Controllable synthesis method of nickel phosphide micro-nano material
A synthesis method and technology of nickel phosphide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphide, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of toxicity, long hydrothermal time, and high reaction temperature, and achieve easy recovery, simple operation, and reaction conditions. mild effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
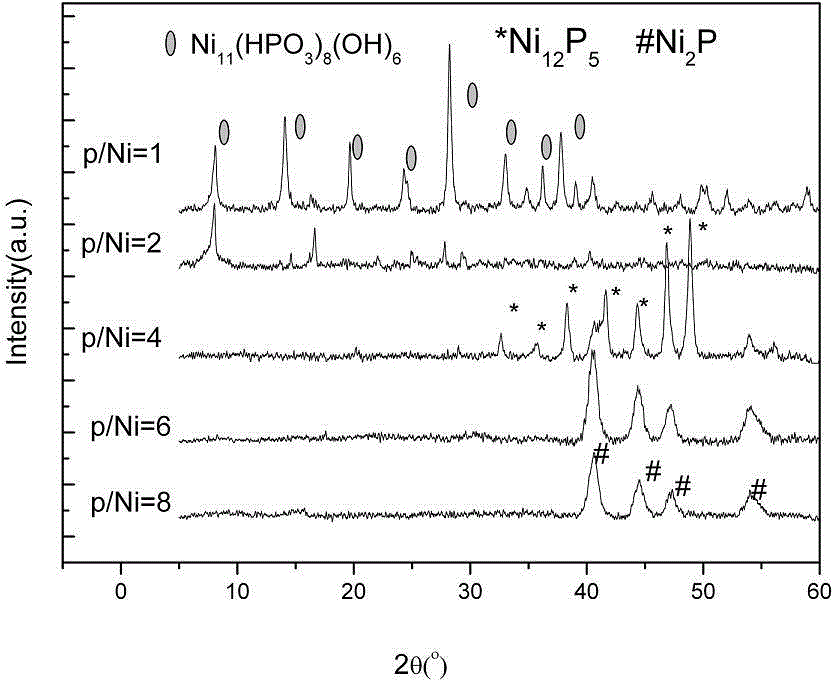
[0032] Synthesis of Ni by Changing the Phosphorus-Nickel Ratio 2 P or Ni 12 P 5 : select the P / Ni molar ratio to be 1 / / 1, 2 / 1, 4 / 1, 6 / 1, 8 / 1 respectively for hydrothermal synthesis. It is only described when the P / Ni molar ratio is 6. Put 10.9009g (0.0375 moL) of nickel nitrate and 50mL of distilled water into a 100mL beaker, stir well until the solution is clear, then add 6.975g (0.225moL) of fully ground red phosphorus. Put the beaker in a water bath with electromagnetic stirring at 60°C for aging for 2 hours, then transfer the suspension into a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined autoclave, seal it, and place it in a constant temperature drying oven at 120°C for 12 hours. No surfactant was added in the experiment. After the reaction, the reactor was taken out and cooled to room temperature naturally. The black solid matter in the autoclave was collected, and centrifuged and washed with hot ethanol and distilled water in order to remove unreacted inorganic substances do...
Embodiment 2
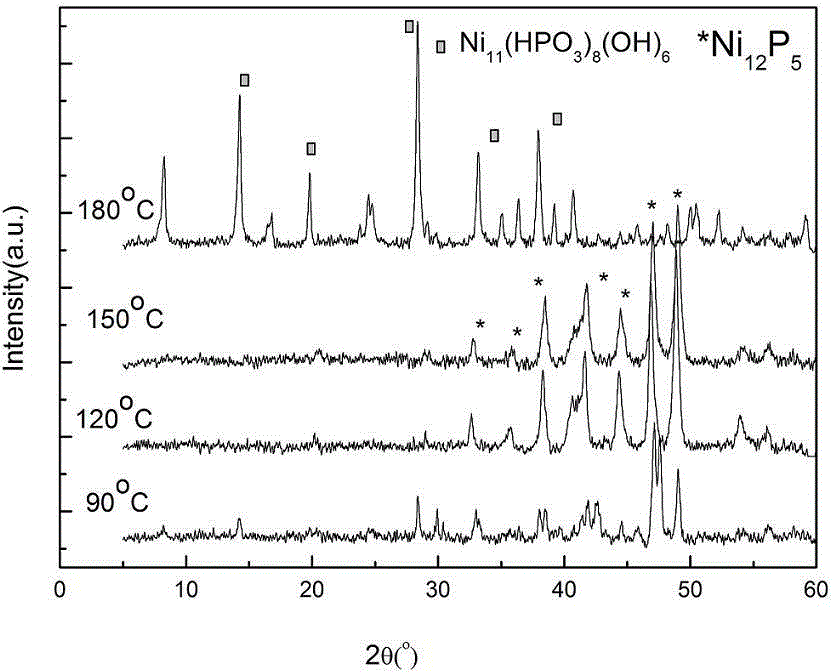
[0035] Synthesis of Ni by changing the hydrothermal temperature 12 P 5 : Put 10.9009g of nickel nitrate (0.0375mol) and 50ml of distilled water into a 100ml beaker, stir well until the solution becomes clear, then add 4.65g (0.15mol) of fully ground red phosphorus. The hydrothermal reaction temperature was set at 90 o C. 120 o C. 150 o C and 180 o C, the reaction time is 12h, the solvent is water, and no surfactant is added. All the other operating steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0036] figure 2 X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) spectra of synthesized products at different temperatures when n(P) / n(Ni)=4. It can be seen from the figure that when P / Ni=4, the reaction temperature is 90 o C, at 2θ=32.7 o , 35.8 o , 38.4 o , 41.7 o , 44.4 o , 47.0 o , 49.0 o The series of diffraction peaks that appear are attributed to Ni 12 P 5 (PDF22-1190), showing that the resulting product is mainly Ni 12 P 5 , but there are still many impurity peaks in the resulting spec...
Embodiment 3
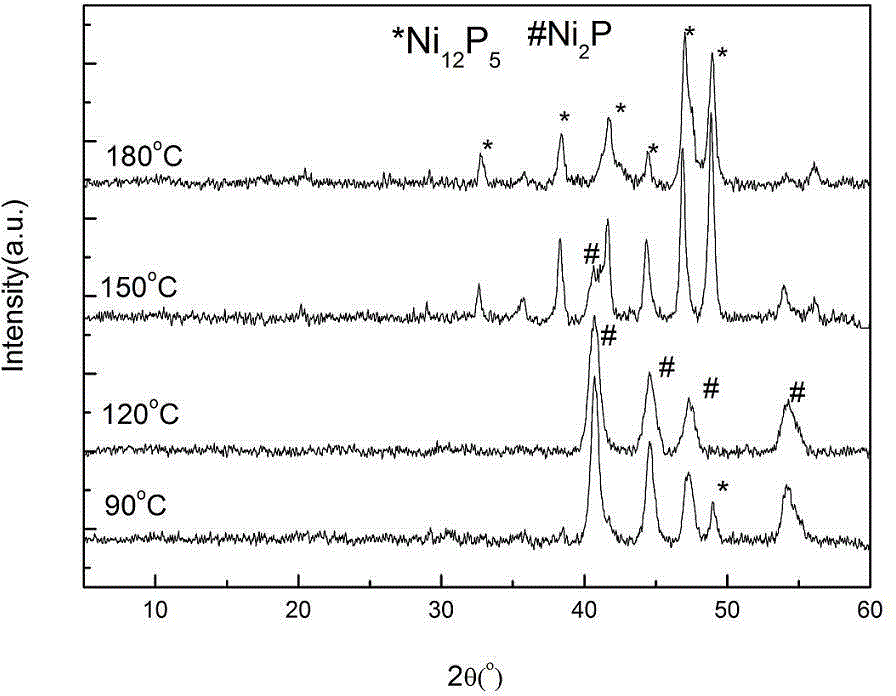
[0039] Synthesis of Ni by changing the hydrothermal temperature 12 P 5 or Ni 2 P: Put 10.9009g of nickel nitrate (0.0375mol) and 50ml of distilled water in a 100ml beaker, stir well until the solution becomes clear, then add 9.3g (0.3mol) of fully ground red phosphorus. The hydrothermal reaction temperature was set at 90 o C. 120 o C. 150 o C and 180 o C, the reaction time is 12h, the solvent is water, and no surfactant is added. All the other operating steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0040] Figure 4 X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) spectra of synthesized products at different temperatures when n(P) / n(Ni)=8. It can be seen from the figure that when the reaction temperature is 90 o C, at 2θ=40.8 o , 44.6 o , 47.3 o , 54.4 0 The characteristic diffraction peaks appearing at can be attributed to Ni 2P(PDF03-0953), the peak intensity is larger, but at 2θ=38.4 o , 49.0 o There is also a characteristic diffraction peak with low intensity, which can be attributed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com