Porous membrane based on aminated copolymer microspheres and polyacetal and preparation method of porous membrane
An amination and poly-polyaldehyde technology, applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems of weak film mechanical properties, weak force between microspheres, low space utilization rate of microsphere membranes, etc., and achieve high cost performance and improved strength. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The preparation method of the porous membrane based on aminated copolymerized microspheres and polyaldehyde, the specific steps are as follows:
[0043] 1. Synthesis of precursor microspheres
[0044] Styrene (St) and butyl acrylate (BA) are used as monomers, and the molar ratio of the two is 8:1. First add water as a solvent 100ml, and the total amount of monomers added is 10wt% of the solvent, and then add the total amount of monomers Mass 1wt% cross-linking agent divinylbenzene (DVB), add 1wt% initiator potassium persulfate (KPS) of the total mass of the monomers, then react at a constant temperature of 70°C for 8h, and wash and centrifuge repeatedly with alcohol and water at the end of the reaction The solid product, namely the precursor microspheres P(St-BA), was ultrasonically dispersed in methanol to prepare a microsphere solution with a mass fraction of 10%;
[0045] 2. Preparation of Surface Aminated Microspheres
[0046] Add ethylenediamine to the precursor ...
Embodiment 2
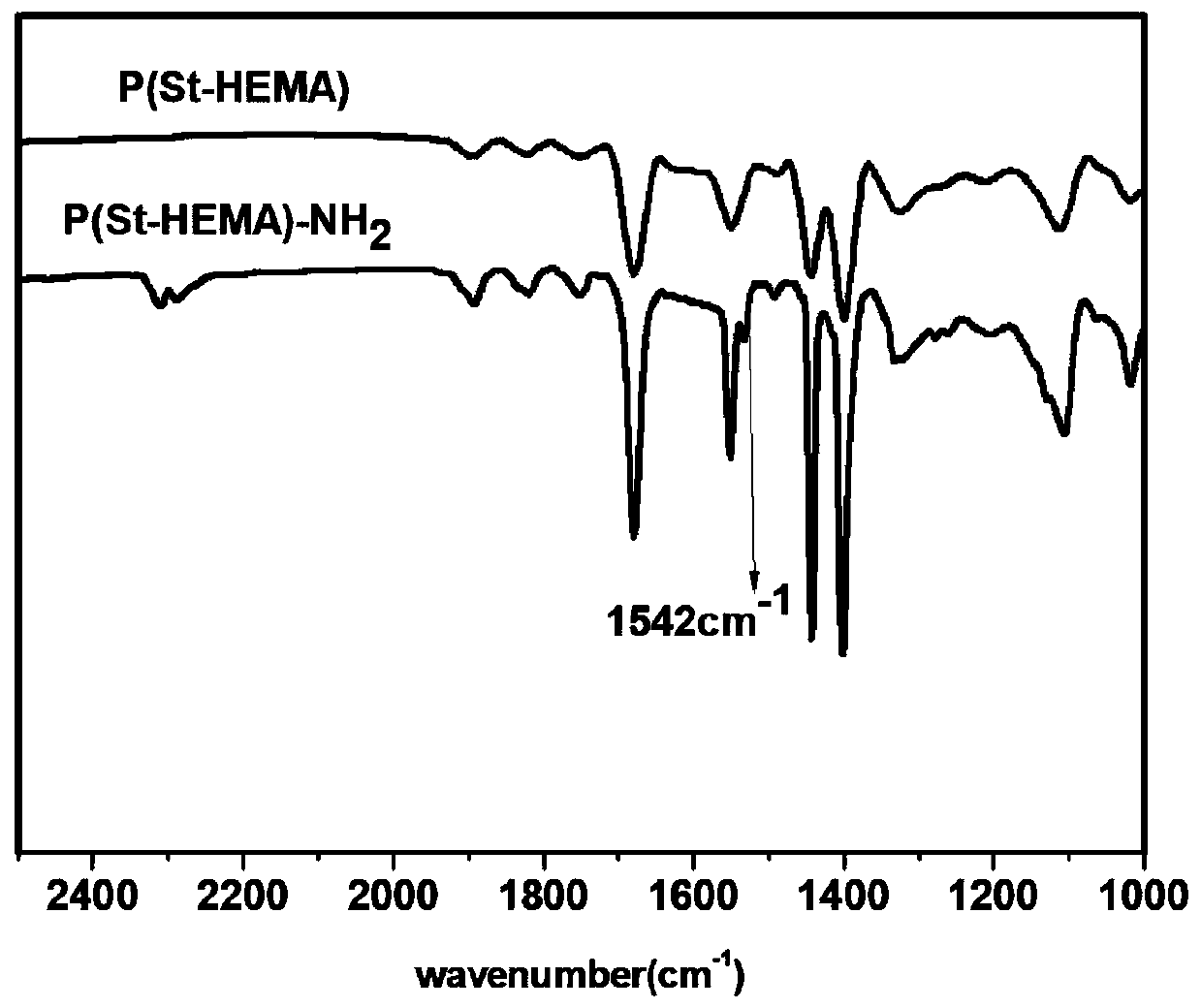
[0063] The difference between embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is that embodiment 2 changes the monomer type of acrylates in the mixed monomer, and replaces butyl acrylate monomer with hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), thereby exploring The effect of different acrylate monomers on aminolysis and the effect of hypercrosslinking on different monomers.
[0064] Such as figure 2 As shown, the peak of 1542cm-1 amino groups by FT-IR indicates that after surface amination, amino groups that did not appear before surface amination appear on the copolymerized microspheres, which proves that different acrylate monomers have no effect on surface amination.
[0065] Such as Figure 8B As shown, it can be seen by SEM that the morphology of the side of the self-assembled microsphere layer P (St-HEMA) microspheres is smooth, and the microspheres are stacked layer by layer.
[0066] Such as Figure 9B As shown, it can be seen through SEM that the morphology of the side surface of the layer-by...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is: embodiment 2 has removed the benzene cycloalkene in the mixed monomer, and the benzene cycloalkene monomer is changed into methyl methacrylate (MMA), and butyl acrylate mono While changing the proportion of the total amount of monomers to the solvent, the influence of non-benzenecycloolefin monomers on the copolymerized microspheres and the influence of the super-crosslinked film on the film morphology were discussed.
[0069] Such as image 3 As shown, the mass percentage of the total amount of monomer relative to the solvent analyzed by the particle size data is 10%, 20%, and 30%, and the size of the P(MMA-BA) microspheres varies from small to large, which proves that the total amount of monomer is relative to the solvent. The higher the mass percentage, the larger the particle size of the microspheres.
[0070] Such as Figure 8C As shown, it can be seen by SEM that the morphology of the side of the P(MMA-BA)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com