Large-scale preparation of high-crystallinity prussian blue analogue for sodium ion battery based on'water-in-salt 'microreactor principle
A sodium-ion battery and ion battery technology, which is applied in the preparation and application of manganese-based Prussian blue analogues, can solve problems such as poor cycle stability, increased production costs, and cumbersome process flow, and achieve good rate performance, less defects, and The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) Manganese sulfate monohydrate (4mmol) and sodium ferrocyanide decahydrate (6mmol) were thoroughly mixed and ground according to the molar ratio of 1:1.5, the mixture was transferred to a stainless steel ball mill jar (50mL), and zirconia ball mill beads were added (Ball to material ratio is about 10:1), at 300rmp speed, mechanical ball milling in air atmosphere for 24h, the product was washed 3 times with deionized water, washed 1 time with ethanol, to remove impurities and unreacted raw materials, in a vacuum oven at 120 After drying at ℃ for 12h, the product MnHCF-S was obtained.
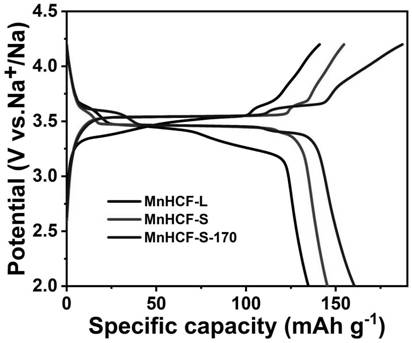
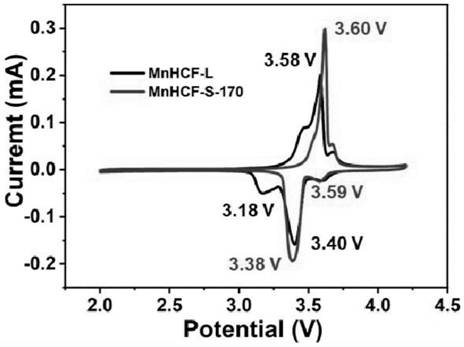
[0030] (2) Heat treatment: the product MnHCF-S obtained in (1) is heated at 1°C·min in an argon atmosphere -1 The heating rate was raised to 170 °C, and the temperature was kept for 12 hours to obtain the target product, namely MnHCF-S-170 material. figure 1 Shown is the scanning electron microscope image of the MnHCF-S-170 material, and it can be seen that it presents an elliptical sh...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is that there is no step (2) in Example 1, and other conditions are exactly the same as Example 1 to obtain the MnHCF-S material.
[0036] The scanning electron microscope picture of the MnHCF-S material that embodiment 2 obtains is as figure 2 As shown, it presents an oval shape similar to that of MnHCF-S-170.
Embodiment 3
[0038] (1) MnHCF-L was prepared using the same materials as in Example 1. Manganese sulfate monohydrate (4mmol) was dispersed in 40mL deionized water, and magnetically stirred at room temperature for 3h to form solution A, and sodium ferrocyanide decahydrate (6mmol) was dissolved in 40mL deionized water to form solution B.
[0039] (2) Pour A into solution B under continuous stirring, and then age the resulting mixed solution at room temperature for 24 h. The product was washed three times with deionized water and once with ethanol to remove impurities and unreacted raw materials, and the collected product was dried in a vacuum oven at 120°C for 12 hours. The resulting sample was labeled MnHCF-L.
[0040] The scanning electron micrograph of the MnHCF-L material that embodiment 3 obtains is as image 3 As shown, it presents an oval shape of 10-100 nm.
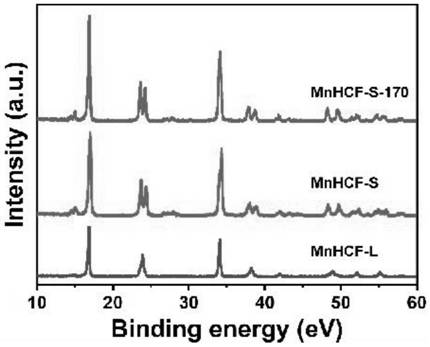
[0041] Figure 4 It is the XRD comparison diagram of the three products of Examples 1-3, which can prove that the products...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com