Copper-indium-galliun-selenium film solar cell and its preparation method
A technology for solar cells and copper indium gallium selenide, which is applied to circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the technological process and increasing the production cost, and achieves the effects of simple battery structure, improved production yield and simple process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
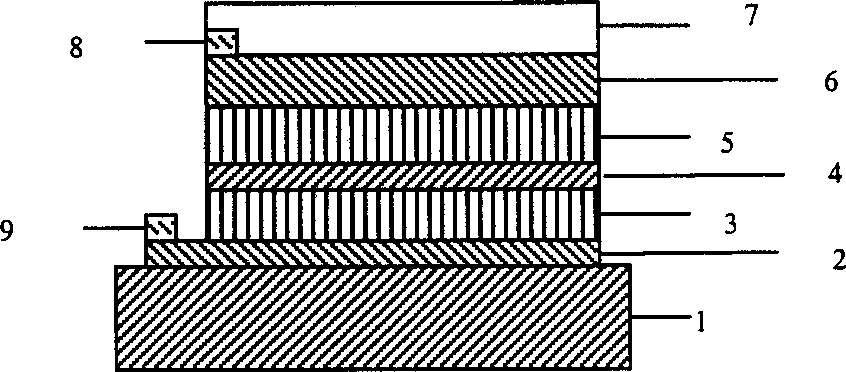
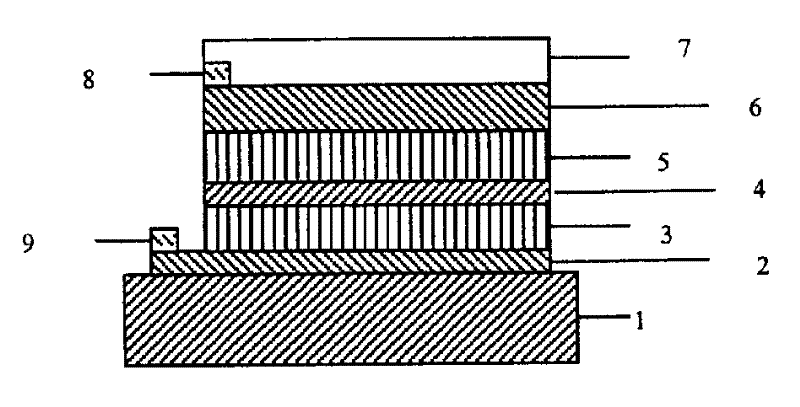
[0025] The preparation method of the ZnS window layer 5 may be electroless plating or vacuum evaporation. Among them, electroless plating can be selected to contain Zn +2 (0.1-0.3M), ammonia water (5-8M, PH=10.5-11.0), thiourea (NH 2 CSNH 2 , 0.3-0.9M) bath, temperature at 60-85 ° C, electroless ZnS layer. Among them, the vacuum evaporation method can choose ZnS crystal particles, which can be realized by thermal evaporation or electron beam evaporation. The film thickness is 70-220nm.
[0026]The transparent electrode 6 can be selected from zinc aluminum oxide (ZAO) or indium tin oxide (ITO), etc., wherein the preparation method of zinc aluminum oxide can use metal target sputtering, and the zinc aluminum oxide thin film with the best performance is made of zinc aluminum oxide ceramic target Prepared by radio frequency or high frequency AC magnetron sputtering. The thickness of this layer is 0.10-0.35 μm. ITO is generally prepared by magnetron sputtering using ceramic t...
Embodiment 1
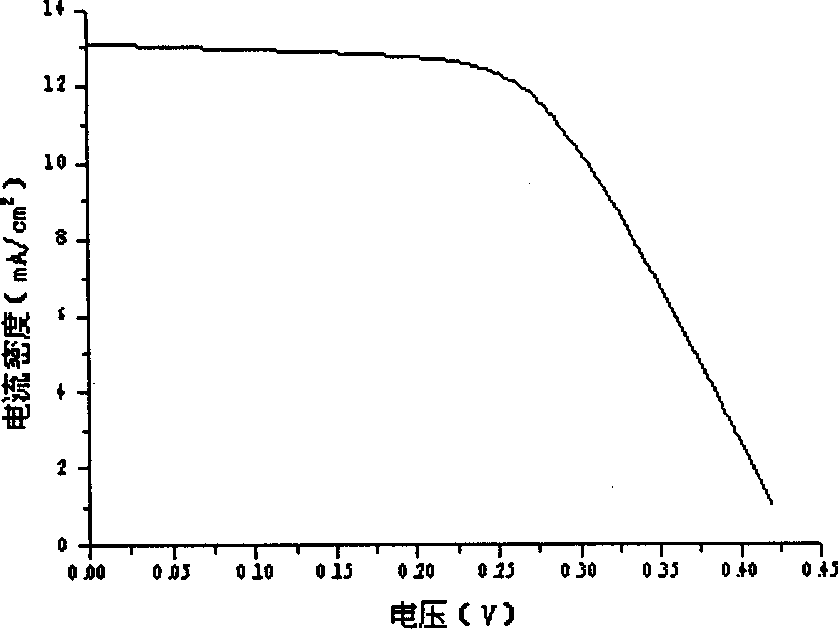
[0029] On the surface of soda-lime glass, a Cu-Mo alloy back electrode was deposited by sputtering with Cu and Mo alloy targets, with a thickness of about 1.45 μm. The content of Cu in the prepared Cu-Mo alloy film was 6%. Then, the co-evaporation method is used, that is, Cu, In, Ga, Se are used for reactive evaporation to form Cu(In, Ga)Se on the substrate. 2 The thin film starts to evaporate sulfur when its thickness grows to 2.0 μm. The substrate temperature is 350°C, and the evaporation rate is 6 / S. A sulfur-containing preliminary layer was formed with a thickness of about 50 nm. Then, under an argon protective atmosphere, annealing is performed at 500° C. for 15 minutes to form a CIGSS thin film. After cleaning and drying with argon, immerse at room temperature containing 0.1MZn +2 , 7M ammonia water, 0.6M thiourea solution, take it out after 30 seconds, raise the temperature of the plating solution to 85°C, and dip it repeatedly five times to form a dense ZnS film lay...
Embodiment 2
[0031] On the surface of soda-lime glass, a Cu-Mo alloy back electrode was deposited by sputtering with Cu and Mo alloy targets, with a thickness of about 1.45 μm. The content of Cu in the prepared Cu-Mo alloy film was 15%. After cleaning and drying with argon gas, a preliminary layer containing Cu, In and Ga was formed on the substrate by magnetron sputtering, and its thickness was 1.2 μm. On its surface, a selenium layer with a thickness of 0.7 μm was evaporated, and kept at 500° C. for 20 minutes in an atmosphere of selenium. Subsequently, co-evaporation of sulfur and indium is carried out. The substrate temperature is 450° C., and after vacuum annealing at 500° C. for 10 minutes, a CIGSS film with a thickness of about 35 nm is formed. Immerse at room temperature containing 0.2MZn +2 , 6M ammonia water, 0.8M thiourea solution, take it out after 30 seconds, raise the temperature of the plating solution to 80°C, and dip it five times repeatedly to form a dense ZnS thin film...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com