Primer group, kit and method for detecting pathogenic microorganisms based on targeted sequencing
A technology of pathogenic microorganisms and detection kits, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of low detection sensitivity, high requirements for transportation and storage, and low extraction efficiency, and achieve high detection throughput, no host interference, and sequencing costs low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0119] Embodiment 1 pathogen selection and primer design
[0120] In this example, primers were designed for the following three types of pathogens, namely bacterial pathogens, fungal pathogens and viral pathogens.
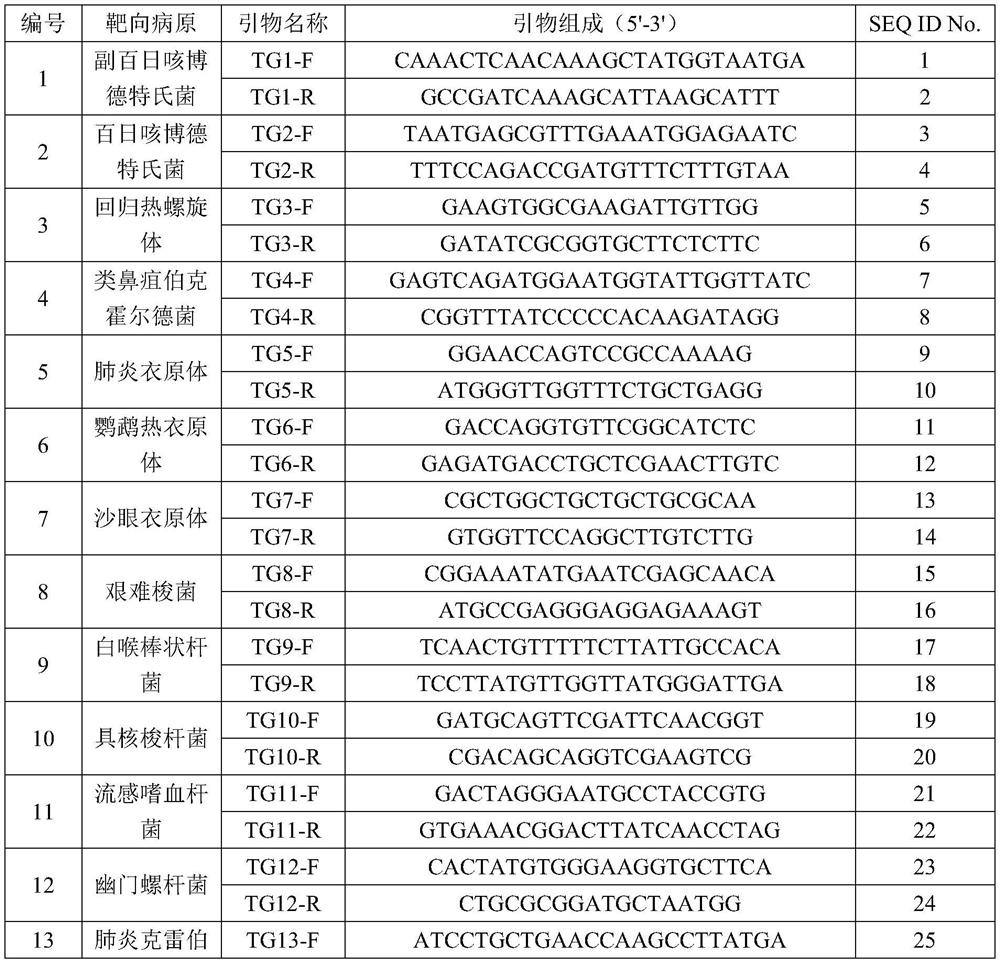
[0121] The bacterial pathogens targeted are shown in Table 1:
[0122] Table 1 Bacterial pathogens
[0123] Bordetella parapertussis Burkholderia pseudomallei Listeria monocytogenes Bordetella pertussis Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Chlamydia psittaci Chlamydia trachomatis Clostridium difficile Corynebacterium diphtheriae Fusobacterium nucleatum Haemophilus influenzae Helicobacter pylori Klebsiella pneumoniae Legionella pneumophila Relapsing hot spirochetes Mycobacterium abscessus Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium bovis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycoplasma pneumoniae Neisseria gonorrhoeae Orientia tsutsugamushi Pseudomonas aeruginosa Staphylococcus pyogenes Chlamydia pneumoniae Streptococcu...
Embodiment 24
[0138] Example 24 Pathogenic microorganism detection of alveolar lavage fluid samples
[0139] BALF samples from 4 suspected infected patients were collected: Case1-BALF, Case2-BALF, Case3-BALF and Case4-BALF. The clinical symptoms of 4 patients were suspected of respiratory tract infection, and the clinical culture results were negative, and other tests did not clarify the type of infection and the type of pathogenic microorganisms.
[0140] Using the primer set or kit in Example 1, the alveolar lavage fluid sample was detected, and a parallel quality control was added. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0141] 1. Total DNA Extraction
[0142] Extract the total DNA of the sample using the Total DNA Extraction Kit (MeiG Medicine), and extract according to the steps in the instructions:
[0143] (1) Take 400 μL alveolar lavage fluid sample into a 2 mL centrifuge tube, add 40 μL Lysis Enzyme, 400 μL buffer PM and 5 μL RNA Carrier, vortex evenly, mix by invert...
Embodiment 3
[0228] Example 3 Detection of pathogenic microorganisms in alveolar lavage fluid and blood samples of the same patient
[0229] One case of blood and alveolar lavage fluid samples from a patient suspected of infection was collected. The clinical symptoms of the patient were suspected of respiratory tract infection and bloodstream infection. The results of clinical blood culture and sputum culture were negative, and other tests did not clarify the type of infection and the type of pathogenic microorganism.
[0230] Using the primer set or kit of Example 1, the alveolar lavage fluid and blood samples were detected, and parallel quality control was added.
[0231] Total DNA extraction and quality control, multiplex PCR amplification and purification of amplification products, adapter sequence PCR amplification and purification of amplification products, library quality control, high-energy sequencing and data analysis methods were all the same as in Example 2.
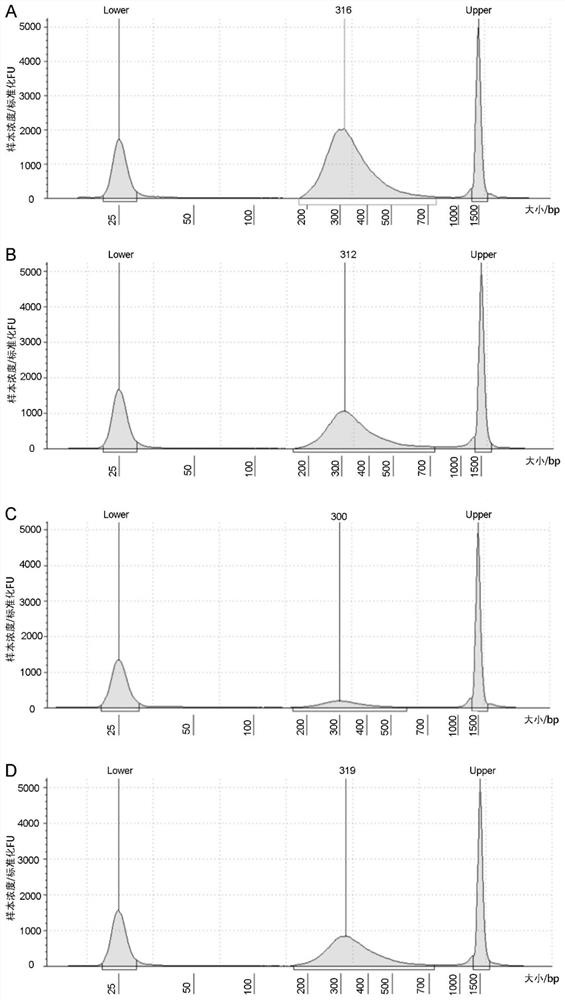
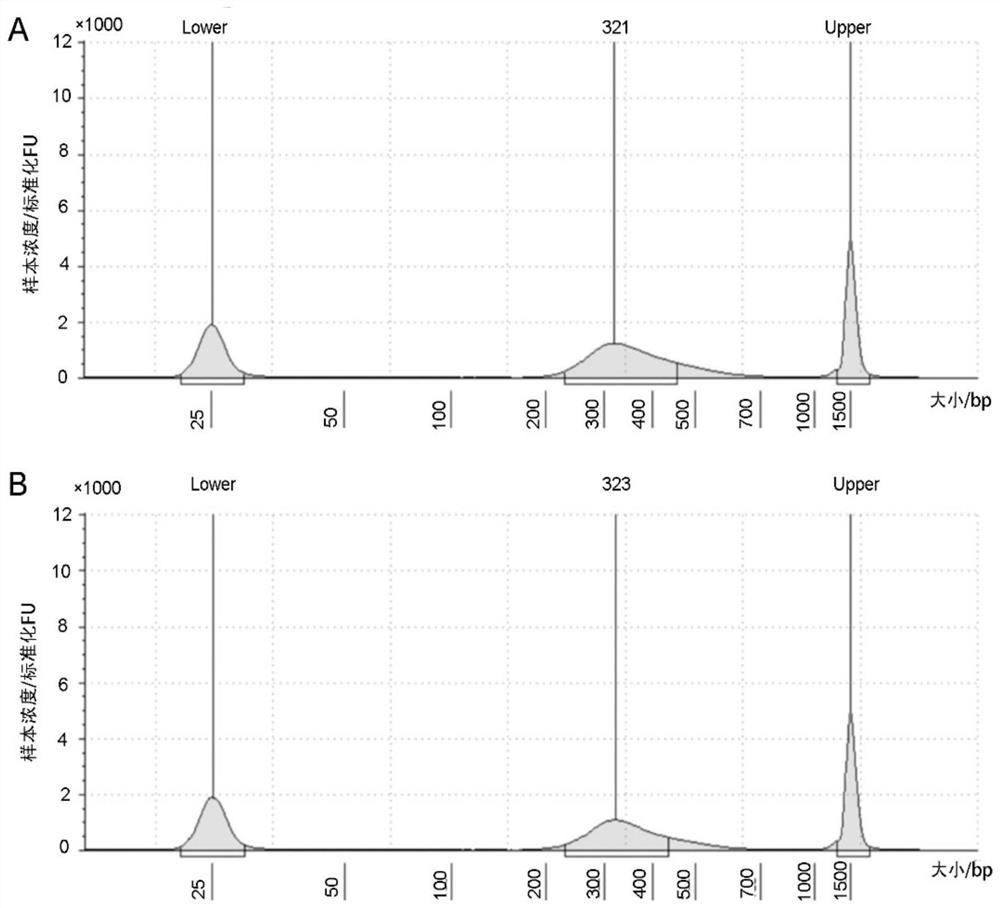
[0232] In the lib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com