Resource utilization method for iron sludge
A technology of recycling and iron slime, applied in the field of industrial waste recycling, can solve the problems of endangering human health, hazards, occupation, etc., achieve high environmental protection and economic value, and the effect of simple and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Raw materials: the reduced iron slime produced in the reduction process of iron powder used in the production of H acid, wherein the nitrous value (the equivalent of amino organic chemicals) is 1.87g / Kg, the water content is 21%, and the iron content is 65% ( by mass of iron oxide).
[0040] Processing steps:
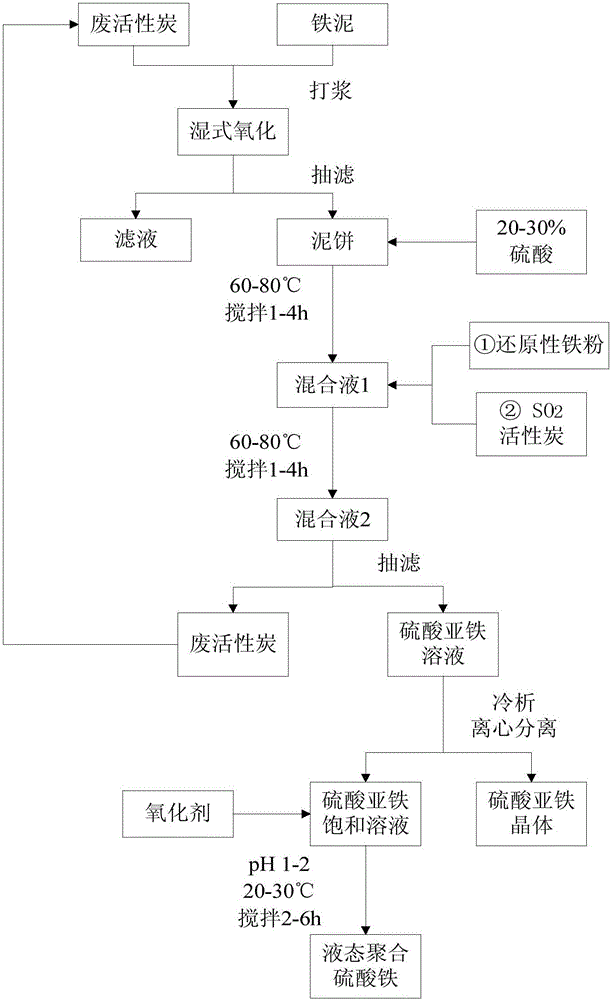
[0041] (1) Wet oxidation: Add 250mL of water and 0.3g of activated carbon to 100g of reduced iron sludge to make a slurry to make a slurry and measure the COD of the clear liquid. Put the slurry in a wet oxidation reaction kettle, keep the temperature in the kettle at 260°C, stir at 300rpm, and the pressure at 5MPa, react for 2 hours and then filter and separate to obtain iron mud cake and filtrate. The COD of the filtrate was detected again, and the calculation showed that the removal rate of organic matter in iron sludge by wet oxidation was 95.23%.
[0042] (2) Pickling: Mix 66mL of 98% sulfuric acid with 466mL of water to make dilute sulfuric acid with a ma...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Raw materials: Iron sludge produced by a water treatment plant Fenton to treat papermaking wastewater. The iron sludge mainly remains organic matter such as lignin, macromolecular carbohydrates, and unsaturated fatty acids. Its water content is 85%, and its iron content is 18% (based on the mass of iron oxide).
[0054] Processing steps:
[0055] (1) Wet oxidation: Take 200g of Fenton iron sludge, add 250mL of water and 0.5g of activated carbon to make a slurry and measure the COD of the clear liquid. Put the beating liquid in the wet oxidation reaction kettle, keep the temperature in the kettle at 230°C, stir at 300rpm, and the pressure is 2MPa. After 1 hour of reaction, the iron mud cake and filtrate are obtained by suction filtration, and the COD of the filtrate is measured. The calculation shows that the wet oxidation treatment has a great impact on The COD removal rate of organic matter in iron sludge is 92.56%.
[0056] (2) Pickling: Mix 37mL of 98% sulfuric aci...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Raw materials: When using Fenton technology to treat printing and dyeing wastewater, chemical sludge with high organic content is produced, mainly containing dyes, sizing, additives, fiber impurities and other substances, and the iron content is 68% (calculated by the mass of iron oxide).
[0062] (1) Wet oxidation: Take 100g of Fenton iron sludge, add 200mL of water and 0.5g of activated carbon to make a slurry and measure the COD of the supernatant. Put it in a wet oxidation reaction kettle, keep the temperature in the kettle at 280°C, stir at 300rpm, and the pressure at 4MPa. After 2 hours of reaction, the iron mud cake and filtrate are separated by suction filtration, and the COD of the filtrate is measured. It can be known by calculation that the removal rate of organic matter in iron sludge by wet oxidation treatment is 93.87%.
[0063] (2) Pickling: 35mL of 98% sulfuric acid mixed with 480mL of water (the mass fraction of sulfuric acid is 21.2%) was added to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com