Method for degrading carbon tetrachloride by two-step anaerobic biological enhancement method
A technology of carbon tetrachloride and anaerobic organisms, which is applied in the field of water pollution control, can solve the problem that the formation and accumulation heat of chlorinated intermediate products have not been fundamentally resolved, so as to avoid inhibition, ensure anaerobic environment, and simplify the operation process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
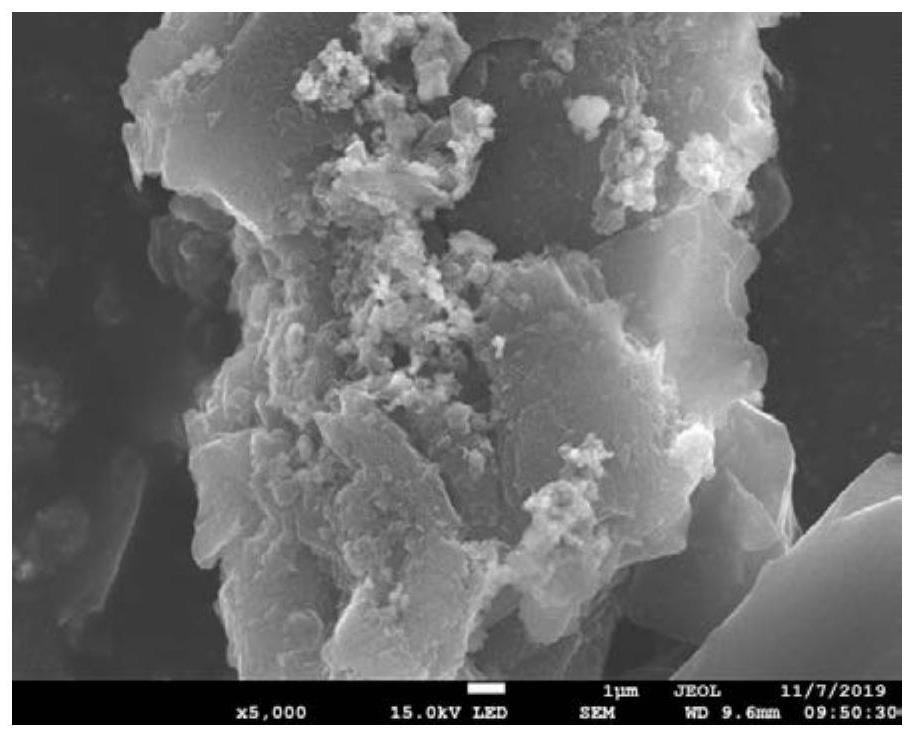
[0042] Preparation of nano-sized zero-valent iron supported on activated carbon.
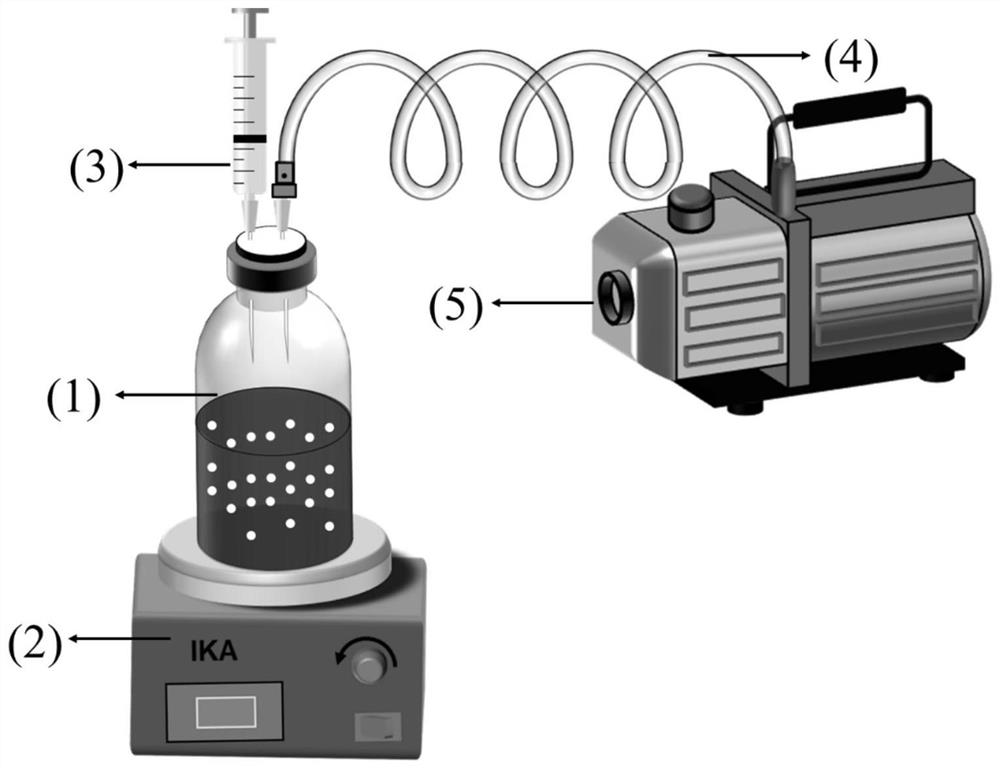
[0043] see figure 1 Preparation device, prepare 500mL mixed solution containing ferrous ion and activated carbon, which contains 20g / LFeSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 20g / L 200-mesh activated carbon and 10g / L polyvinylpyrrolidone, transfer the solution to a 1L solvent bottle, cover with an anaerobic rubber stopper, tighten the screw cap, vacuumize for 40min to remove oxygen, and place in a 200°C oven Leave it for 12 hours to load ferrous ions on activated carbon. After loading, the closed reaction vessel was placed on a magnetic stirrer and freshly prepared 100 mL of 1 M NaBH 4 The solution was slowly injected into the mixed solution containing ferrous ions with a syringe ( figure 1 ), magnetic stirring can make NaBH 4 Fully contact with ferrous ions and quickly discharge the generated hydrogen, and discharge a large amount of hydrogen generated by the reaction by vacuuming during the reaction process and m...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Chloroform anaerobic degradation enrichment culture and dichloromethane anaerobic degradation enrichment culture were obtained.
[0058]The river sediment collected from Xihe River in Shenyang City was used as the inoculation source. The content of organic matter in the above sediment is 8g / Kg, and the content of dissolved oxygen is 0.2mg / L. After collection, it is sealed and stored in a glass bottle.
[0059] Aliquot 100mL inorganic salt medium into 160mL glass serum bottles with N headspace 2 / CO 2 (80 / 20, v / v), add 5 mM sodium lactate as a carbon source, add 5 μL chloroform (liquid phase concentration 0.56 mM) or 5 μL dichloromethane (liquid phase concentration 0.73 mM) as an electron acceptor through a microsyringe, and ultrasonically dissolve. The culture medium and bottom mud were transferred into an anaerobic glove box, and 2 g of bottom mud was added to each bottle of culture medium as an inoculum source. The inoculated glass serum bottle was sealed with a ru...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Comparative experiments on the inhibitory effects of nano-zero-valent iron and activated carbon-loaded nano-zero-valent iron on the degradation ability of chloroform degradants in enrichment culture.
[0066] The specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0067] Aliquot 100mL inorganic salt medium into 160mL glass serum bottles with N headspace 2 / CO 2 (80 / 20, v / v), add 5mM sodium lactate as carbon source, 10mL hydrogen as electron donor, 5μL chloroform (liquid phase concentration 0.56mM) as electron acceptor, with 3% (v / v) transfer amount Inoculate with LSCF-1. Nano-sized zero-valent iron with an iron content of 12.5 mg and nano-sized zero-valent iron supported by activated carbon were added respectively, and cultured at 30° C. in the dark.
[0068] Chloroform and its degradation products in the culture were detected regularly by gas chromatography with flame ionization detector (GC-FID).
[0069] Depend on Figure 8 It can be seen that 2.7 μmol of dichlorometh...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com