Microbial preparation method of dibutyl phthalate
A technology of dibutyl phthalate and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of preparation of dibutyl phthalate, can solve the problems of low sample recovery rate, high separation cost, small sample injection volume and the like, and achieves high separation efficiency, The effect of wide distribution system and large injection volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] 1.1 Selection of strains
[0029] The Verticillium lecani strain CGMCC NO.3.4505 (obtained from scale insects) used was purchased from the Culture Collection and Management Center of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and stored in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0030] 1.2 Culture of strains
[0031] 1.2.1 First-level slant seed culture
[0032] Put the strain with the preservation number CGMCC NO.3.4505 into a test tube containing PDA slant medium, put it in an incubator, and cultivate it for 7 days at a temperature of 25°C and a relative humidity of 75%. Mycelia will cover the slant and produce spores .
[0033] Incline medium: 200g potato, 20g agar, 20g glucose, 1000ml distilled water.
[0034] 1.2.2 Secondary liquid seed culture
[0035] Add about 40ml of liquid culture medium into a 100ml Erlenmeyer flask, and sterilize it under high pressure at 1.5pa / kg for 30 minutes. After cooling, inoculate the first-grade strains into the liqu...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1.1 Selection of strains
[0056] The Verticillium lecani strain CGMCC NO.3.4504 (obtained from scale insects) used was purchased from the Culture Collection and Management Center of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and stored in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0057] 1.2 The cultivation of the bacterial strain is the same as in Example 1.
[0058] 1.3 The extraction of metabolites is the same as in Example 1.
[0059] 1.4 Separation and purification of the crude extract by high-speed countercurrent chromatography is the same as in Example 1.
[0060] 1.5 GC and GC / MS analysis are the same as in Example 1.
[0061] 2 results
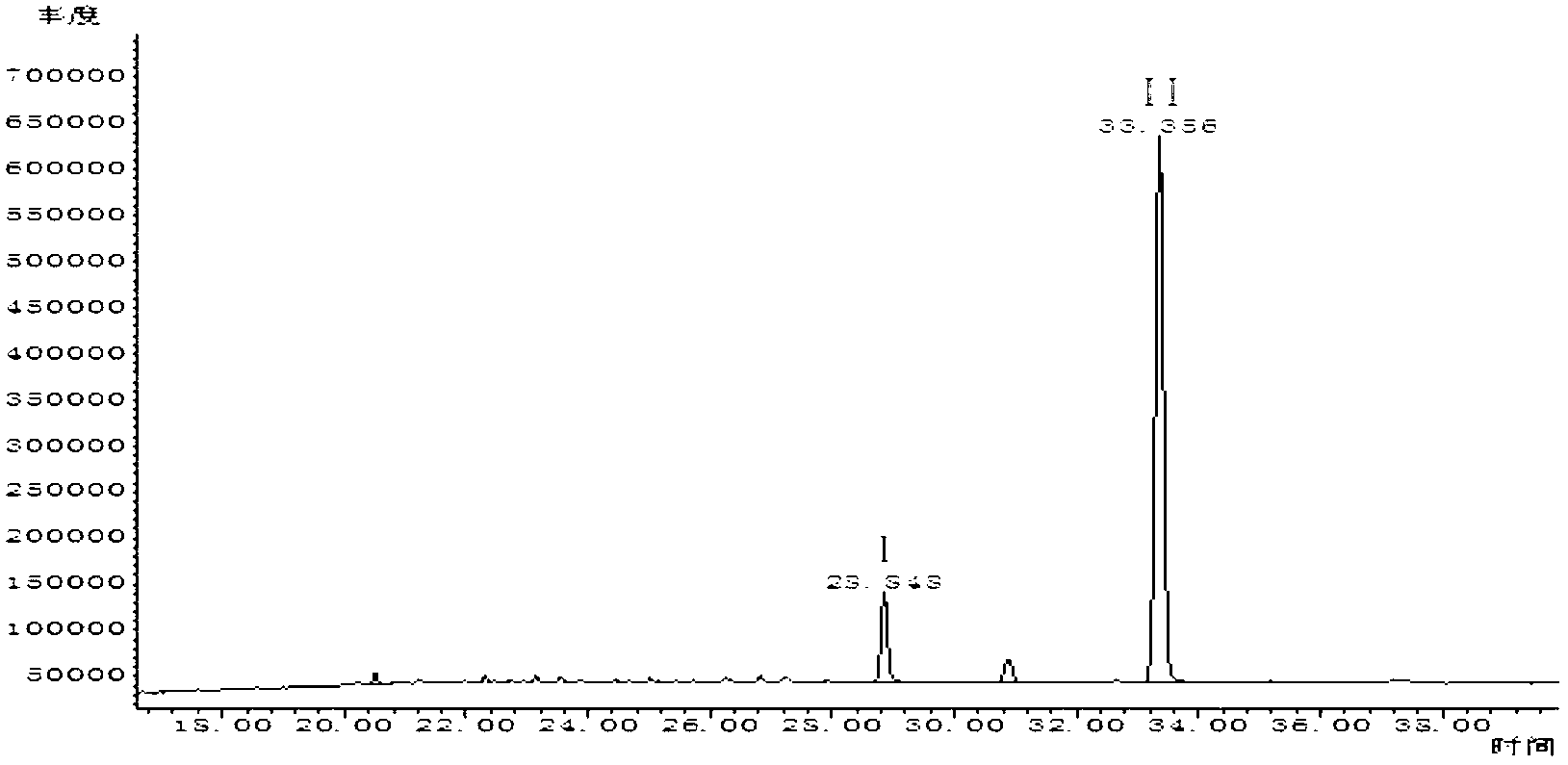
[0062] GC / MS ion current chromatogram of colorless oily liquid produced by strain CGMCC NO.3.4504 ( Figure 7 ), the main component is DBP after searching the spectral library.
Embodiment 3
[0064] 1.1 Selection of strains
[0065] The used Beauveria tenella (CGMCCNO.2382) was isolated from the carcasses of Chinese pine forest caterpillars in Wafangdian Village, Shatuozi Township, Chengde County, Hebei Province. CGMCC), and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
[0066] 1.2 The cultivation of the bacterial strain is the same as in Example 1.
[0067] 1.3 The extraction of metabolites is the same as in Example 1.
[0068] 1.4 Separation and purification of the crude extract by high-speed countercurrent chromatography is the same as in Example 1.
[0069] 1.5 GC and GC / MS analysis are the same as in Example 1.
[0070] 2 results
[0071] GC / MS ion current chromatogram of colorless oily liquid produced by strain CGMCC NO.2382 ( Figure 8 ), the main component is DBP after searching the spectral library.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com