A double-induced homologous recombination marker-free vector plasmid and its application
A vector plasmid and homologous recombination technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low deletion efficiency, no dual inducible promoters, no selective marker gene excision, etc., and achieve the effect of high transformation efficiency and high excision rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) Cloned the 2kb upstream regulatory sequence of the heat shock protein hsp70 (heat shockprotein70) 5' end of tomato, rice, cabbage and Arabidopsis, and designed the regulators of four plants with different lengths and different elements by analyzing the promoter elements The sequence fragments were connected with the GUS (β-glucuronidase) reporter gene, and constructed together with the selection marker gene module of the glufosinate resistance gene bar driven by the CaMV35 promoter to form the hsp70 promoter function detection vector. The four vectors will be used for functional verification of the heat shock-induced activity of the heat shock protein hsp70 promoter in tomato, rice, Chinese cabbage and Arabidopsis.
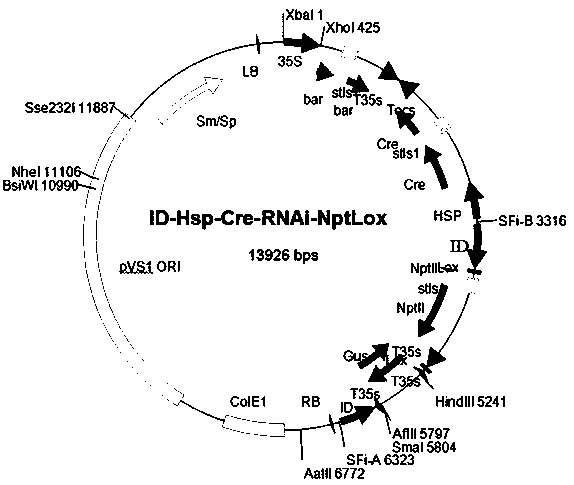
[0027] (2) Connect the four hsp70 5'-end upstream regulatory sequence fragments to the recombinase gene Cre gene, and connect them in series with the SV40 promoter-bar gene module, and insert them into two reverse loxP sites and two reverse loxP sites resp...
Embodiment 2
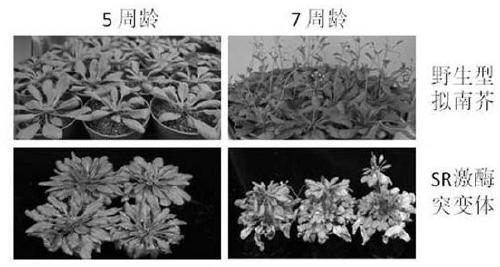
[0030] Example 2 The reverse reaction system of point-specific recombination was used to knock out the Arabidopsis SR1 gene.
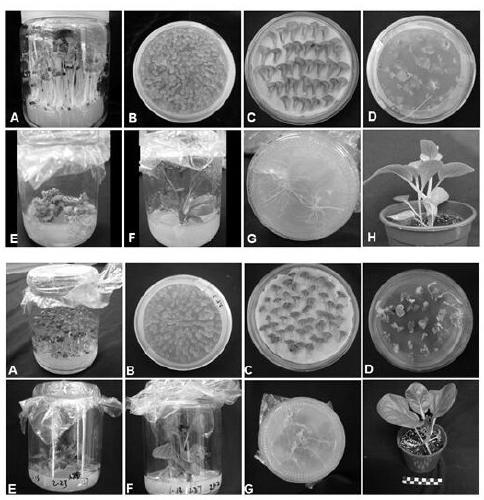
[0031] SR1 is a lethal protein. Both overexpression and knockout can lead to plant death. This plasmid system uses an inducible promoter to induce the expression of the target gene, and can control the expression of the lethal protein according to the induced expression time and expression abundance. A small RNAi fragment of SR1 gene that regulates SR1 kinase activity was cloned from Arabidopsis thaliana by PCR method. After cloning and sequencing, it was assembled under the Estradiol-induced promoter with a small restriction site, and expressed in the target A tag (HA) is added to the 3-end of the gene to construct an intermediate vector for the expression element. In the T-DNA segment of the plant bivalent expression vector, the 35s: NptⅡ: nos expression element is located between the Lox sites arranged in the same direction, and then a series of int...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 Applying the reverse reaction system of point-specific recombination to carry out the production of Chinese cabbage-type rapeseed WRKY31 Gene knockout.
[0033] WRKY31 is a transcription factor, both overexpression and knockout result in abnormal silique development and failure to harvest seeds. This plasmid system uses an inducible promoter to induce the expression of the gene of interest, depending on whether the seeds need to be harvested WRKY31 expression. Cloned from Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) by PCR WRKY31 After cloning and sequencing, the RNAi gene fragment was assembled under the Estradiol-induced promoter with small restriction sites, and a tag (HA) was added to the 3-end of the target gene to construct an intermediate expression element vector. In the T-DNA segment of the plant bivalent expression vector, the 35s: NptⅡ: nos expression element is located between the Lox sites arranged in the same direction, and then a series of intermediate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com