Processing method for recovering nickel, chromium and iron from stainless steel factory waste residue
A treatment method and technology for waste residues, applied in the recycling of chromium and waste residues, recovery of nickel and iron from stainless steel plant waste residues, can solve the problems of inefficient separation, high cost, and excessive accumulation and storage, and achieve metal resources. The effect of high utilization rate, complete separation of ferrochromium and high metal recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
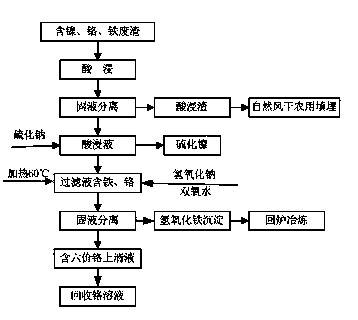
[0020] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
[0021] A batch of waste slag from a cold-rolled stainless steel sheet factory in Tianjin, the main components of which are shown in the table:
[0022] Main chemical composition of dry waste residue (mass fraction)
[0023] Element chromium iron nickel copper zinc magnesium content(%) 13.49 26.2 11.76 0.64 0.33 1.2
[0024] Weigh two parts of dry waste residue (put some of the waste residue in a constant temperature drying oven in advance, and dry at 105°C for 3 hours.) 100g each is placed in a 1000mL glass beaker. Set the mass fraction to 15%H 2 SO 4 Mixed acid with 35% citric acid in a volume ratio of 1:4. Add 500mL of mixed acid to the above two 100g waste residues respectively, and fully stir in a constant temperature magnetic stirrer at room temperature. The pH of the reaction solution was measured with a magnetic pH meter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com