Degradable acid-sensitive polyaspartamide copolymer and its preparation method and use
A polyasparagine and copolymer technology, applied in the field of copolymers, can solve problems such as slow drug release, and achieve the effects of maintaining curative effect, excellent biocompatibility, and improving bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
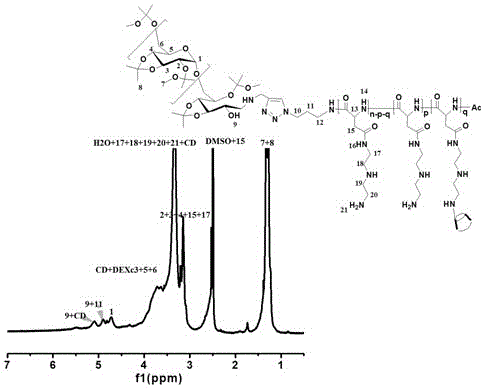
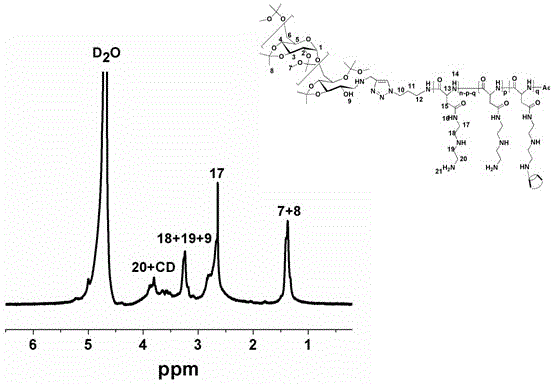
[0049] Example 1: Preparation of biodegradable acid-sensitive amphiphilic block copolymer
[0050] 1.1 Preparation of N-carboxylic acid anhydride of L-benzyl aspartate:
[0051] Benzyl L-aspartate (5.7 g) was vacuum-dried for at least 2 hours, then added 200 mL of ethyl acetate, and heated to reflux at 90 °C for 0.5 h. Another weighed triphosgene solid (2.93 g) was dissolved in 60 mL of ethyl acetate, and then the solution was slowly added dropwise to the solution of L-aspartic acid benyl ester, and stirred thoroughly until clear. All operations were performed under the protection of dry argon. Stop heating, wash with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution 2 to 3 times in a 500 mL separatory funnel to remove excess triphosgene, add saturated sodium chloride to break the emulsion, and make the solution clear. Pour the reaction solution into a 500 mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and dry for more than half an hour to remove water. After drying, f...
Embodiment 2
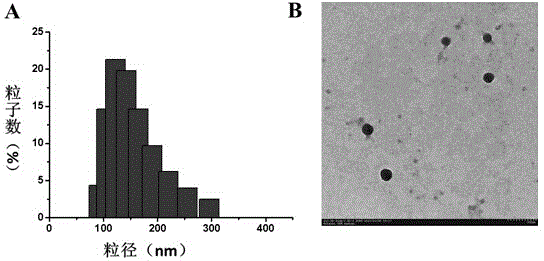
[0062] Preparation of Polymer Nanocarriers Loading Hydrophobic Drugs and Basic Performance Test
[0063] 2.1 Preparation of polymer nanocarriers loaded with hydrophobic drugs:
[0064] Dissolve AC-DEX-PAsp(DET)-CD polymer (2.5 mg) and doxorubicin hydrochloride (0.45 mg) in 1 mL of dichloromethane and 100 L of chloroform, respectively, and add doxorubicin hydrochloride in chloroform Add 4 L of triethylamine to adjust to hydrophobic doxorubicin, and mix the two evenly. Take 41 L of pure water as the internal water phase, and add it dropwise to the mixed solvent under ultrasonic conditions in a water bath to form a milky red water / oil (W / O) colostrum solution. Then, the colostrum system was added dropwise to 6 mL of the external aqueous phase under ultrasonic conditions of the probe to form a water / oil / water (W / O / W) composite system. Finally, transfer it to a constant temperature magnetic stirrer, stir at 30°C for 3 h to remove the organic phase to obtain a blue-purple ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Preparation and Basic Performance Test of Polymer AC-DEX-PAsp(DET)-CD Nanoparticles Simultaneously Loading Hydrophobic Drugs and Plasmid DNA
[0069] 3.1 Preparation of polymer nanoparticles loaded with hydrophobic drugs and plasmid DNA
[0070] The polymer AC-DEX-PAsp(DET)-CD (2.5 mg) and doxorubicin hydrochloride (0.45 g) were dissolved in 1 mL of dichloromethane and 100 L of chloroform, respectively, and then added to the chloroform solution of doxorubicin hydrochloride Add 4 L of triethylamine to make it hydrophobic doxorubicin, and finally mix the two evenly. Take a certain amount of DNA aqueous solution as the inner water phase (determined according to different N / P=1; N / P=12; N / P=24; N / P=42; N / P=60; N / P=72 The amount of DNA added) was added dropwise to this mixed solvent under ultrasonic conditions in a water bath to form a milky red water / oil (W / O) colostrum solution. Then this solution was slowly added to 6 mL of pure water under the ultrasonic condit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com