A high-throughput screening method for membrane imprinting of genetically engineered bacteria secreting lipase
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and lipase genes is applied in the field of bioengineering to achieve the effects of cost saving, wide application range, and sensitive and accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1: Screening of lipase genetically engineered bacteria with different enzyme-producing activities
[0044]The Rhizomucor miehei lipase gene rml and the pPIC9K plasmid were digested with EcoR I and Not I at the same time, connected with T4 ligase, transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells, and the transformed cells were coated with 100ug / mL ampicillin On the LB plate of penicillin, culture upside down at 37°C for 12-16 hours, pick 2-5 single colonies from the plate, inoculate in LB liquid medium, shake overnight at 37°C and 250r / min. A small amount of plasmid DNA was extracted with a plasmid kit, identified by double enzyme digestion with EcoRI and Not I, and the successfully ligated pPIC9K-rml plasmid was obtained. The pPIC9K-rml plasmid was linearized with SalI and electrotransformed into the host Pichia pastoris GS115, spread on the MD plate, and cultured at 28°C for 2-3 days to obtain the lipase gene of Rhizomucor miehei with different enzyme production a...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2: High-throughput screening of lipase genetically engineered bacteria mutant library
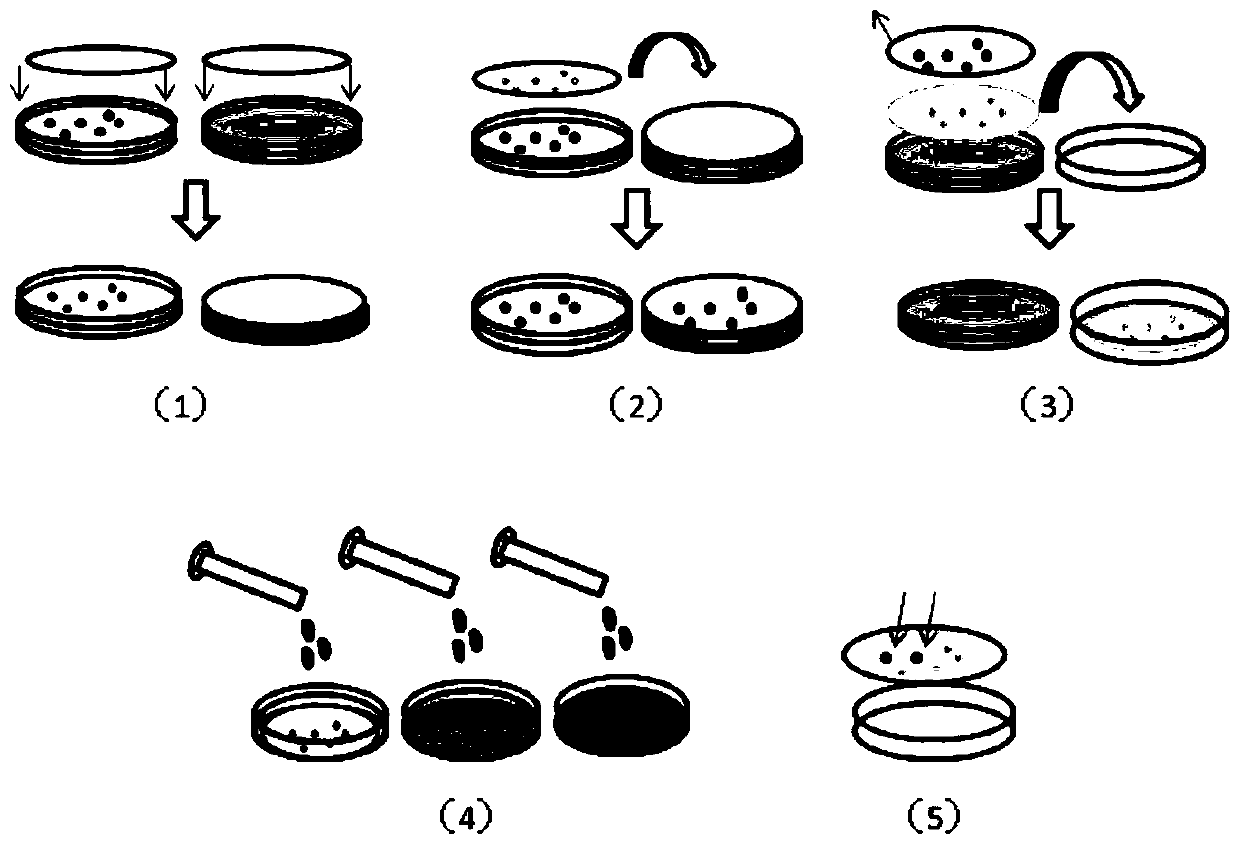
[0049] The Rhizomucor miehei lipase gene is transformed by the error-prone PCR method and transformed into Pichia pastoris X33. The transformation method is the same as described in Example 1, and the transformed Pichia pastoris X33 is inoculated on a solid containing YPD. The medium has a diameter of 9 mm on a petri dish, and cultured at 30° C. to obtain a mutant library of Rhizomucor miehei lipase Pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacteria. Place a cellulose acetate membrane with a diameter of 9mm flat on the YPD solid medium, press lightly with a coating rod to completely wet the filter paper membrane and drive out air bubbles, transfer all the colonies to the cellulose acetate membrane, and culture the YPD solid Store the base plate at 4°C; place a nylon membrane of the same size with a pore size of 0.45 μm on another BMMY solid medium plate with 1% methanol added to...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: High-throughput screening of high-temperature-resistant lipase genetically engineered bacteria
[0053] The Rhizomucor miehei lipase gene is transformed and transformed into Pichia pastoris GS115 by the method of error-prone PCR. The transformation method is the same as that described in Example 1, and the transformed Pichia pastoris GS115 is inoculated on the solid containing MD. The medium has a diameter of 9 mm on a petri dish, and cultured at 30° C. to obtain a mutant library of Rhizomucor miehei lipase Pichia pastoris genetically engineered bacteria. Place the filter paper membrane with a diameter of 9mm flat on the MD solid medium, press lightly with a coating rod to completely wet the filter paper membrane and drive away the air bubbles, so that all the colonies are transferred to the PVDF membrane, and place the MD solid medium plate on Store at 4°C; place a PVDF membrane of the same size with a pore size of 0.22 μm on another BMMY solid medium plate ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com