Medicament elution bracket for promoting esoderma repair and preventing vascular restenosis
A technique for eluting stents and restenosis, applied in the fields of stents, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve problems such as stents that cannot be effectively solved at the same time, and achieve the effects of reducing stent thrombosis, promoting endothelial repair, and reducing restenosis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
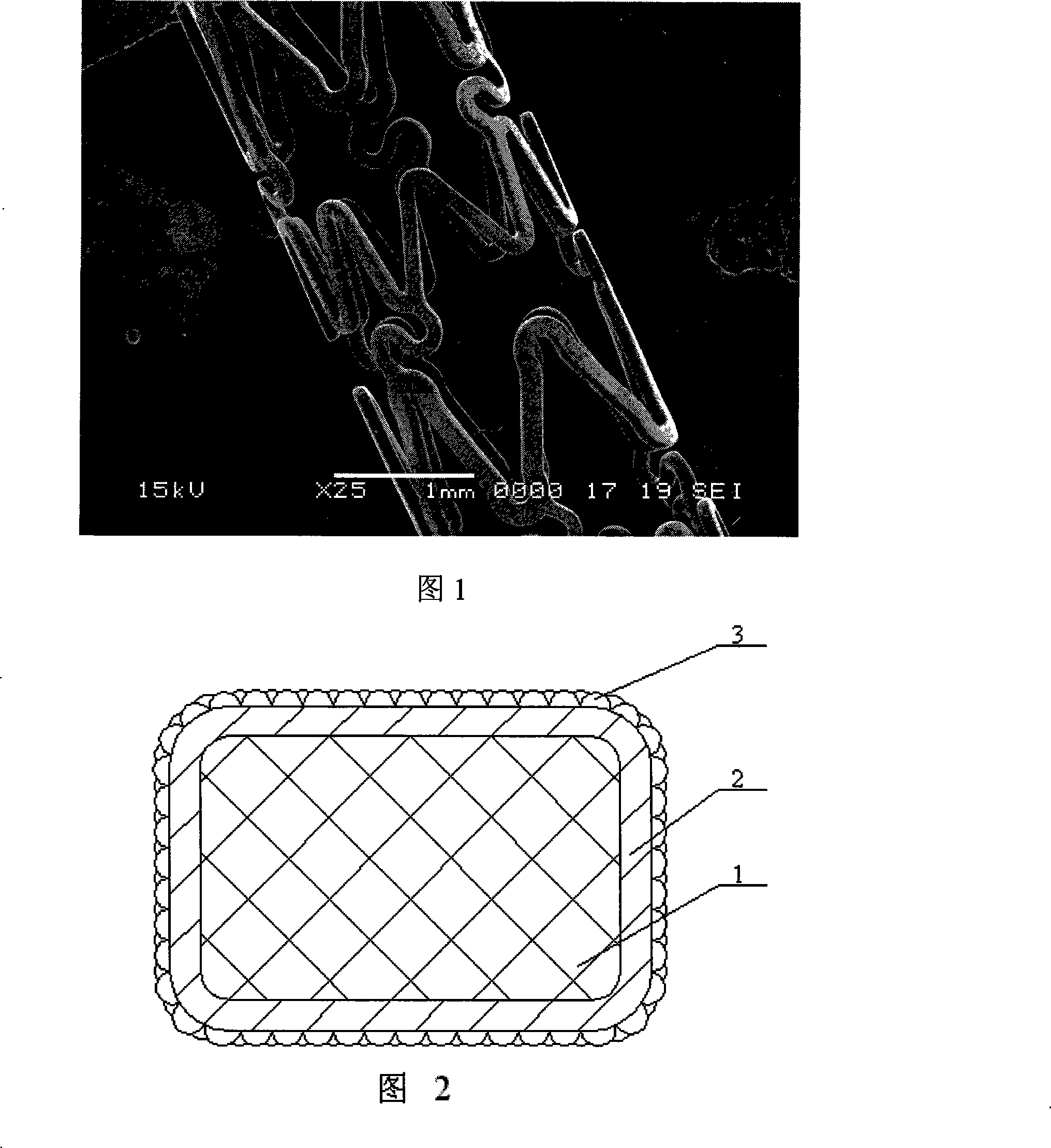
[0020] Embodiment 1: (See Figures 1-3) In this embodiment, the drug-eluting stent that promotes endothelial repair and prevents restenosis is composed of a stent matrix, an intermediate layer, and an antibody coating from the inside to the outside. The base of the bracket is mesh; the material of the base of the bracket is stainless steel, polymer, nickel-titanium alloy, magnesium alloy, tantalum or gold. The middle layer includes at least one drug layer composed of one or more of diarsenic trioxide, tetraarsenic hexaoxide and organic arsenic, wherein the organic arsenic is p-aminophenylarsine acid, sodium p-aminophenylarsine or 3-nitro- 4-Hydroxyphenylarsineic acid. When the drug layer is a mixture, the arsenic trioxide, tetraarsenic hexaoxide and organic arsenic are mixed in any ratio. The antibody in the antibody coating is a monoclonal antibody, a polyclonal antibody, an animal antibody or a human antibody capable of recognizing and adsorbing endothelial progenitor cells,...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific embodiment two: (see Fig. 2, Fig. 3) the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the intermediate layer also comprises at least one layer of controlled release layer, and the material of controlled release layer is macromolecule material, and macromolecule material is polymer. Wherein said polymer is polyester, chitosan, cellulose, extracellular matrix, polylactic acid polyglycolic acid copolymer, styrene-isobutylene-styrene copolymer, hydroxystyrene-isobutylene-hydroxystyrene Copolymers and their derivatives, polyvinyl alcohol grafted polylactic acid polyglycolic acid copolymer, phosphorylcholine and L-polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid polylactic acid copolymer, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVAC), polymethacrylic acid n-Butyl ester (PBMA), methyl methacrylate (MMA), polycaprolactone or polyurethane.
[0025]In this embodiment, the controlled release layer is located between the stent matrix and the drug layer, or between the d...
specific Embodiment approach 3
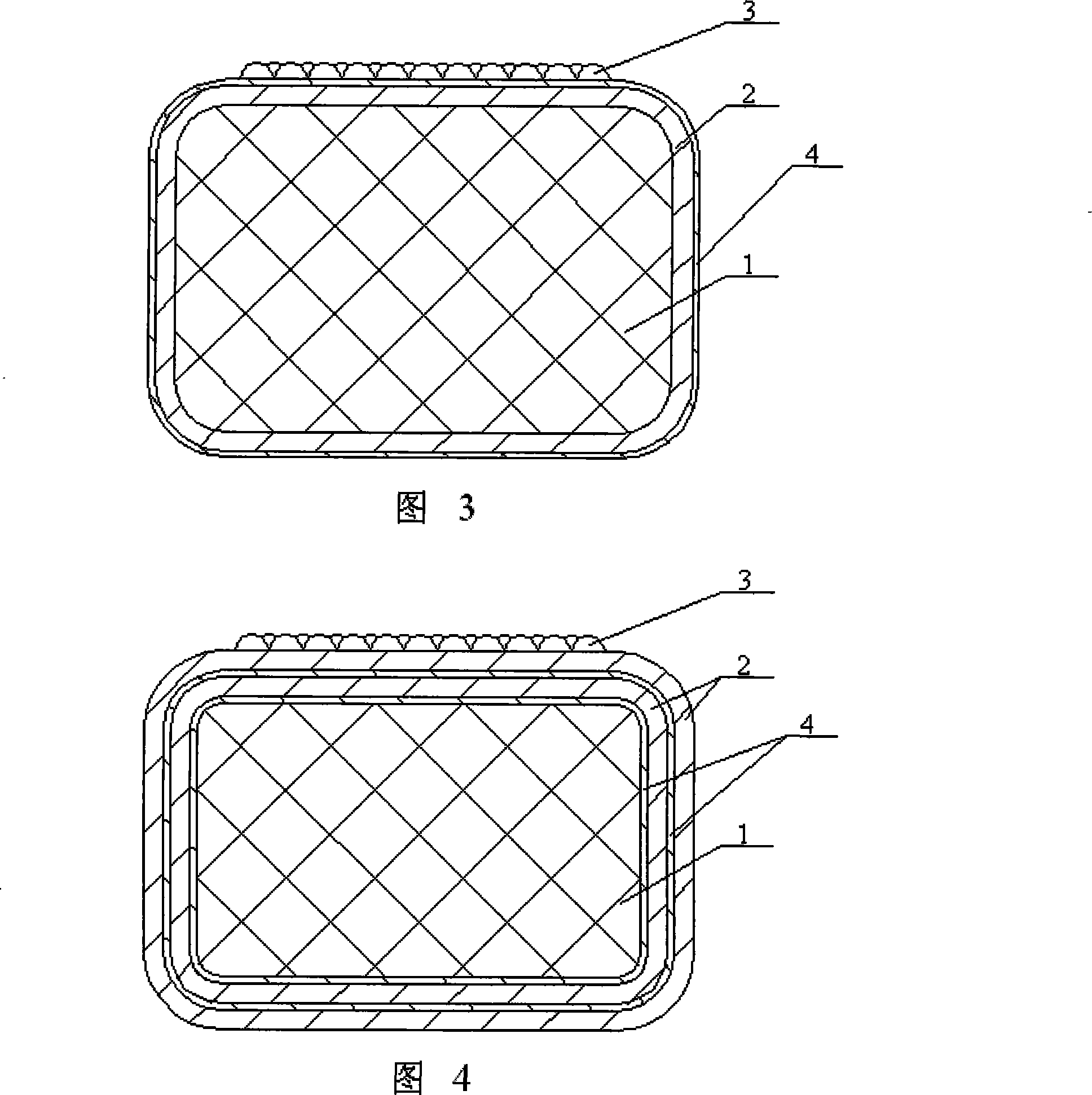
[0027] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the middle layer of the drug-eluting stent that promotes endothelial repair and prevents restenosis is made of one or more of arsenic trioxide, tetraarsenic hexoxide, and organic arsenic. A composition of arsenic-containing drugs and polymers. When the arsenic-containing medicine is a mixture, the diarsenic trioxide, tetraarsenic hexaoxide and organic arsenic are mixed in any ratio; the total weight of the arsenic-containing medicine is 5-200 micrograms. Wherein the organic arsenic is p-aminophenylarsine, sodium p-aminophenylarsine or 3-nitro-4-hydroxyphenylarsine.
[0028] In this embodiment, the ratio of the polymer material and the drug component can be added as needed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com