 particles described in this example were taken from the urban area of Dalian City.
[0025] Example: PM 2.5 Effects of full chemical composition particle exposure on free radical metabolism in human lung epithelial cells
[0026] First, culture and expose human lung epithelial cells, the steps are as follows:
[0027] Human lung epithelial cells were seeded on a six-well plate at a seeding density of 1×10 5 cells / mL, the volume of the culture medium in each well of the six-well plate is 3mL, the culture medium is serum-free, and added: bovine pituitary extract 2ml / 500ml, hydrocortisone 0.5ml / 500mL human epidermal growth factor 0.5ml / 500ml, adrenal gland Insulin 0.5ml / 500ml, Insulin 0.5ml / 500ml, Transferrin 0.5ml / 500ml, Iodothyronine 0.5ml / 500ml, Retinoic Acid 0.5ml / 500ml and Gentamicin / Aphotericin-B 0.5m / 500ml, to simulate the normal growth conditions of cells. Cultivate in the incubator for 24h (37°C, 5% CO 2 ), when the cells entered the logarithmic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com