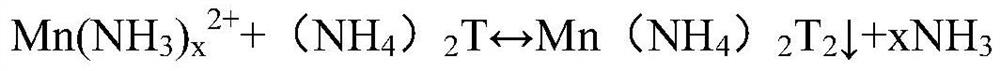Comprehensive recovery method of waste sodium-ion battery
A technology of sodium-ion batteries and recycling methods, which is applied in the field of comprehensive recycling of waste sodium-ion batteries, and can solve problems such as environmental threats, increased battery recycling costs, and secondary pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A comprehensive recovery method for waste sodium ion batteries, the specific process is:
[0037] (1) Pretreatment of waste sodium-ion batteries: Disassemble the shell of waste sodium-ion batteries, soak and discharge waste sodium-ion batteries in 0.13wt% sodium chloride, place in a sintering furnace at a temperature of 155°C, and evaporate the internal electrolyte of the battery for 3 hours and 36 minutes. Crushing, using a multi-stage vibrating sieve to sieve out the battery case and aluminum foil current collector, and the under-sieve is battery black powder;
[0038] (2) Battery black powder leaching treatment: 150g of black powder and 12g of sodium carbonate were mixed and ground for 54 minutes, 80mL of 0.54mol / L sodium sulfite and 1.5L of 3.27mol / L ammonia liquid were added, leached at 53°C, and solid-liquid separation was obtained The leaching solution and solid are dissolved by adding dilute sulfuric acid with a concentration of 0.21 mol / L to the solid, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A comprehensive recovery method for waste sodium ion batteries, the specific process is:
[0042] (1) Pretreatment of waste sodium-ion batteries: Disassemble the shell of waste sodium-ion batteries, soak and discharge waste sodium-ion batteries in 0.13wt% sodium chloride, place in a sintering furnace at a temperature of 155°C, and evaporate the internal electrolyte of the battery for 3 hours and 36 minutes. Crushing, using a multi-stage vibrating sieve to sieve out the battery case and aluminum foil current collector, and the under-sieve is battery black powder;
[0043] (2) Battery black powder leaching treatment: 150g of black powder and 7.5g of sodium carbonate were mixed and ground for 69 minutes, 60mL of 0.54mol / L sodium sulfite and 1.2L of 3.27mol / L ammonia liquid were added, leached at 53°C, and solid-liquid separation Obtain leaching solution and solid, dissolve the solid with dilute sulfuric acid with a concentration of 0.21mol / L, separate the carbon residue, s...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A comprehensive recovery method for waste sodium ion batteries, the specific process is:
[0047] (1) Pretreatment of waste sodium-ion batteries: Disassemble the casing of waste sodium-ion batteries, soak and discharge waste sodium-ion batteries in 0.04wt% sodium sulfate, place in a sintering furnace at a temperature of 185°C, evaporate the electrolyte inside the battery for 3h23min, and crush , Use a multi-stage vibrating sieve to sieve out the battery case and aluminum foil current collector, and the under-sieve is battery black powder;
[0048] (2) Battery black powder leaching treatment: 120g of black powder and 10g of ammonium sulfate were mixed and ground for 87 minutes, 75mL of 0.54mol / L sodium sulfite and 1.0L of 3.35mol / L ammonia liquid were added, leached at 64°C, and solid-liquid separation was obtained The leaching solution and solid are dissolved by adding dilute hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 0.46mol / L to dissolve the solid, and the carbon resid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com