Method for preparing cartilage tissue engineering scaffold from human umbilical cord Wharton jelly and cartilage tissue engineering scaffold
A cartilage tissue, Wharton's glue technology, applied in tissue regeneration, prosthesis, medical science, etc., can solve the problems of stem cell differentiation ability is inferior to type II collagen, unfavorable nutrients and waste transport, small pore size and porosity, etc. Excellent scaffold properties, loose pore arrangement, and easy absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
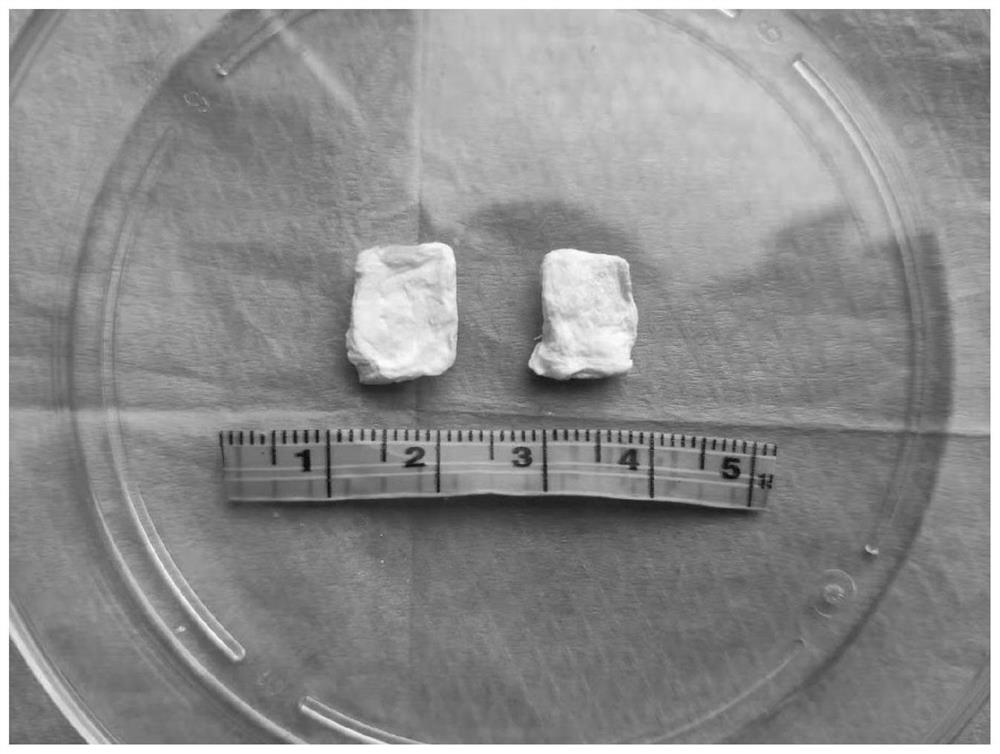
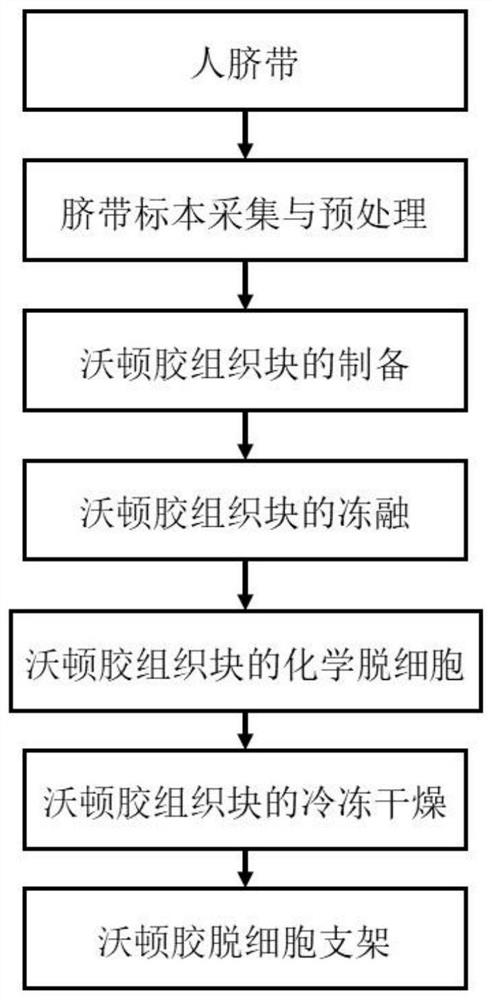
[0041] In this embodiment, a method of preparing cartilage tissue engineering brackets in human umbilical cord Warten is as follows (such as figure 1 Disted):
[0042] (1) Umbilical belt specimens collection and premium:
[0043] Inject 300ml antibiotic (penicillin: 10,000 units / 100ml, streptomycin: 50,000 units / 100ml) in the 500ml plastic grooming, will be taken in the obstetric surgery The umbilical belt specimens of the uterinestormation immediately placed in the spanking bottle; in the umbilical cord extent 30min, washed repeatedly with PBS solution until the umbilical cord surface and the internal naked eyes were unable to see blood clots and foreign objects; pull the clean umbilical cord straightened , Put into ordinary refrigerator cold freezer - 20 ° C for 1 h with sterile wrap
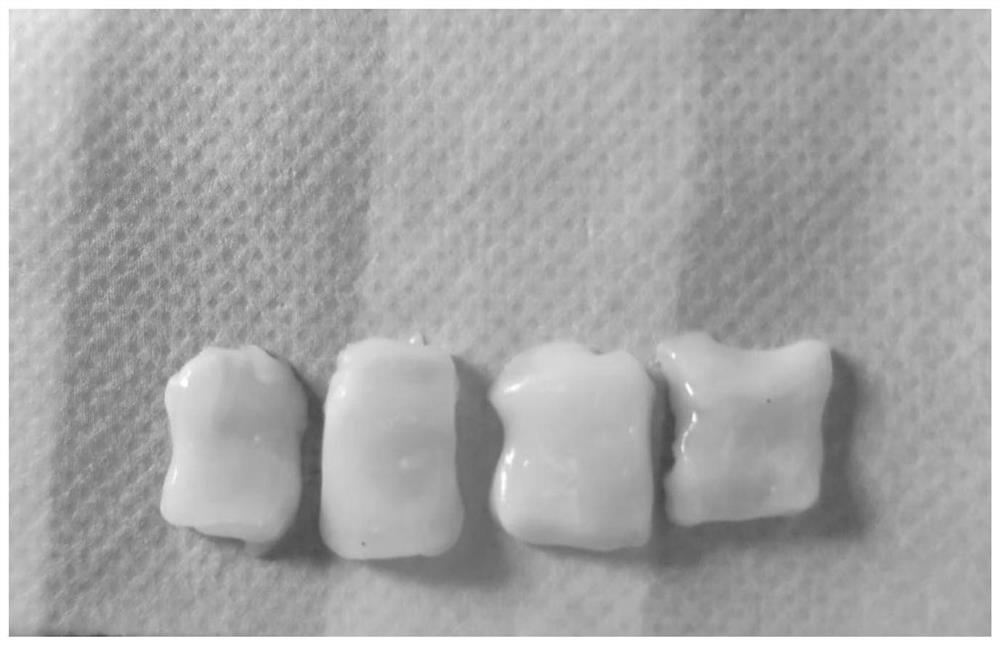
[0044] (2) Preparation of Wharton gum tissue block
[0045] The longitudinal long axis of the umbilical cord after pre-opening is cut into a cylindrical tissue tissue tall higher than about 10...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com