Process for preparing particle-reinforced magnesium-base composite material by vacuum pressure impregnation
A technology of vacuum pressure impregnation and composite materials, which is applied in the field of composite materials, and can solve the problems of complex usage costs of impregnation equipment, large amount of filling protective gas, and large volume of pressure vessels, and achieve perfect stability, good interface bonding, and production high efficiency effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
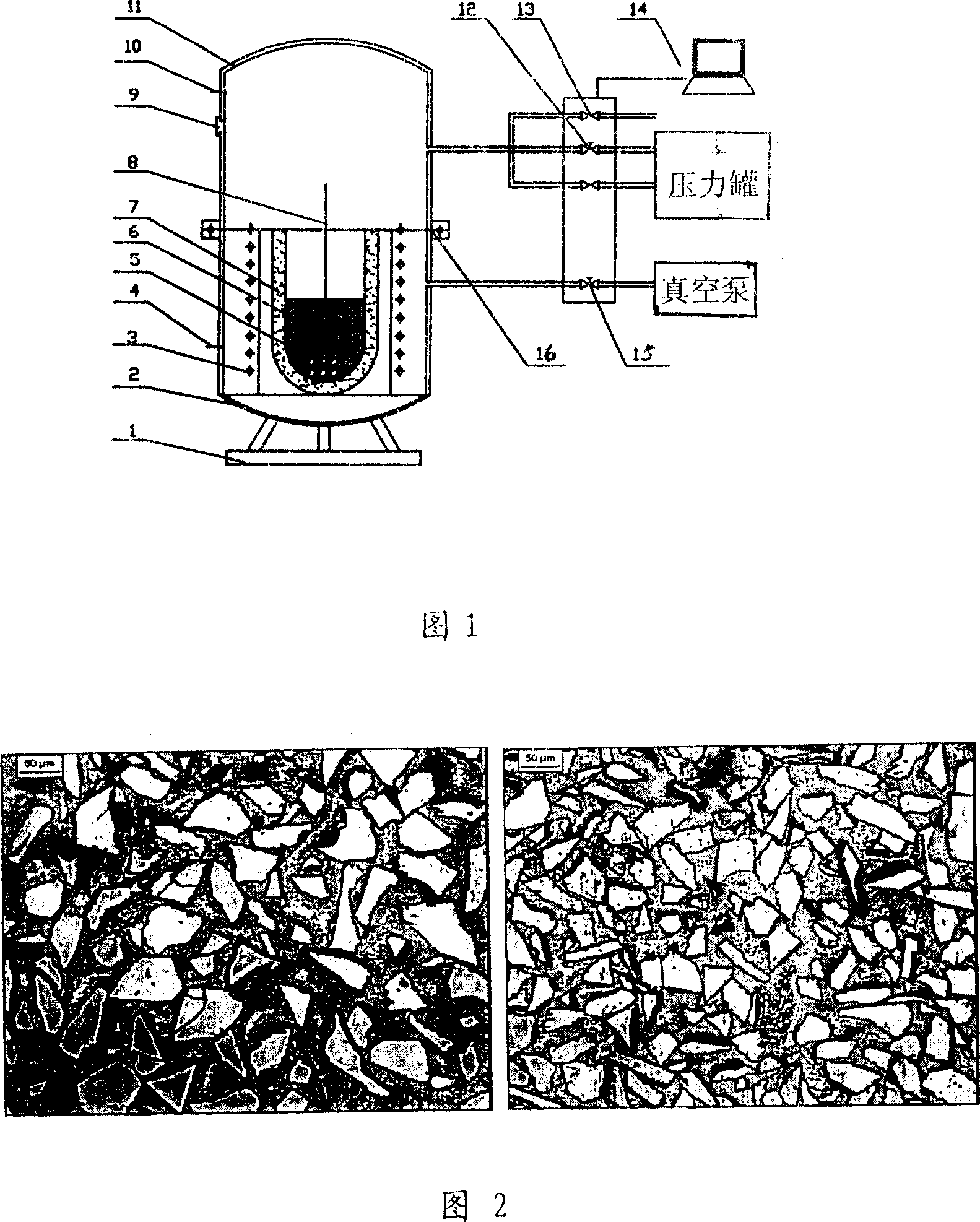
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] This example is the preparation of silicon carbide particle reinforced magnesium-based composite material.
[0020] (1) Reinforcing phase treatment: Magnesium alloy AZ91D is used as the matrix material, and silicon carbide particles with an average particle size of 32 μm are used as the reinforcing phase. The surface of the silicon carbide particles is modified with silane coupling agent KH-570, and then heated at 150 °C. room drying;
[0021] (2) Preparation of prefabricated parts: After drying at 150°C, after uniform mixing with 3% lithium stearate powder, 6% epoxy resin powder, and 6% ammonium dihydrogen phosphate powder, the laser power is 40W, and the scanning speed is 1500mm / s, the sintering distance is 0.1mm, and the powder layer thickness is 0.15mm, and the laser sintered part is sintered and formed, and the laser sintered part is gradually heated to 700 ° C for secondary baking to obtain a silicon carbide preform;
[0022] (3) Preparation of composite materia...
Embodiment 2
[0025] This example is the preparation of silicon carbide particle reinforced magnesium-based composite material.
[0026] (1) Reinforcing phase treatment: Magnesium alloy AZ91D is used as the base material, and silicon carbide particles with an average particle size of 11 μm are used as the reinforcing phase. The surface of the silicon carbide particles is cleaned with 5% dilute HCL solution, and then dried at 200°C;
[0027] (2) Preparation of prefabricated parts: Vibrate the dried silicon carbide particles into low-carbon steel pipes as prefabricated parts, and dry them at 300°C;
[0028] (3) Preparation of composite materials: fix the preform in the resistance furnace in the pressure vessel, sprinkle a layer of RJ-2 flux accounting for 0.2% of the mass of the charge, then place magnesium alloy AZ91D ingots around the preform, and then sprinkle Add a layer of RJ-2 flux; seal the upper and lower tanks, continue to heat the prefabricated parts and magnesium alloy ingots, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] This example is the preparation of boron carbide particle-reinforced magnesium-based composite material.
[0032] (1) Reinforcement phase treatment: Magnesium alloy AZ91D is used as the base material, and boron carbide (B4C) particles with an average particle size of 20 μm are used as the reinforcement phase. The surface of the boron carbide particles is cleaned with pure water, and then dried at 150 °C;
[0033] (2) Preparation of prefabricated parts: Vibrate the dried boron carbide particles into low-carbon steel pipes as prefabricated parts, and dry them at 250°C;
[0034] (3) Preparation of composite materials: fix the preform in the resistance furnace in the pressure vessel, sprinkle a layer of potassium chloride and magnesium chloride (KCl+MgCl 2 ) each 50% flux, and then place magnesium alloy AZ91D ingots around the prefabricated part, and then sprinkle a layer of potassium chloride and magnesium chloride 50% flux; Continue to heat the block and start vacuuming....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com