Low-density polyethylene super hydrophobic sheets/containers with controllable rolling angle and preparation method thereof
A technology of low-density polyethylene and super-hydrophobic sheet, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other household utensils, stoppers, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome process, expensive price, cumbersome steps, etc. The method is simple and easy, and the processing time Short, low-cost preparation effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
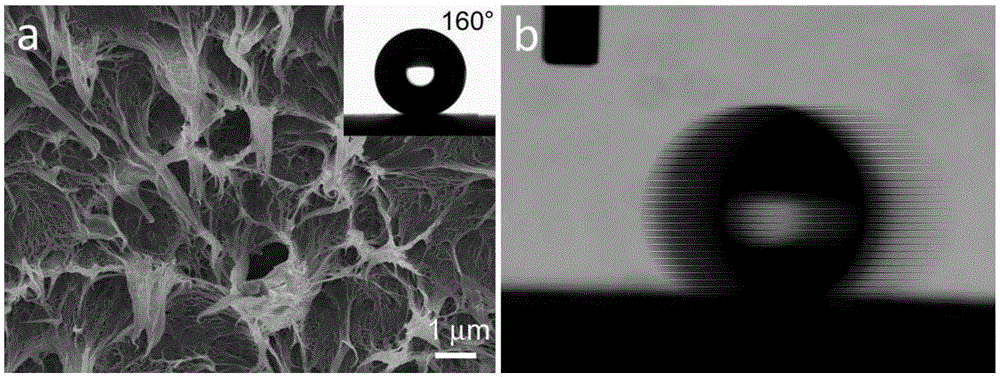
[0019] In this example, put 20g of low-density polyethylene pellets into a mold of 85*115*2mm, preheat the mold for 5 minutes at 140°C with a flat vulcanizer, hold the pressure for 5 minutes under the condition of holding pressure 10MPa, and cool to room temperature Prepare low-density polyethylene sheets, then laminate the two low-density polyethylene sheets in a mold of 85*115*4mm and place them in a flat vulcanizing machine, preheat at 120°C for 3 minutes, and press at 5MPa The lower pressure was maintained for 2 minutes, and after cooling to room temperature, the laminated low-density polyethylene sheets were peeled off by hand to obtain a low-adhesion low-density polyethylene superhydrophobic sheet. figure 1 It is a scanning electron microscope photo and a contact angle (160°) test photo of low-density polyethylene peeled off at 120°C under lamination (lamination) conditions, and a video screenshot of water droplets rolling on an inclined low-density polyethylene surface. ...
Embodiment 2
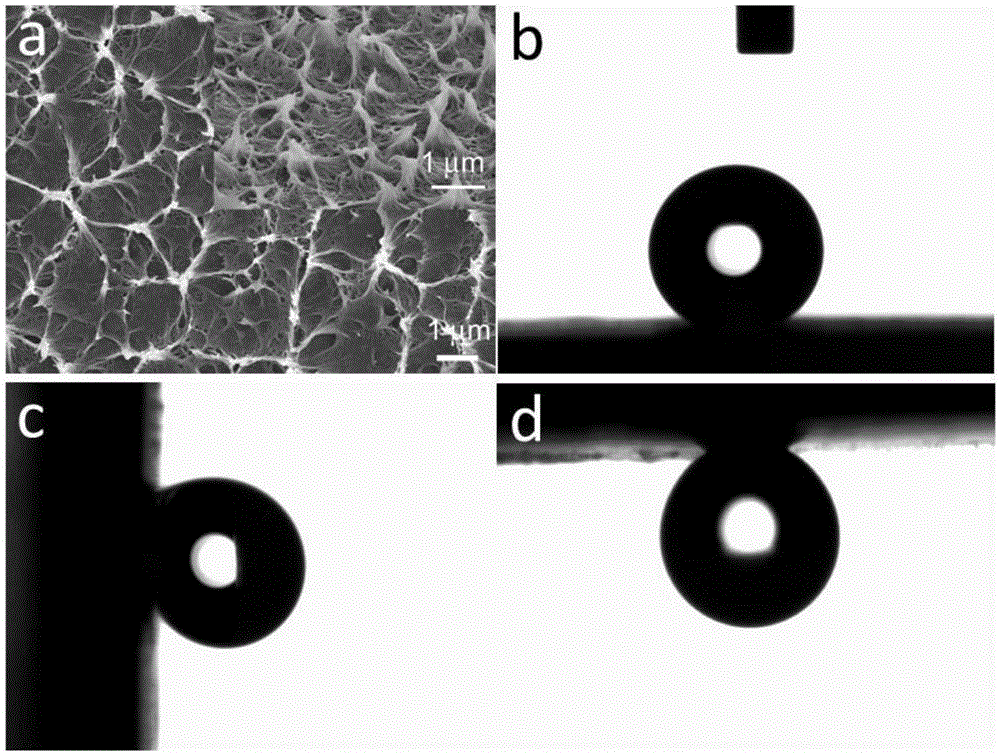
[0021] In this example, put 10g of low-density polyethylene pellets into a mold of 85*115*1mm, preheat the mold for 5 minutes at 120°C with a flat vulcanizer, hold the pressure for 3 minutes at a holding pressure of 5 MPa, and cool to room temperature Prepare low-density polyethylene sheets, then stack the two low-density polyethylene sheets in a mold of 85*115*2mm and put them in a flat vulcanizing machine, preheat at 108°C for 3 minutes, and press at 5MPa Hold the pressure for 3 minutes, and after cooling to room temperature, use iron tongs to peel off the laminated low-density polyethylene sheets in front to obtain a high-adhesion low-density polyethylene superhydrophobic sheet. figure 2 It is a scanning electron micrograph of the surface of low-density polyethylene peeled off under lamination (lamination) conditions at 108°C and a photo of water droplets on the surface of the low-density polyethylene facing upward, 90° vertical, and inverted.
Embodiment 3
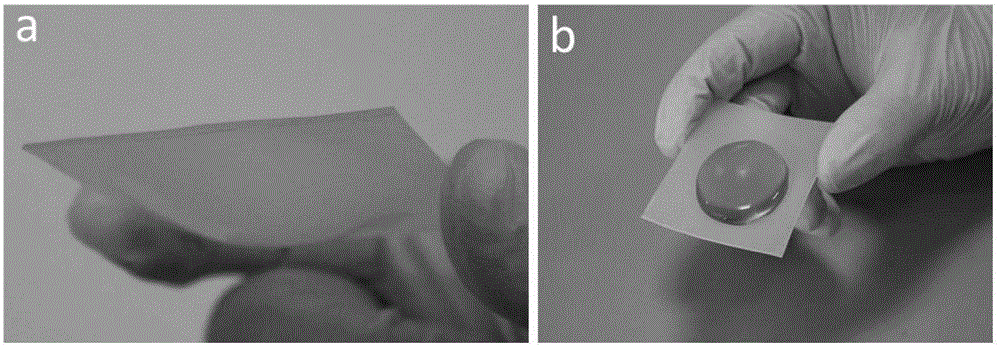
[0023] In this example, put 10 g of low-density polyethylene pellets into a mold of 85*115*1mm, preheat the mold for 5 minutes at 130°C with a flat vulcanizer, hold the pressure for 2 minutes at a holding pressure of 5 MPa, and cool to room temperature Prepare low-density polyethylene sheets, and then stack the two low-density polyethylene sheets in a 85*115*2mm mold and put them into a flat vulcanizing machine, preheat at 125°C for 3 minutes, and heat at 5MPa Keep the pressure under pressure for 3 minutes, quickly transfer the laminated sheets to the curved surface concave mold and make it fit the curved surface mold. After cooling down to room temperature, iron the laminated low density polyethylene The sheet is peeled off to obtain a low-adhesion low-density polyethylene superhydrophobic curved surface container. image 3 It is a photo of a low-density polyethylene superhydrophobic curved concave container and a photo of a blue copper sulfate aqueous solution.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com