Edible straw rotting fungus culture medium and preparation method thereof
A technology of cultivation substrate and edible fungus, which is applied in the direction of botany equipment and method, preparation and application of organic fertilizer, etc., can solve the problems of difficult treatment of industrial biomass waste, poor operability, atmospheric environment pollution, etc., and achieve high Edible value and medicinal value, reduce the contamination rate of miscellaneous bacteria, and high biological efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
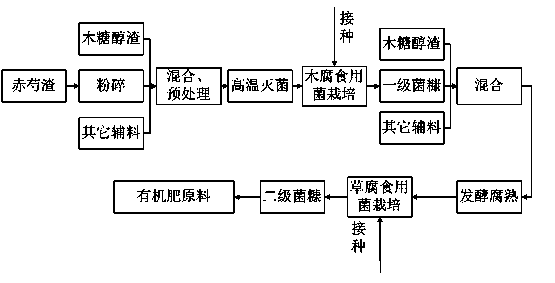
[0037] (1) Grinding of Radix Paeoniae Rubra: The residue of Radix Paeoniae Rubra is crushed into particles with a size of 0.5-3mm by an edible mushroom sawdust crusher.
[0038] (2) Cultivation substrate formula for wood-rot edible fungus: 58% red peony residue, 30% xylitol residue, 10% bran, 1% corn flour, 0.5% calcium carbonate, and 0.5% gypsum. Add milk of lime and water to adjust the pH to 7 and control the moisture content to 65%.
[0039] (3) Mixing and pretreatment: Mix all materials evenly according to the above formula.
[0040] (4) High-temperature sterilization: After the matrix is bagged, 0.15MP is sterilized at 125°C for 2 hours.
[0041] (5) Cultivation of wood-rot edible fungi: After the substrate is cooled, inoculate Pleurotus eryngii. The first-grade fungus chaff formed after the fruiting of Pleurotus eryngii is used for the cultivation of Coprinus comatus.
[0042] (6) Grass-rot edible fungus matrix formula: 50% of first-grade fungus chaff crushed into s...
Embodiment 2
[0046] (1) Grinding of Radix Paeoniae Rubra: The residue of Radix Paeoniae Rubra is crushed into particles with a size of 0.5-3mm by an edible mushroom sawdust crusher.
[0047] (2) Cultivation substrate formula for wood-rot edible fungus: 70% red peony residue, 12.8% xylitol residue, 15% bran, 1% corn flour, 1% calcium carbonate, and 0.2% gypsum. Add milk of lime and water to adjust the pH to 8 and control the moisture content to 65%.
[0048] (3) Mixing and pretreatment: Mix all materials evenly according to the above formula.
[0049](4) High-temperature sterilization: After the matrix is bagged, 0.15MP is sterilized at 125°C for 2 hours.
[0050] (5) Cultivation of wood-rot edible fungi: After the substrate is cooled, inoculate Flammulina velutipes. The first-grade fungus chaff formed after Flammulina velutipes fruiting is used for the cultivation of Coprinus comatus.
[0051] (6) Other steps are carried out according to Example 1. Biological efficiency is 85%
Embodiment 3
[0053] (1) Grinding of Radix Paeoniae Rubra: The residue of Radix Paeoniae Rubra is crushed into particles with a size of 0.5-3mm by an edible mushroom sawdust crusher.
[0054] (2) Wood rot edible fungus matrix formula: 45% red peony residue, 32% xylitol residue, 5% bran, 15% cottonseed hull, 1% corn flour, 1% calcium carbonate, and 1% gypsum. Add milk of lime and water to adjust the pH to 10 and control the moisture content to 65%.
[0055] (3) Mixing and pretreatment: Mix all materials evenly according to the above formula.
[0056] (4) High-temperature sterilization: After the matrix is bagged, 0.15MP is sterilized at 125°C for 2 hours.
[0057] (5) Cultivation of wood-rot edible fungi: After the substrate is cooled, inoculate Pleurotus ostreatus. The first-grade fungus bran formed after Pleurotus ostreatus fruiting is used for the cultivation of Agaricus bisporus.
[0058] (6) Grass rot edible fungus matrix formula: 40% of first-grade fungus chaff crushed into small ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com