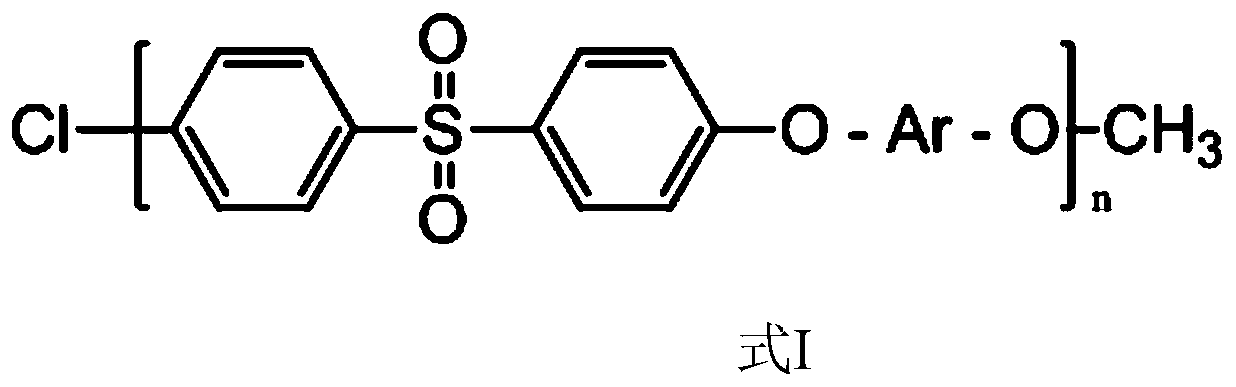
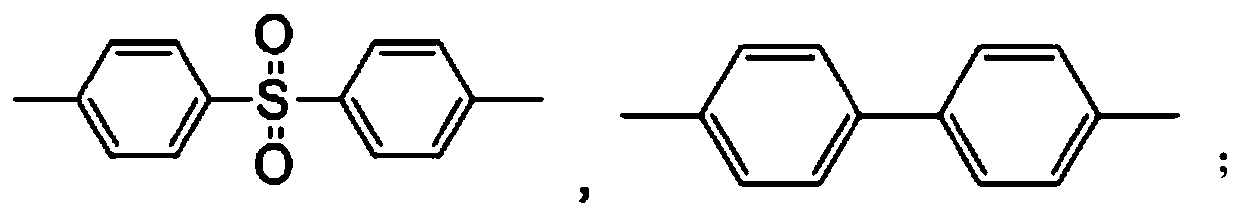
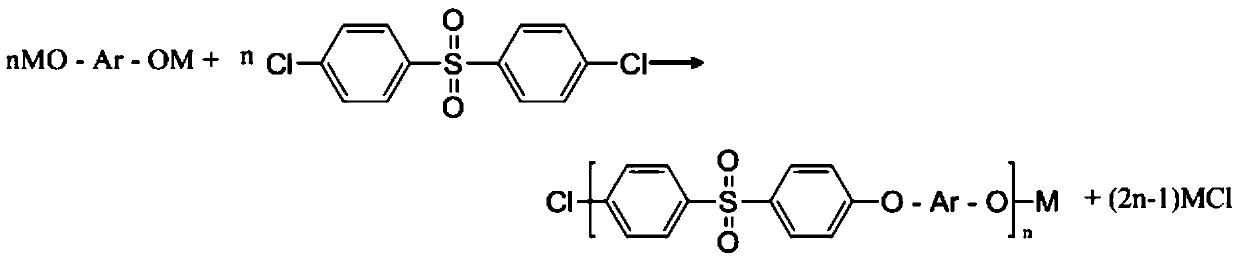
High thermal-stability capped sulfone polymer, preparation method and application in tableware thereof
A high thermal stability, polymer technology, applied in the application, table utensils, table utensils, etc., can solve problems that affect diet health, easy to burn, colorants are not resistant to acid and alkali, etc., to achieve mildew resistance, excellent resistance The effect of high temperature resistance, toughness and high strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] In this embodiment, a method for preparing a highly thermally stable end-capped sulfone polymer comprises the following steps:
[0066] (1) Salt-forming reaction: Add 93.10g (0.5mol) of 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl to a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a nitrogen pipe, a condensing water separator, and a stirrer in sequence according to the ratio in Table 1 and 147.17g (0.5125mol) 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone, then add 426g solvent sulfolane, stir and heat up to 80°C to dissolve the monomer until the solution is transparent, add 55.65g sodium carbonate, then add 80mL xylene, continue Under stirring, the temperature is raised to 140°C and the salt-forming reaction begins. The azeotrope formed by the water and xylene produced in the system is blown out by the protective gas into the condenser tube, condensed and dripped into the water separator for stratification, and the xylene in the upper layer flows back into the system. Medium; keep the temperature in the r...
Embodiment 2
[0075] The method is basically the same as that in Example 1. Add 93.10g (0.5mol) 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl and 145.37g (0.50625mol) 4,4'-dichlorodiphenylsulfone, then 520ml sulfolane solvent, stir and heat up Dissolve the monomer at 80°C until the solution is transparent, add 55.65g of sodium carbonate, then add 80mL of toluene, continue to stir and raise the temperature to 140°C to start the salt formation reaction, and collect water, keep the temperature in the range of 160°C-180°C, when there is no Water is generated, which proves that the salt is completely formed, then distills and releases toluene, gradually raises the temperature to 230°C and starts the polymerization reaction at a constant temperature for 3 hours until the torque of the stirring motor remains unchanged, indicating that the viscosity of the system is basically constant. Cool down to 180°C, add 0.56g (0.00625mol ) mixed solution of dimethyl carbonate and 6g sulfolane, continue to react for 30min; stop stirr...
Embodiment 3
[0077] The method is basically the same as that of Example 1, and 125.135 g (0.5 mol) of 4,4'-dihydroxydiol was sequentially added to a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a nitrogen pipe, a condensing water separator, and a stirrer according to the proportions in Table 1. Phenylsulfone and 145.877g (0.508mol) 4,4'-dichlorodiphenylsulfone, and then 520ml of N-methylpyrrolidone solvent, stirred and heated to 80 ° C to dissolve the monomer until the solution was transparent, added 55.65g of sodium carbonate, and then added 80mL of xylene, continue to stir and raise the temperature to 140°C to start the salt-forming reaction. The azeotrope formed by the water and xylene produced in the system is blown out by the protective gas into the condenser, condensed and dropped to the water separator for stratification. Reflux toluene into the system again; keep the temperature at about 190°C, and when the collected water is close to the theoretical value (9g), continue to reflu...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com