Ex-vivo priming for generating cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for non-tumor antigens to treat autoimmune and allergic disease
a technology of priming, which is applied in the field of ex-vivo priming for generating cytotoxic t lymphocytes specific for non-tumor antigens to treat autoimmune and allergic diseases, can solve the problems of allergic diseases and autoimmune diseases, and achieve the effect of preventing the development and progression of diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Manufacture of Drosophila Antigen-Presenting Cells
[0243] The Schneider S2 cell line was prepared from Drosophila melanogaster (Oregon-R) eggs according to published procedures and has been deposited with the American Type Culture Collection (CRL 10974). S2 cells are grown in commercial Schneider's Drosophila medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum.
[0244] The pRmHa-3 plasmid vector for expressing MHC Class I and co-stimulatory proteins in S2 cells was derived from the pRmHa-1 expression vector constructed as described in the literature. It contains a metallothionein promoter, metal response consensus sequences and an alcohol dehydrogenase gene bearing a polyadenylation signal isolated from Drosophila melanogaster.
Complementary DNAs for Fransfection were Prepared as Follows:
[0245] HLA-A2.1 and β-2 microglobulin: Reverse transcription-PCR from K562 cells using primers derived from the published sequence. [0246] B7.1: Reverse transcription-PCR from K562 cells using primers...
example 2
Trial of Cytotoxic T Cell Infusions Against IgE Producing Cells
Purpose of Trial
[0259] This example teaches the effectiveness of cytotoxic T Cell infusions in the treatment of allergic diseases as assessed according to the following factors: [0260] 1. Safety and toleration of re-infused autologous CTLs after in vitro immunization; [0261] 2. Kinetics of infused CTLs in the systemic circulation factoring in limiting dilution analysis; [0262] 3. Whole body disposition of CTLs by radioscintigraphy; [0263] 4. Cell composition of biopsied nodules by immunohistology (CTLs, TH, NK, B cells); and [0264] 5. Regression of measurable lesions and duration of response over two months.
Treatment with Ex Vivo Generated Autologous CTLs
[0265] All patients will receive, at least, a single infusion of autologous CTLs. The number of cycles and the dose of cells administered to each patient are summarized in Table 1. The number of cells generated in vitro is dependent on patient-related factors such ...
example 3
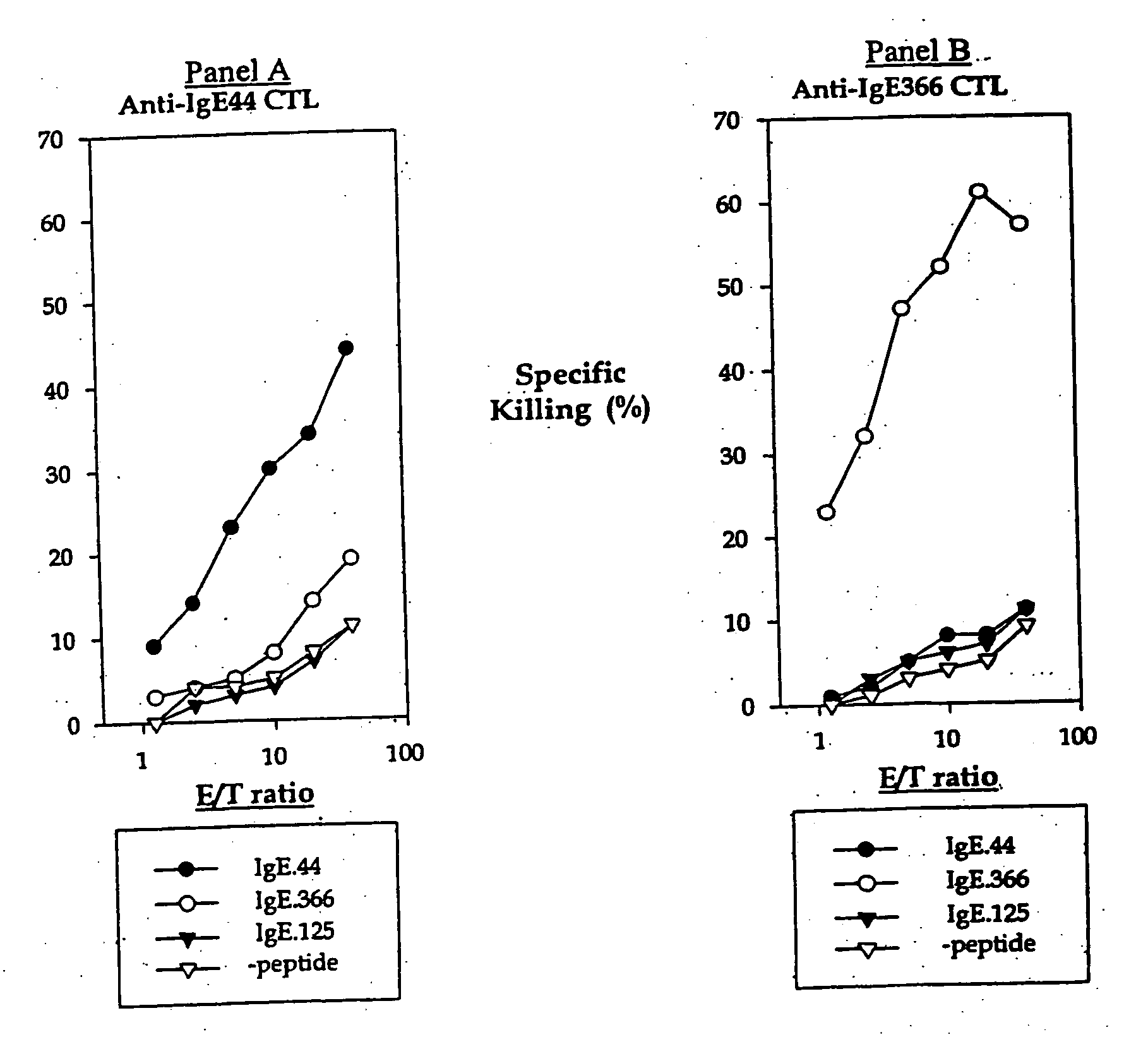
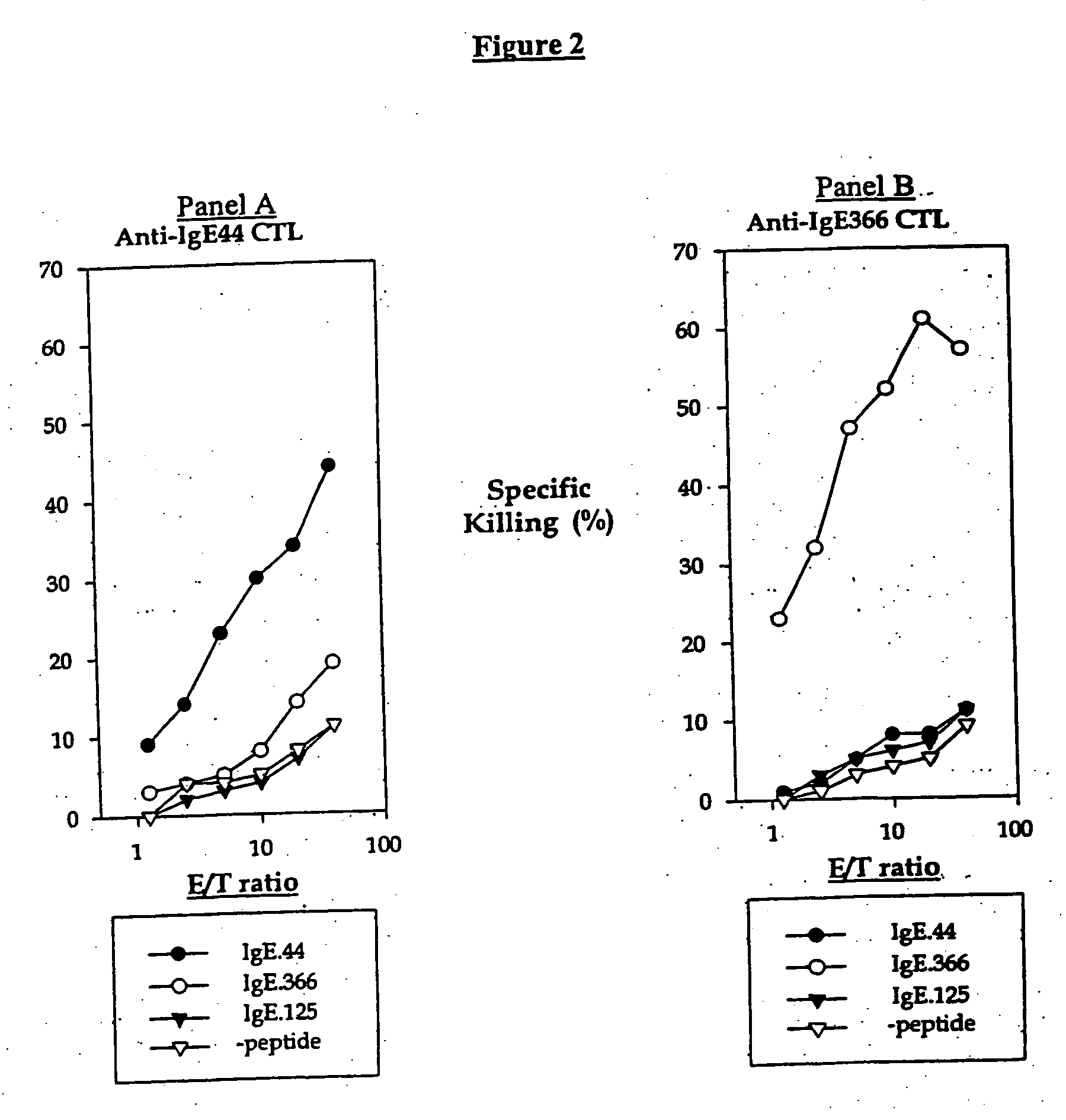
[0269] IgE plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma. Here, we show that cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) specific for antigenic peptides derived from IgE molecule can be generated in vitro by stimulating resting naive CD8 T cells with IgE peptides presented by artificial antigen presenting cells. The IgE specific CTLs lyse the target cells loaded with IgE peptides in vitro and inhibit antigen specific IgE response in vivo. In addition, adoptive transfer of the IgE specific CTL to an asthmatic mouse model can inhibit the development of lung inflammation and airway hypersensitivity. Thus, IgE specific CTL may provide a treatment for allergic asthma and other IgE-mediated allergic diseases.
[0270] Cytotoxic T lymphocytes are derived from resting naïve CD8 T cells. In the present of antigens and co-stimulations, resting naïve CD8 T cells can be activated and differentiated into armed cytotoxic T cells, which can destroy the target cells that express the antigens. CTL...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adhesion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com