CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductors) semiconductor integrated circuit with high irradiation resistance and preparation method thereof
A technology of integrated circuits and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of wasting active area area, poor resistance and capacitance characteristics, increasing process steps and complexity, and cost, so as to reduce charge Trapping centers, preventing latch-up effects, and reducing device defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
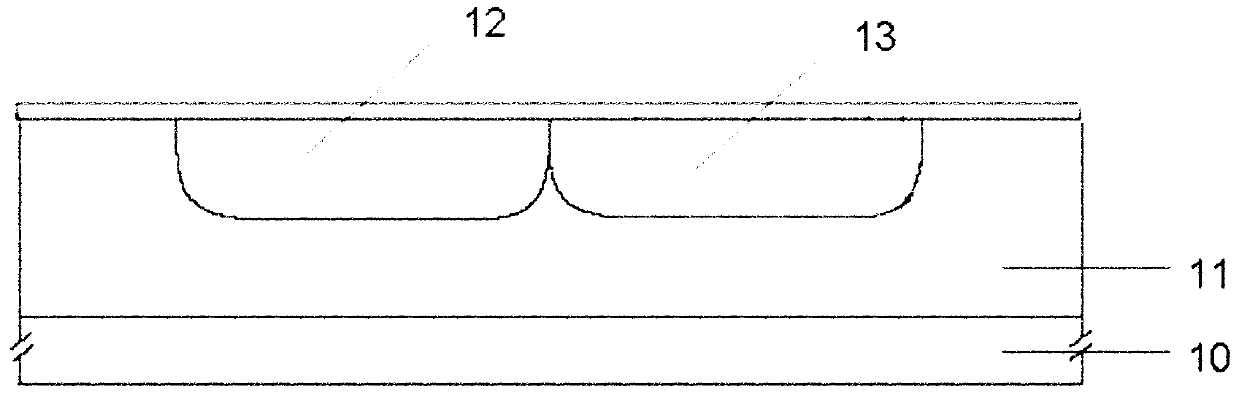
[0032] The substrate is a p-type silicon wafer 10, and a p-epitaxial layer 11 is grown, and the thickness of the p-epitaxial layer 11 is about 5.0 μm. see Figure 4 , forming a double well process, thermally growing on the surface of the p- epitaxial layer 11 with a thickness of about 150 The masking oxide layer is used to protect the surface from contamination and reduce injection damage. The n-well implantation region is photolithographically etched, and phosphorus is implanted to form the n-well 12 , and the p-well implantation region is photolithographically etched, and boron is implanted to form the p-well 13 .
[0033] For deep trench etching see Figure 5 , using hydrofluoric acid to remove the masking oxide layer, and thermally grow a thin oxide layer 20 with a thickness of about 150 As a corrosion protection layer for the source region when the upper silicon nitride film is removed; then use LPCVD to deposit silicon nitride 21 as a barrier layer for chemical mech...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The substrate is a p-type silicon wafer 10, on which a p- epitaxial layer 11 is grown with a thickness of about 5.0 μm. see Figure 4 , forming a double well process, the thermal growth thickness is about 120 The masking oxide layer is used to protect the surface from contamination and reduce implantation damage. The n-well injection region is photolithographically implanted with phosphorus to form the n-well 12, and the p-well implantation region is photolithographically implanted to form the p-well 13.
[0039] For deep trench etching see Figure 5 , use hydrofluoric acid to remove the masking oxide layer, and thermally grow a thin oxide layer 20 with a thickness of about 120 As a corrosion protection layer for the source region when the upper silicon nitride film is removed; then use LPCVD to deposit silicon nitride 21 as a barrier layer for chemical mechanical polishing to protect the active region from over-polishing by CMP; photolithography for deep trench iso...
Embodiment 3
[0044] The substrate is a p-type silicon wafer 10, on which a p- epitaxial layer 11 is grown with a thickness of about 5.0 μm. Then perform deep groove etching, and thermally grow a thin oxide layer 20 with a thickness of about 150 As a corrosion protection layer for the source region when the upper silicon nitride film is removed; then use LPCVD to deposit silicon nitride 21 as a barrier layer for chemical mechanical polishing to protect the active region from over-polishing by CMP; photolithography for deep trench isolation Region 22, and then use DRIE to etch through the entire epitaxial layer to obtain deep grooves. Deep trench oxide filling, thermally grown trench liner silicon oxide 30, thickness about 150 Then HWP is used to fill the trench with silicon oxide 31 .
[0045] Deep trench oxide polishing - nitride removal see Figure 7 , using CMP to polish the trench silicon oxide, and then hot phosphoric acid to remove the silicon nitride.
[0046] A double well pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com