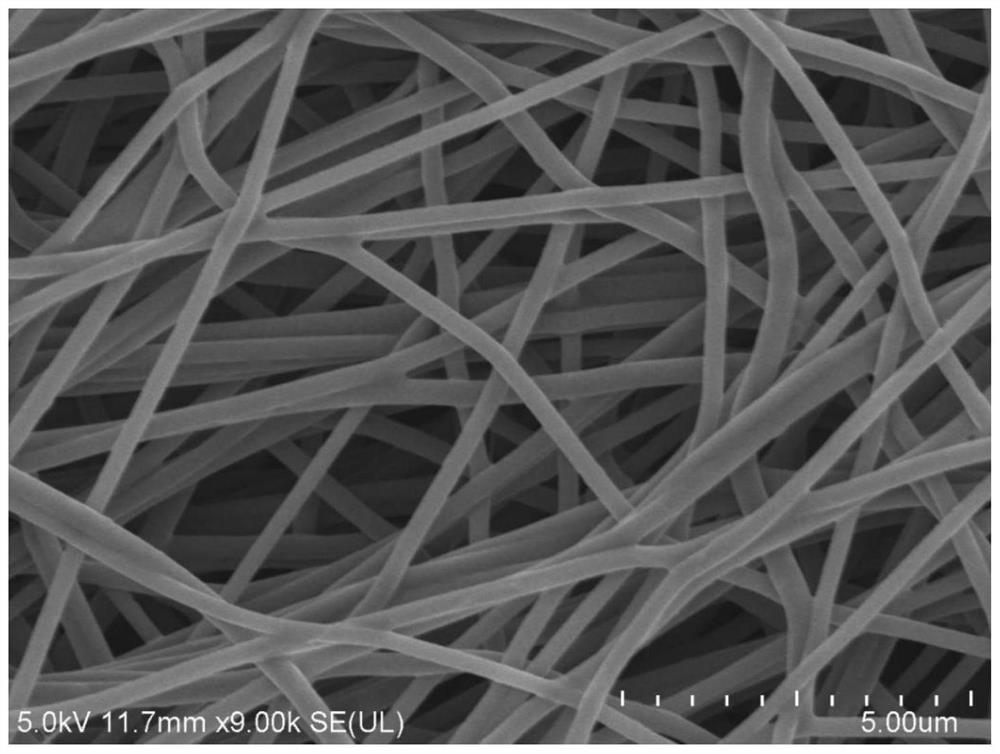
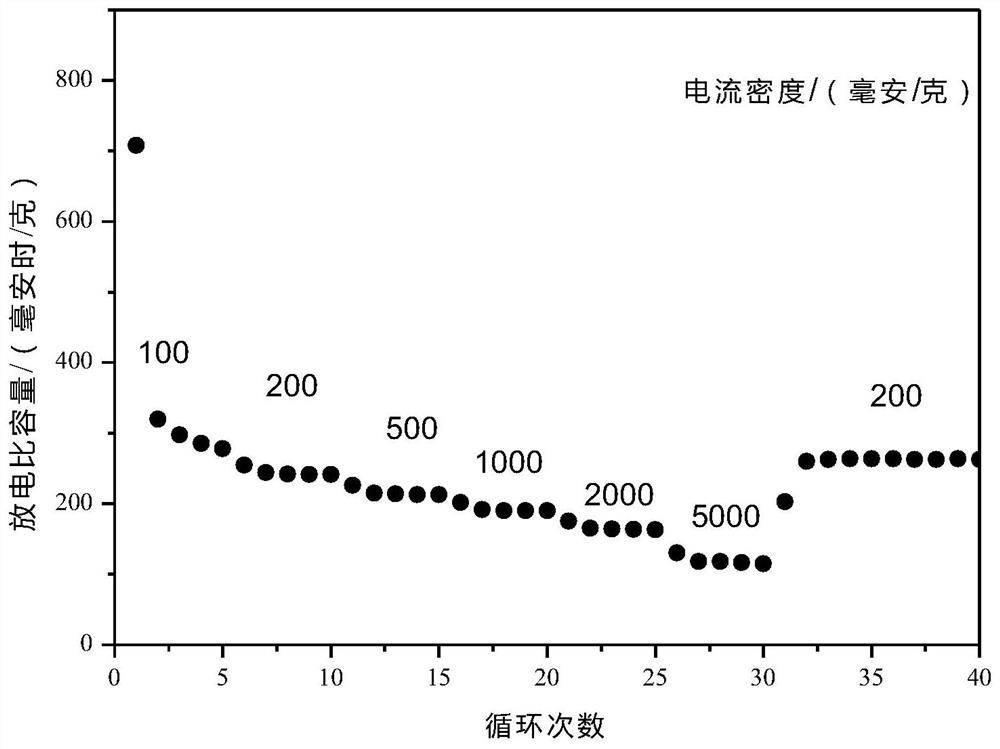
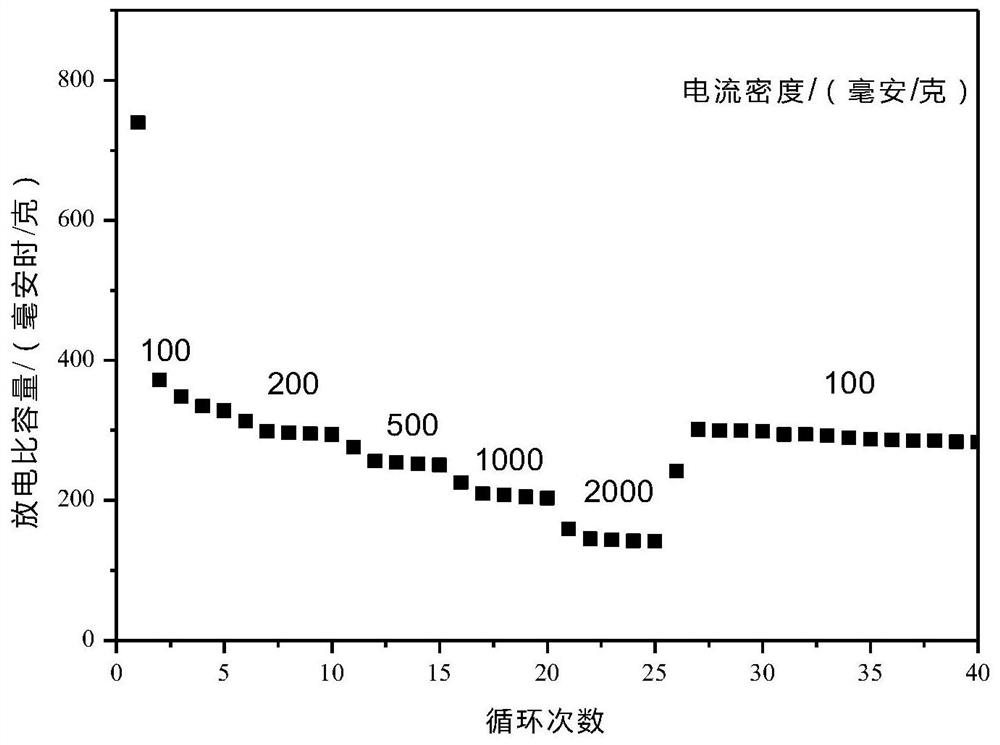
Preparation method and application of molybdenum phosphide/carbon fiber composite material
A composite material and carbon fiber technology, applied in the direction of phosphide, fiber chemical characteristics, rayon manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of difficult removal of long-chain organic solvents, corrosiveness, phosphine toxicity, etc., to improve cycle stability, The effect of strong solubility and high redox activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] (1) Mix 0.5 mL of 70% phytic acid solution with 9.5 mL of DMF, add 0.5 g of phosphomolybdic acid and 1.5 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone, and fully stir to form a uniform spinning solution.
[0034] (2) Fill the spinning solution in step (1) into a syringe and connect it with a 0.7mm needle. Electrospinning is carried out by using an electrospinning device to obtain a phosphomolybdic acid / PVP composite fiber membrane. Among them, the aluminum foil-wrapped cylinder is used as the receiver, the negative high voltage is -2kV, the positive high voltage is 14kV, the receiving distance is 15cm, the relative humidity is 50%, and the ambient temperature is 50°C.
[0035] (3) Place the phosphomolybdic acid / PVP composite fiber membrane obtained in step (2) in a temperature-programmed muffle furnace, set the heating rate at 2°C / min, and react in an air atmosphere of 280°C for 2h. Then it was transferred to a tube furnace, and the temperature was raised to 700°C at a rate of 5°C / min und...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Mix 1 mL of 70% phytic acid solution with 9 mL of DMF, add 0.5 g of phosphomolybdic acid and 0.6 g of polyacrylonitrile, and fully stir to form a uniform spinning solution.
[0040] (2) Fill the spinning solution in step (1) into a syringe and connect it with a 0.7mm needle. Electrospinning is carried out by using an electrospinning device to obtain a composite fiber membrane. Among them, the aluminum foil-wrapped cylinder is used as the receiver, the negative high voltage is -2kV, the positive high voltage is 14kV, the receiving distance is 15cm, the relative humidity is 50%, and the ambient temperature is 50°C.
[0041] (3) The composite fiber membrane obtained in step (2) was placed in a temperature-programmed muffle furnace with a heating rate of 2° C. / min, and reacted in an air atmosphere of 280° C. for 1 h. Then it was transferred to a tube furnace, and the temperature was raised to 800°C at a rate of 2°C / min under a nitrogen atmosphere and kept for 2h. After...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Mix 0.5mL of 70% phytic acid solution with 9.5mL of DMF, add 0.25g of phosphomolybdic acid and 1.5g of polyvinylpyrrolidone, and fully stir to form a uniform spinning solution.
[0045](2) Fill the spinning solution in step (1) into a syringe and connect it with a 0.7mm needle. Electrospinning is carried out by using an electrospinning device to obtain a phosphomolybdic acid / PVP composite fiber membrane. Among them, the aluminum foil-wrapped cylinder is used as the receiver, the negative high voltage is -2kV, the positive high voltage is 14kV; the receiving distance is 15cm; the relative humidity is 40%, and the ambient temperature is 55°C.
[0046] (3) Place the phosphomolybdic acid / PVP composite fiber membrane obtained in step (2) in a temperature-programmed muffle furnace, set the heating rate at 2°C / min, and react in an air atmosphere of 230°C for 2h. transferred to a tube furnace under Ar / H 2 Atmosphere (volume ratio Ar:H 2 =0.95:0.05), the temperature was r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com