Method for synthesizing L-lactide from chiral L-lactic acid produced by using lignocellulose biomass as raw material
A technology of lignocellulose and biomass, which is applied in the field of producing chiral L-lactic acid and synthesizing L-lactide, can solve the problems of difficult raw materials, low utilization rate, low yield and yield of cellulose lactic acid, and achieve high chirality High degree, significant economic benefits, and the effect of reducing the difficulty of operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
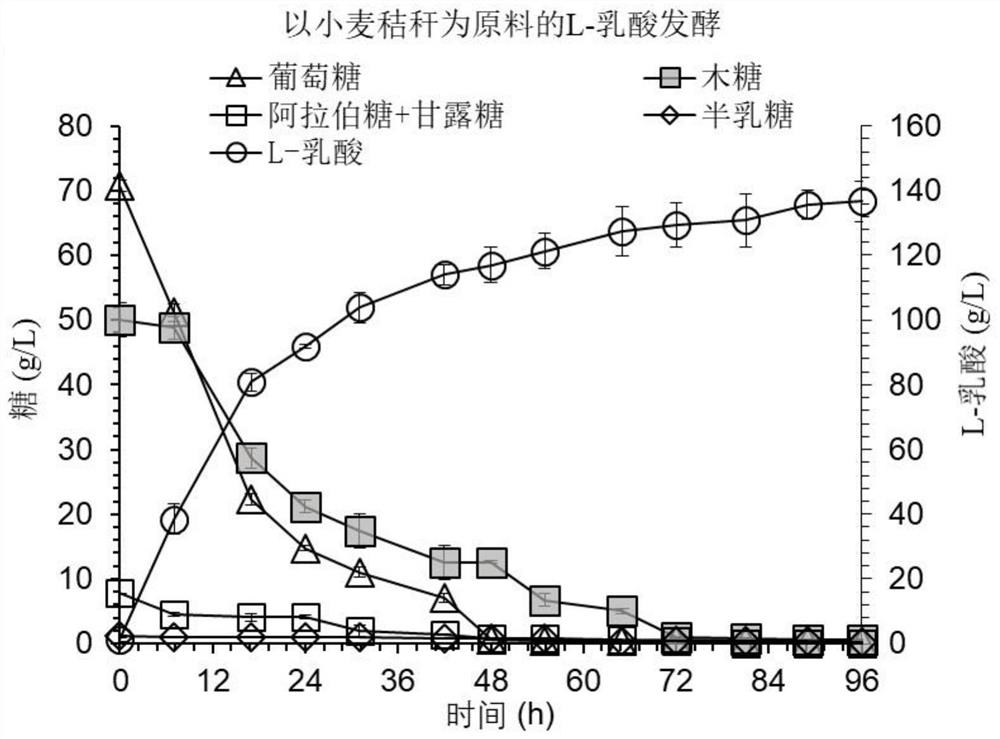
[0046] Example 1: A method for synthesizing L-lactide using chiral L-lactic acid produced from wheat straw as raw material 1. Ultimate biodegradation of pretreated wheat straw to remove inhibitors
[0047] After the wheat straw is pretreated with dry dilute acid, the pH of the material is adjusted to 5 with 20% (w / w) calcium hydroxide or calcium carbonate, and 10% (w / w) of Cladosporium Amorphotheca resinae is added For ZN1 seeds, 3 kg of uniformly mixed wheat straw and Cladosporium resinifera seeds were loaded into a 15L bioreactor for solid-state biodegradation under the conditions of aeration rate of 0.5vvm and temperature of 28°C. During the biodegradation process, the content of the main inhibitors in the material was determined by high performance liquid chromatography. At 36 hours, furfural, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, vanillin and syringaldehyde were completely consumed.
[0048] 2. Using high solid content pretreatment and detoxified wheat straw to ferment cellulose L-lac...
Embodiment 2
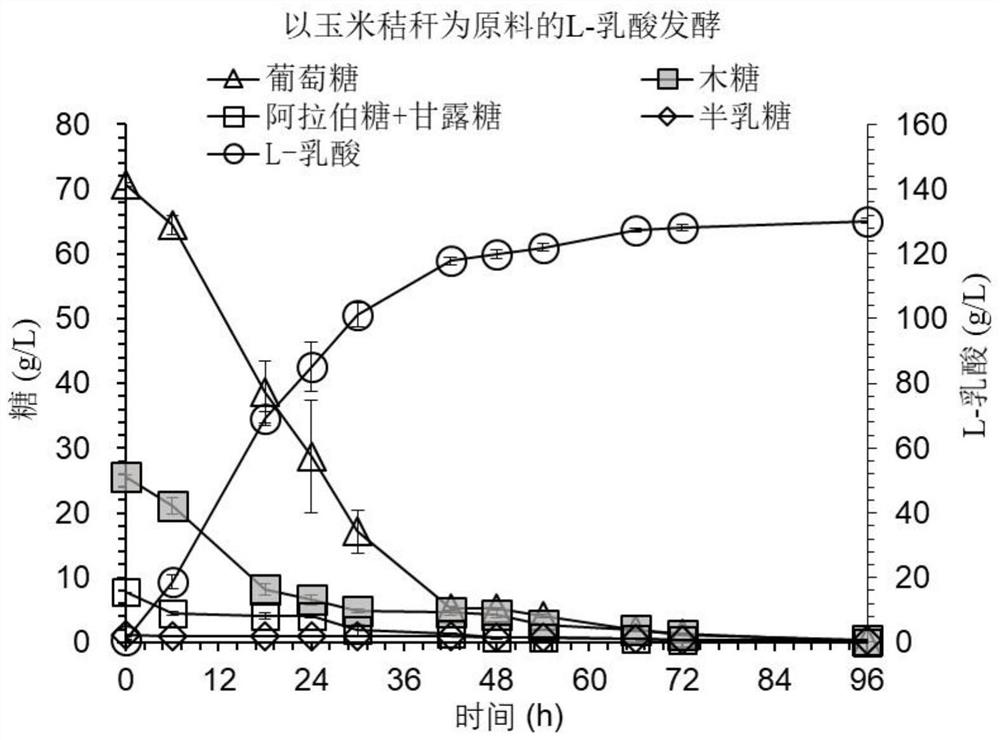
[0059] Example 2: A method for synthesizing L-lactide from chiral L-lactic acid produced from corn stalks as raw material 1. Final biodegradation of pretreated corn stalks to remove inhibitors
[0060] After corn stalks were pretreated with dry dilute acid, the pH of the material was adjusted to 4.8 with 25% (w / w) calcium hydroxide or calcium carbonate, and the cultivated Paecilomyces variotii FN89 (CGMCC17665) seeds were Inoculate in the material at a ratio of 20% (w / w), mix evenly, take 4kg of corn stalks and Cladosporium resinifera seeds mixture and put it into a plastic box, and carry out static biodegradation in a constant temperature incubator (37°C). During the biodegradation process, high performance liquid chromatography was used to measure the content of main inhibitors in the materials. After testing, furfural, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, vanillin and syringaldehyde were completely consumed within 48 hours.
[0061] 2. Using 30% (w / w) solid content pretreatment and det...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com