A kind of anti-infection silica biological tissue adhesive and its application
A technology of biological tissue and mesoporous silica, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of toxic side effects of antibiotics, abuse, and limited antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
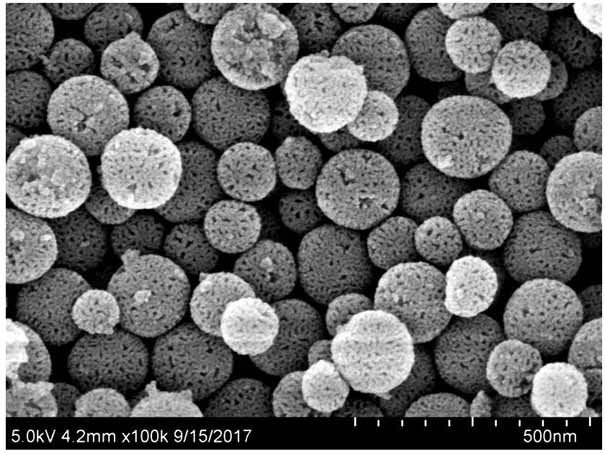
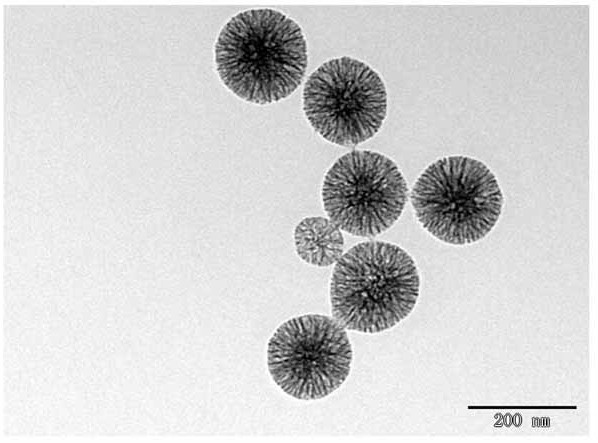
[0042] Example 1 Preparation of mesoporous silica
[0043] Sample 1
[0044]Weigh 0.3g of CTAB into a 500mL three-neck flask, add 96mL of distilled water, protect the interior of the reaction device with nitrogen, stir magnetically at 70°C for 1 hour to fully dissolve it, weigh 45mL of n-octane, at a rate of 2 drops / second Drop into the above CTAB solution system. Continue to stir for 20 minutes after dripping to form a uniform emulsion. Measure 3.2 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate TEOS dropwise into the above solution at a rate of 2 drops / sec. After dropping, 0.066 g of lysine was weighed and added to the above solution. Then, 8.9 mL of methyl methacrylate monomer was weighed and dropped into the above solution at a rate of 2 drops / sec. After dripping, 113.4 mg of azobisisobutyramidine hydrochloride AIBA was weighed and added to the reaction solution. After the addition was completed, the reaction was continued for 4 hours under magnetic stirring in a water bath at 70°C. ...
example 2
[0055] Example 2 Preparation of lysozyme-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles
[0056] 40 mg of lysozyme was weighed and placed in a 10 mL vial, 8 mL of PBS solution with pH 6.8 was added, and the lysozyme was fully dissolved by magnetic stirring at 200 rpm for 1 hour at 4°C. Then, 20 mg of the mesoporous silica nanoparticles prepared in Example 1 were weighed and placed in the above-mentioned lysozyme solution, and continued to be magnetically stirred at 200 rpm for 3 hours at 4°C. After stirring, the mixture was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 3 minutes, and the supernatant was removed to obtain mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with lysozyme protein.
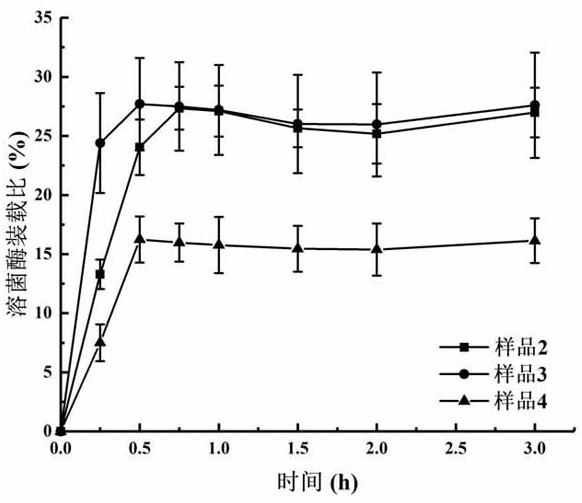
[0057] During the above preparation process of lysozyme-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles, samples were taken at 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 45 minutes, 1 hour, 1.5 hours, 2 hours, and 3 hours, respectively. The sampling method was as follows: 500 μL of the stirring solution was drawn and centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 3 mi...
example 3
[0060] Example 3 Drug release assay of lysozyme-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles
[0061] The remaining solution after loading lysozyme for 3 hours in Example 2 was centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 3 minutes, the solid precipitate was transferred to a 50 mL flat-bottomed flask, and 25 mL of pH 6.8 phosphate buffer was added. medicine for 24 hours. Samples were taken at 15 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 1.5 hours, 2 hours, 3 hours, 4 hours, and 5 hours, respectively. The sampling method is as follows: suck 1000μL of stirring solution and centrifuge at 8000rpm for 3 minutes, then take 500μL of supernatant and store it at 4°C for testing, add 500μL of PBS pH6.8 to the remaining liquid and solid, blow evenly, and add back to release the drug. system.
[0062] The 500 μL supernatant obtained at each time point was mixed with the Coomassie brilliant blue staining solution described in Example 2 and shaken up, and after 3 minutes of dark staining, the ultraviolet-visible absorbance ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com