Organic light-emitting device
An electroluminescent device and a luminescent technology, applied in the direction of electric solid-state devices, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as increasing the use of evaporation sources, increasing device voltage, and limiting the commercialization of OLEDs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0086] Preparation of Compound 1-1
[0087] Single-neck flask was added 2-amino-5-bromo-pyrazine (17.3g, 100mmol), phenanthrene boronic acid (22.2g, 1000mmol), potassium carbonate (41.4g, 300mmol), [1,1'- bis (diphenylphosphino yl) ferrocene] dichloropalladium (0.73g, 1mmol), a solvent of tetrahydrofuran was added 300mL, water 60mL, reaction was refluxed overnight under nitrogen 80 ℃. Solid precipitated out during the reaction. TLC indicated completion of the reaction starting material, the reaction was stopped was cooled to room temperature, the precipitated solid was filtered and rinsed with water and ethanol, respectively, and dried. To give the title compound 1-1 (24.4g, yield 90%).
[0088] Preparation of Compound 1-2
[0089] Intermediate compound 1-1 (22.6g, 83.33mmol) was added with DCM (100mL) in the flask was cooled to 0 deg.] C, was slowly added dropwise ethoxycarbonyl isothiocyanate (10.92g, 83.33mmol), the The reaction solution was elevated to room temperature and sti...
Embodiment 1-1
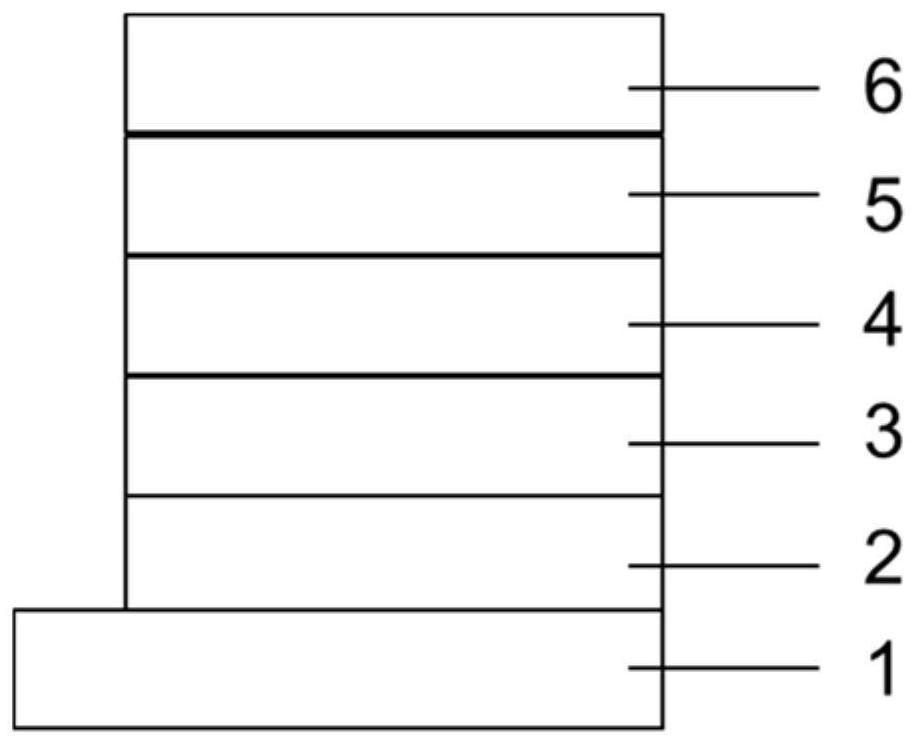
[0136] The glass plate coated with a transparent ITO conductive layer was sonicated in a commercial detergent, rinsed in deionized water, in acetone: ethanol solvent mixture ultrasonic degreasing, baked in a clean environment to completely remove moisture, UV light and ozone cleaning, and low-energy beam strikes the surface of the cation;
[0137] The above-described glass substrate with an anode placed in a vacuum chamber evacuated to 1 × 10 -5 ~ 9 × 10 -3 PA, in the anode layer HT1 film vacuum deposition as a hole transport layer of the device, deposition rate is 0.1nm / s, the total film thickness of 80nm is deposited;
[0138] A light emitting layer on the hole transport layer, light emitting layer comprises a vacuum deposition device, and a host material BFH-1 dye BFD-1, using the multi-source method of co-evaporation of the host material rate is 0.1nm / s, the rate of dye 0.005nm / s, the total film thickness was deposited 20nm.
[0139]Secondary electron emitting layer on t...
Embodiment 1-2
[0144] The glass plate coated with a transparent ITO conductive layer was sonicated in a commercial detergent, rinsed in deionized water, in acetone: ethanol solvent mixture ultrasonic degreasing, baked in a clean environment to completely remove moisture, UV light and ozone cleaning, and low-energy beam strikes the surface of the cation;
[0145] The above-described glass substrate with an anode placed in a vacuum chamber evacuated to 1 × 10 -5 ~ 9 × 10 -3 PA, in the anode layer HT1 film vacuum deposition as a hole transport layer of the device, deposition rate is 0.1nm / s, the total film thickness of 80nm is deposited;
[0146] A light emitting layer on the hole transport layer, light emitting layer comprises a vacuum deposition device, and a host material BFH-1 dye BFD-1, using the multi-source method of co-evaporation of the host material rate is 0.1nm / s, the rate of dye 0.005nm / s, the total film thickness was deposited 20nm.
[0147] Secondary electron emitting layer on ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com