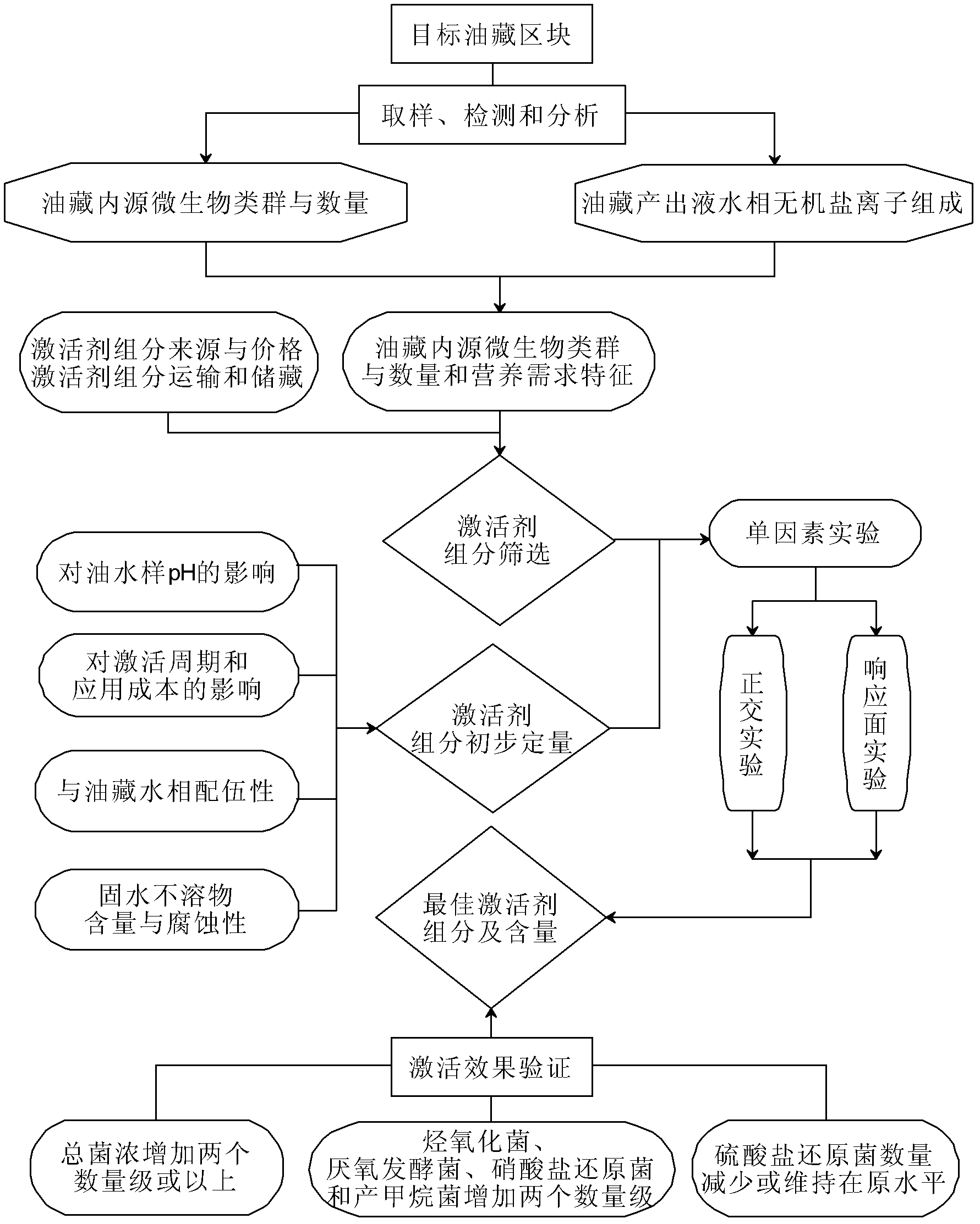
Method for screening high efficiency activator of oil reservoir indigenous microbes
A technology of endogenous microorganisms and activators, applied in the fields of microbial biotechnology and resource and environmental biology, can solve the problems of different types and dosages of activator components in oil reservoirs, lack of screening process, and inability to quickly screen efficient activator components, etc. Achieve the effect of addressing the lack of random and standardized screening methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Determination and Analysis of Inorganic Salt Ion Composition in Reservoir Production Liquid Water Phase
[0047] Referring to JY / T 015-1996 General Rules of Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectrometry and HJ / T 84-2001 Determination of Inorganic Anions in Water Quality by Ion Chromatography, ion chromatography and inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry were used to produce oil reservoirs in this block. The ion composition of the liquid and water phase inorganic salts was measured, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0048] The measurement results show that the total salinity of dipped 3-N12 injected water is 8909.24 mg·l -1 , dipped in 3-X24 and the total salinity of the output liquid water phase is 8524.978mg·l -1 , are within the optimum growth range of microorganisms, and will not adversely affect the growth of microorganisms. Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients are extremely lacking in each well, which cannot meet the growth needs of micr...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Detection and Analysis of Endogenous Microbial Groups and Quantities in Reservoirs
[0053] Referring to the standard SY / T0532-93 "Oilfield Injection Water Bacteria Analysis Method Extinction Dilution Method", the number of endogenous microbial groups in the oil reservoir of block A well was detected and analyzed, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0054] The measurement results show that the concentration of hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria, nitrate reducing bacteria and methanogenic bacteria in well A is low, which are the target bacteria for activation; the concentration of sulfate reducing bacteria is as high as 10 2 cells·ml -1 , reflecting that there are a large number of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the oilfield water injection system and the internal environment of the oil reservoir, which need to be eliminated or inhibited from further growth. Hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria can grow with petroleum hydrocarbons as the only carbon source, and metabo...
Embodiment 3
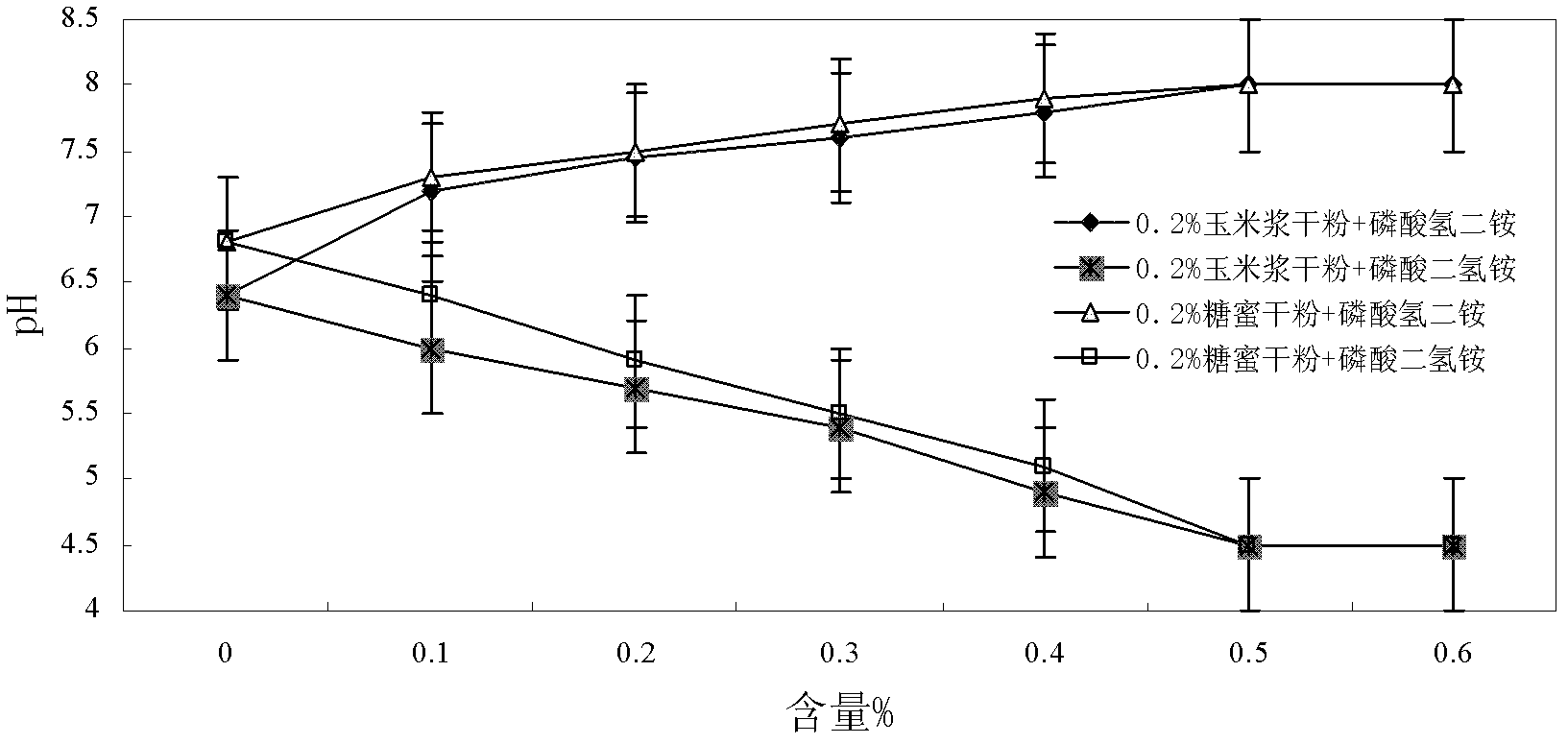
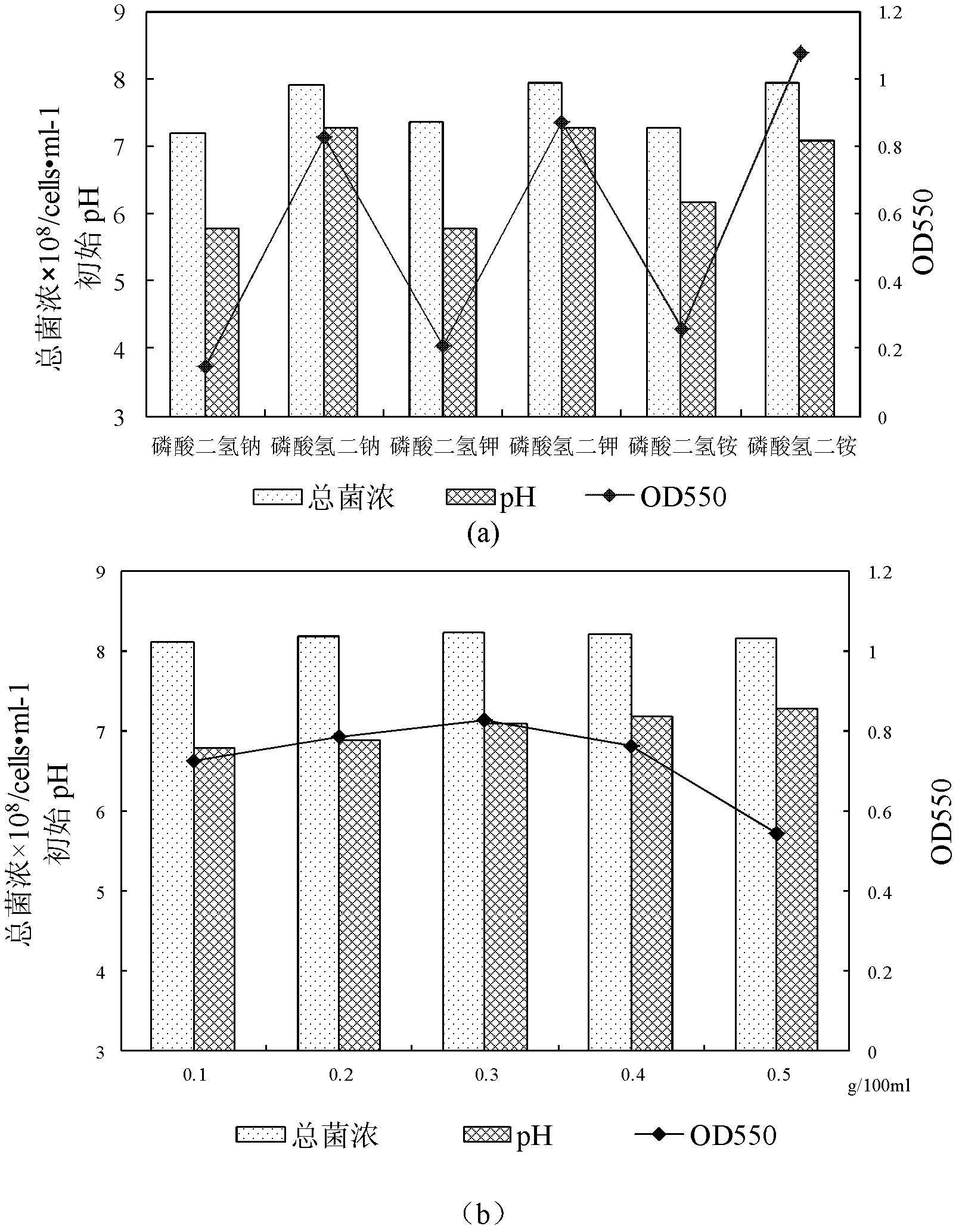
[0058] The screening of embodiment 3 inorganic nutrient salts
[0059] Common inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients mainly include potassium nitrate, sodium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, urea, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, dihydrogen phosphate Ammonium and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium polyphosphate, etc. Among them, ammonium nitrate, ammonium chloride, ammonium sulfate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate and sodium polyphosphate aqueous solution are alkaline, and the pH value is between 8-9; potassium dihydrogen phosphate, phosphoric acid The aqueous solution of sodium dihydrogen and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate is acidic, with a pH value between 4-5. According to the pH of the formation water of the specific oil reservoir, the physical and chemical properties of various nutrien...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com