A kind of 3D printing flexible porous support material and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and porous scaffold technology, applied in the field of regenerative medicine, can solve the problems of limited selection of materials, easy deactivation of active substances, high melt viscosity of polymers, etc., and achieve good adhesion and proliferation, and good biocompatibility , Good effect of fiber toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] The invention provides a method for preparing a 3D printing flexible porous support material, comprising the following steps:
[0035] a) preparing 3D printing ink; the solute of the 3D printing ink is one or more of PLA, PLGA, PCL and PC; the solvent of the 3D printing ink is one or more of NMP, DMF and DMSO ;
[0036] b) under the power of the air source, use the 3D printing ink obtained in step a) to perform 3D printing on the receiving device to obtain the fiber support;
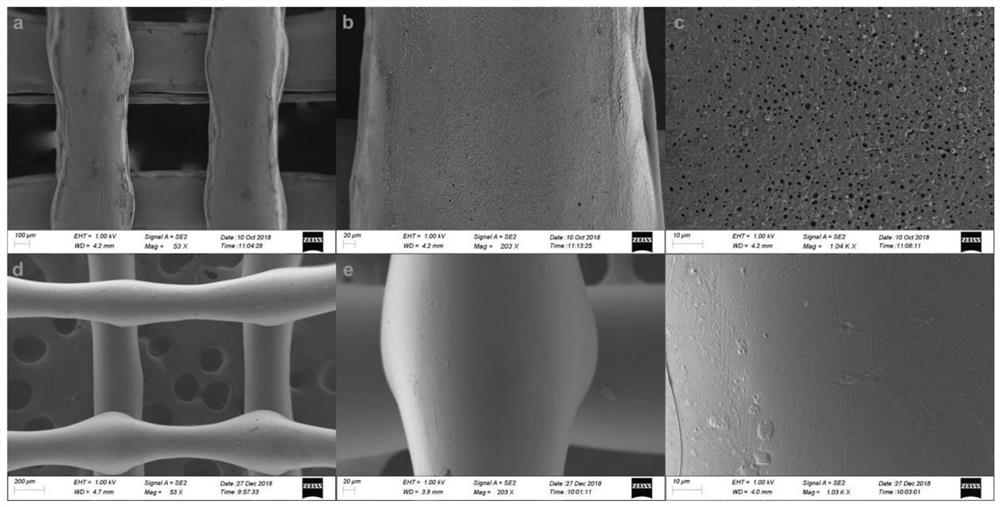
[0037] c) performing solvent replacement on the fibrous scaffold obtained in step b), and freeze-drying to obtain a 3D printed flexible porous scaffold material.
[0038] The present invention first prepares 3D printing ink. In the present invention, the solute of the 3D printing ink is one or more of PLA (polylactic acid), PLGA (polylactic glycolic acid), PCL (polycaprolactone) and PC (polycarbonate), more Preferred is PLGA. The present invention adopts the above-mentioned polyester material, w...
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Preparation of 3D printing ink: prepare 0.40g / mL NMP solution of PLGA, the weight average molecular weight of PLGA is 200,000, the molecular weight distribution is 1.8; the viscosity of the ink is 1600mPa.s.
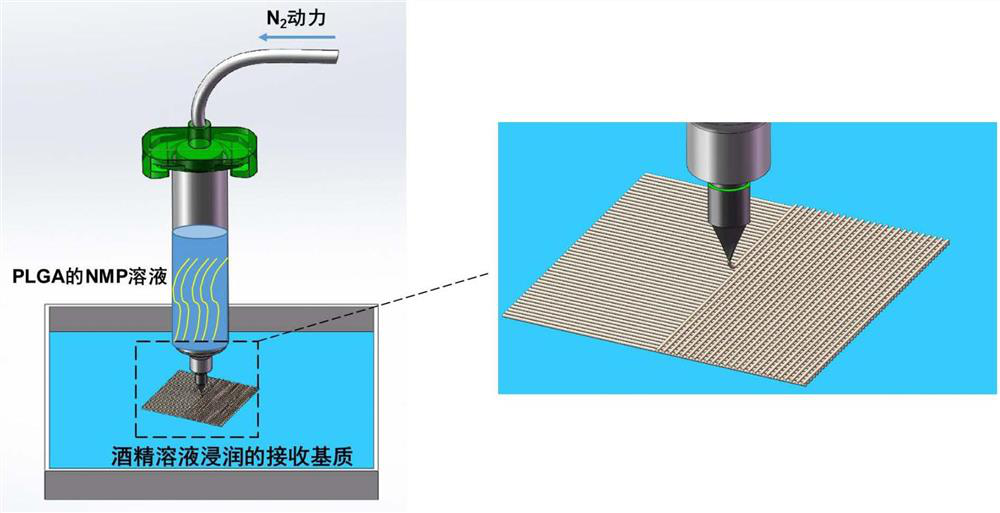
[0055] (2) The dynamic pressure of nitrogen gas is set to 0.25MPa; the size of the printing needle is 400 μm; the filter paper fully soaked by the receiving liquid (50% ethanol solution) is fixed on the receiving plate as the receiving device for printing; the printing temperature is room temperature;
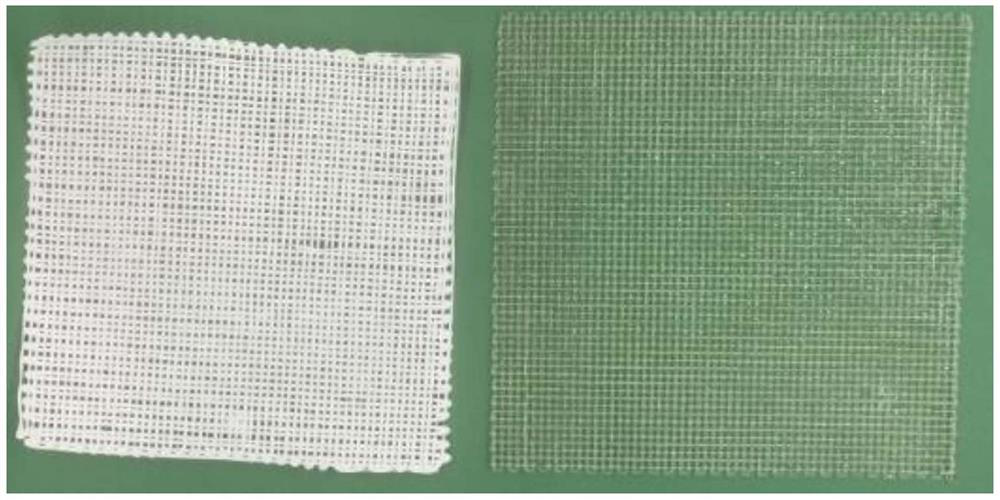
[0056] Add the 3D printing ink obtained in step (1) into the barrel of the direct writing 3D printer, set the printing parameters, and print according to the model designed by SolidWorks. The printing speed is 60mm / s, and the fiber spacing is 300μm. For the schematic diagram of the printing process, see figure 1 Shown; Obtain PLGA fiber support.
[0057] (3) Soak the PLGA fiber scaffold obtained in step (2) in an ethanol solution for replacement for 24 hours, r...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Using the preparation method provided in Example 1, the difference is that: the 3D printing ink is a 0.20 g / mL PLGA NMP solution; and a 3D printing flexible porous scaffold material (20%) is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com