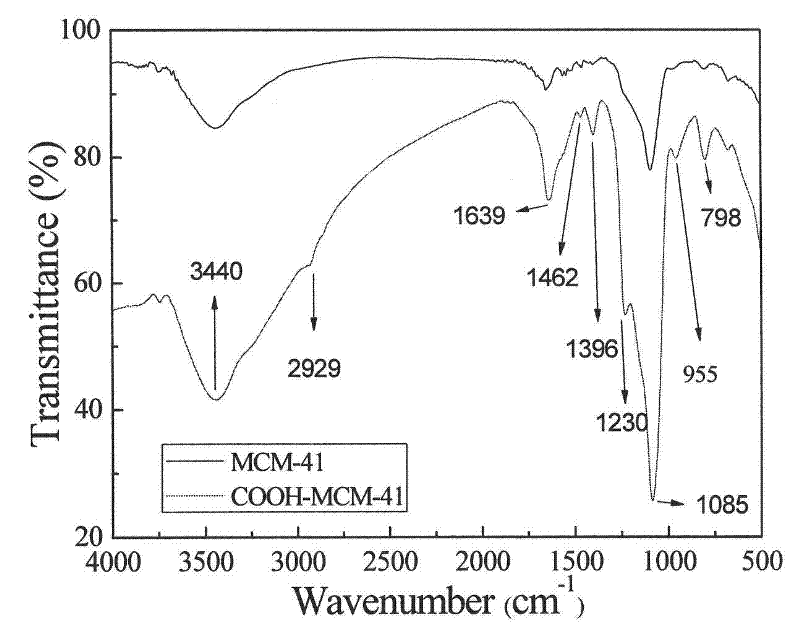
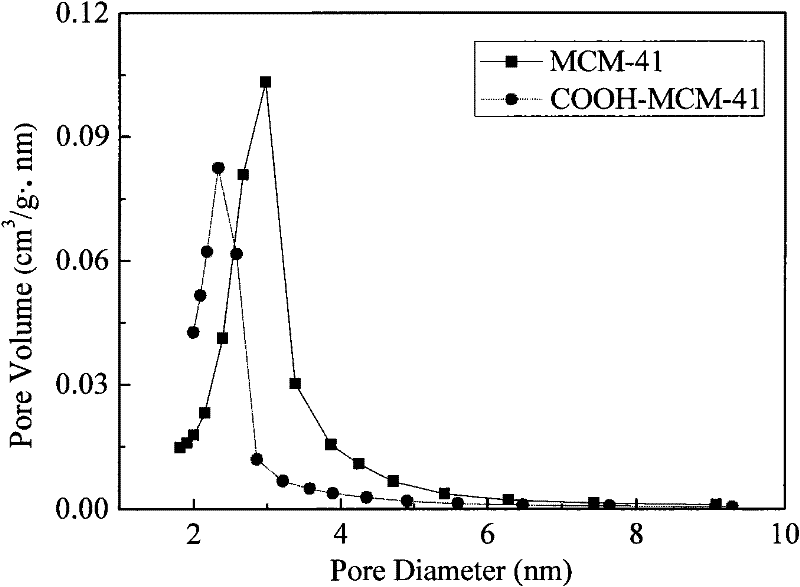
Carboxylated MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve for adsorbing heavy metal ions, and preparation method thereof
A MCM-41, a technology for adsorbing heavy metals, applied in the direction of molecular sieves and alkali exchange compounds, non-metallic elements, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of slow kinetics, easy swelling, poor mechanical stability, etc., and achieve narrow pore size distribution, Easy operation and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: Dissolve 25g of sodium silicate with 30ml of distilled water. Heat and dissolve 6.4 g of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) in 20 ml of distilled water, and after cooling to room temperature, mix it with sodium silicate and stir for 10 min. The pH value of the mixture was adjusted to 10 with sulfuric acid solution (5 mol / L), and the stirring was continued for 80 min, so that the solution became a viscous white gel. Then put it into a 100ml stainless steel hydrothermal reaction kettle with a polytetrafluoroethylene liner, put it in an oven, crystallize at 130°C for 72h, take it out, cool it and filter it, wash it to neutral, and then dry it at 90°C Put the obtained semi-finished product in a muffle furnace overnight, and bake it at 550°C for 5 hours to obtain an all-silicon MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve, which is spherical and has a particle size of 200-300nm. Scanning electron microscope results such as figure 1 , the specific surface area is 1228...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Take 20 mg of the mesoporous adsorbent synthesized in Example 1 in a 50 ml Erlenmeyer flask with a stopper, and add 10 ml of different concentrations of Cu in turn. 2+The prepared solution was adjusted to pH 6 with dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. At 308K, place the Erlenmeyer flask in a shaker and stir for 2 hours. After standing still, filter the supernatant with a 0.45 μm filter membrane. Use an ICP tester to measure the concentration of residual heavy metal ions. Calculate the adsorption amount Q (mg) according to the following formula / g).
[0030] Q=(C 0 -C e )*V / m
[0031] Q-adsorption capacity (mg / g); C 0 -Initial concentration of solution (mg / L); C e - solution equilibrium concentration (mg / L); V - solution volume (L); m - adsorbent dosage (g).
[0032] Adsorption isotherm see Figure 5 , through the Langmuir type linear fitting of the adsorption isotherm, the saturated adsorption capacity of the adsorbent for copper ion...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Embodiment three: take 20 mg of the mesoporous adsorbent synthesized in embodiment one in a 50 ml conical flask with a stopper, and add 10 ml of different concentrations of Pb successively. 2+ The prepared solution was adjusted to pH 6 with dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. At 308K, place the Erlenmeyer flask in a shaker and stir for 2 hours. After standing still, filter the supernatant with a 0.45 μm filter membrane. Use an ICP tester to measure the concentration of residual heavy metal ions. Calculate the adsorption amount Q (mg) according to the following formula / g).
[0034] Q=(C 0 -C e )*V / m
[0035] Q-adsorption capacity (mg / g); C 0 -Initial concentration of solution (mg / L); C e - solution equilibrium concentration (mg / L); V - solution volume (L); m - adsorbent dosage (g).
[0036] Adsorption isotherm see Image 6 , through the Langmuir linear fitting of the adsorption isotherm, the saturated adsorption capacity of the adsorbent for l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com