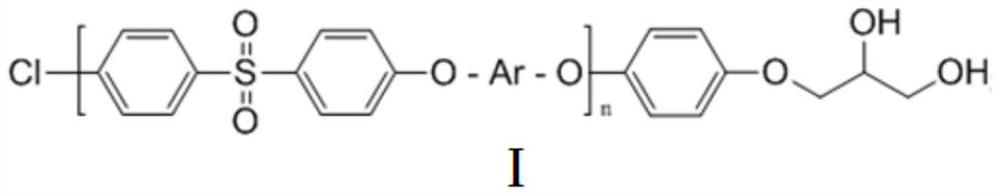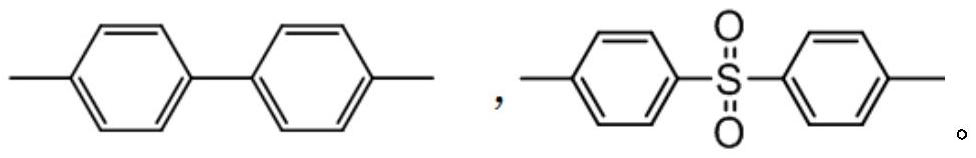Antibacterial sulfone polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of polymer and antibacterial sulfone, applied in the field of antibacterial sulfone polymer and its preparation, can solve the problems of reducing bacterial cell cytoplasmic membrane gradient, changing microbial metabolism, proton dynamic collapse energy, etc. Effectiveness of utilization rate and improvement of material stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
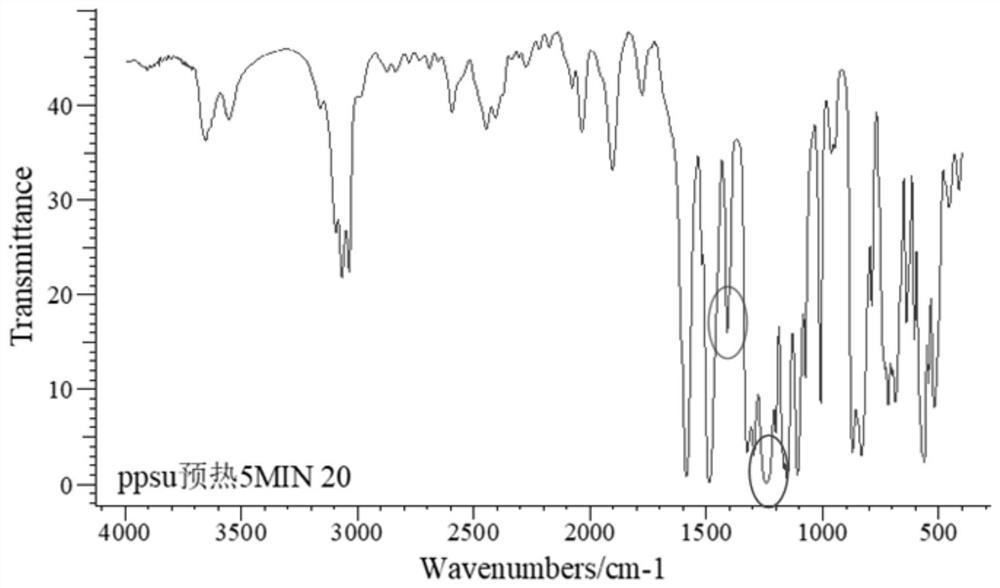
[0046]This embodiment is a method for preparing the end-capped sulfone polymer PPSU with antibacterial properties, including the following steps:
[0047](1) Salt formation reaction: Add 954.3g (5.125mol) 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl and 1435.8g (5mol) to a 10L reaction kettle equipped with a thermometer, a nitrogen pipe, a condensation trap, and a stirrer. ) 4,4'-Dichlorodiphenyl sulfone, then add 4.26kg solvent sulfolane, stir and heat to 80℃ to dissolve the monomer until the solution is transparent, add 556.5g (5.5mol) sodium carbonate, then add 500mL xylene, continue stirring The temperature is raised to 140°C and the salt formation reaction begins. The azeotrope formed by the water produced in the system and xylene is blown out by the protective gas into the condenser, condensed and dripped to the water separator for stratification, and the xylene in the upper layer is returned to the system. ; Maintain the temperature between 200 ~ 210 ℃, when the collected water is close to the theore...
Embodiment 2
[0061]This embodiment is a method for preparing the end-capped sulfone polymer PES with antibacterial properties, including the following steps:
[0062](1) Salt formation reaction: Add 1282.6g (5.125mol) 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl sulfone and 1435.8g (1) in a 10L reactor equipped with a thermometer, a nitrogen pipe, a condensation trap, and a stirrer. 5mol) 4,4'-dichlorodiphenylsulfone, then add 4.26kg solvent sulfolane, stir and heat to 80℃ to dissolve the monomer until the solution is transparent, add 556.5g (5.5mol) sodium carbonate, then add 500mL xylene, continue Under stirring, the temperature is raised to 140°C and the salt formation reaction begins. The azeotrope formed by the water produced in the system and xylene is blown out by the protective gas into the condenser, condensed and dropped to the water separator for layering, and the xylene in the upper layer is returned to the system. Medium; maintain the temperature between 200~210℃, when the collected water amount is close to...
Embodiment 3
[0069]The synthesis steps are the same as in Example 1. Add 931.98g (5.005mol) 4,4'-dihydroxybiphenyl and 1435.8g (5mol) 4,4'-dichlorodiphenylsulfone, and add the weighed chlorophenylglycol Ether 1.01g (0.005mol), lasted 30min. Finally, the end-capped PPSU resin is obtained.
[0070]Direct injection after mixing with high-mixer.
[0071]The injection molding process used for chopsticks is the same as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com