A method for producing pure silver and co-producing metallic aluminum from a waste silver catalyst whose carrier is alumina
A silver catalyst, alumina technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve problems such as increasing recovery costs, and achieve the effects of mature equipment, significant emission reduction, and shortened treatment process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
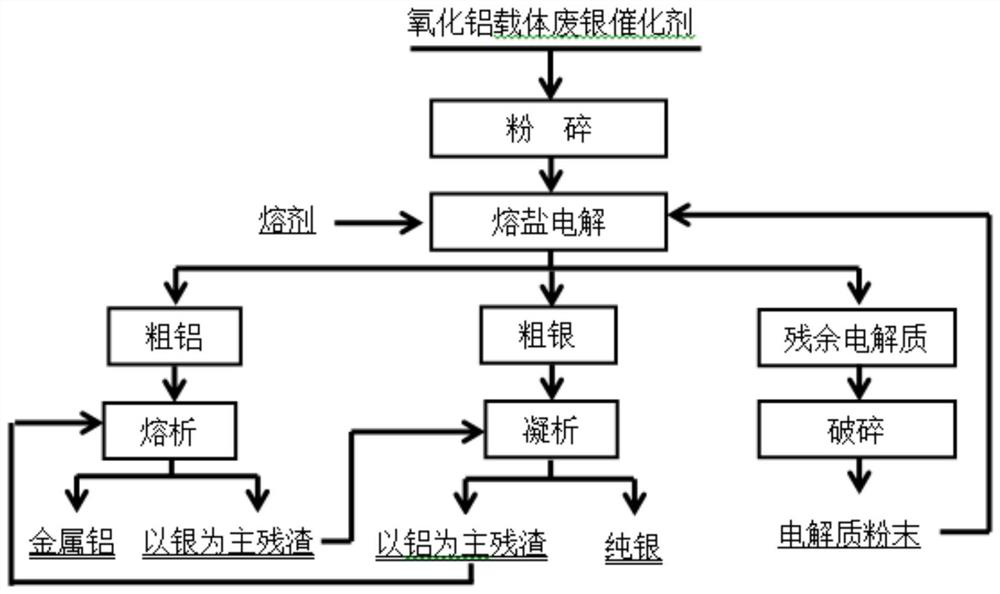
[0023] See attached figure 1 , Conditions: The carrier is the processed carrier alumina silver catalyst mixed with flux, placed in an aluminum electrolytic cell for electrolysis, control parameters: electrolytic cell operating voltage 4.2V, electrolysis temperature 960 ° C, pole distance 5cm, molecular ratio 2.4 , alumina content 2.5%, electrolyte level 22cm, aluminum liquid level 20cm, anode current density 0.64A / cm 2 , the flux is composed of 87% cryolite and 6% calcium fluoride, and the crude aluminum, crude silver and residual electrolyte are obtained respectively, the residual electrolyte is broken and returned to the electrolysis process; the crude aluminum is heated to 670°C by melting method and mechanically stirred for 2.5 hours , the solid-state precipitation of silver-aluminum intermetallic compounds forms an infusible residue, and the rest is liquid metal aluminum. The residue is removed and sent to the coagulation process to recover silver; the crude silver is hea...
Embodiment 2
[0025] See attached figure 1 , Conditions: Mix the waste silver catalyst with carrier alumina and flux, place it in an aluminum electrolytic cell for electrolysis, control parameters: electrolytic cell operating voltage 4.2V, electrolysis temperature 970°C, pole distance 5cm, molecular ratio 2.3, oxidation Aluminum content 2.0%, electrolyte level 22cm, aluminum liquid level 20cm, anode current density 0.65A / cm 2 , the flux is composed of 87% cryolite and 6% calcium fluoride, and the crude aluminum, crude silver and residual electrolyte are obtained respectively, the residual electrolyte is broken and returned to the electrolysis process; the crude aluminum is heated to 680°C by melting method and electromagnetically stirred for 3 hours , the solid-state precipitation of silver-aluminum intermetallic compounds forms an infusible residue, and the rest is liquid metal aluminum. The residue is removed and sent to the coagulation process to recover silver; the crude silver is heate...
Embodiment 3
[0027] See attached figure 1 , Conditions: Mix the residue after wet extraction of silver with a waste silver catalyst whose carrier is alumina carrier and flux, and place it in an aluminum electrolytic cell for electrolysis. 5cm, molecular ratio 2.3, alumina content 3.0%, electrolyte level 22cm, aluminum liquid level 20cm, anode current density 0.64A / cm 2, the flux is composed of 87% cryolite and 6% calcium fluoride, and the crude aluminum, crude silver and residual electrolyte are obtained respectively, the residual electrolyte is broken and returned to the electrolysis process; the crude aluminum is heated to 680°C by melting method and mechanically stirred for 2 hours , the solid-state precipitation of silver-aluminum intermetallic compounds forms an infusible residue, and the rest is liquid metal aluminum. The residue is removed and sent to the coagulation process to recover silver; the crude silver is heated to 1030°C by coagulation method, and then heated at 7°C / The t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com