Application of submicron carbon oxide balls as medium in MALDI-MS
A technology of micron carbon oxide and carbon oxide spheres, which is applied in measuring devices, material analysis through electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve problems affecting the stability and repeatability of mass spectrometry detection, complicated preparation process, and limited applicability, etc. Achieve the effects of eliminating background interference, good water solubility, and improving repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
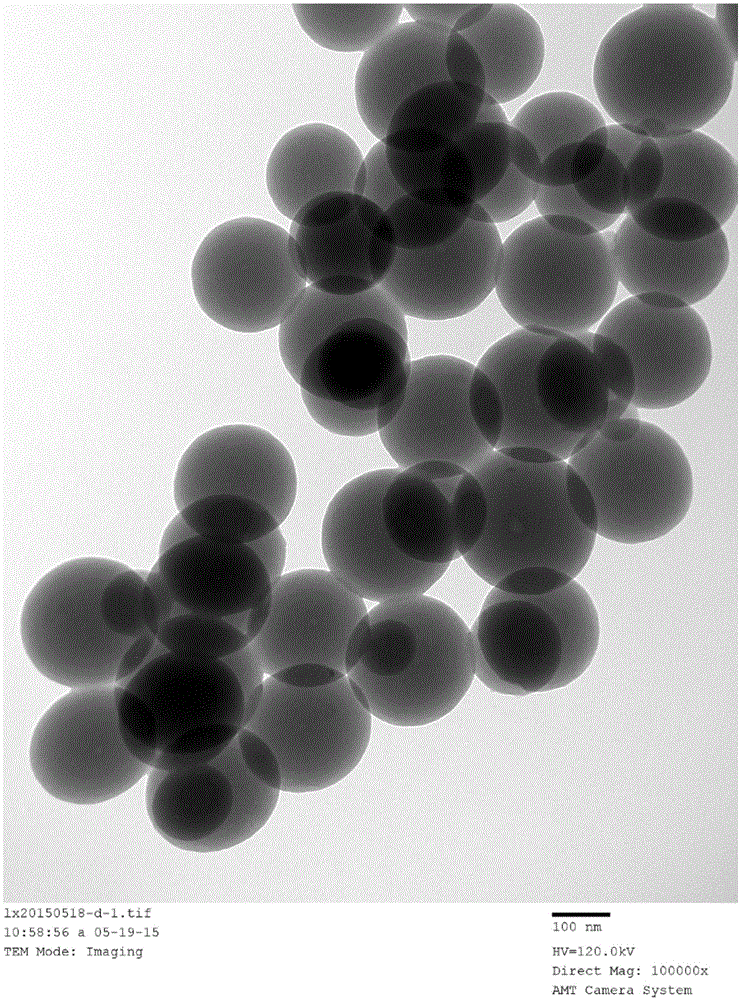
[0035] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the carbon oxide sphere that diameter is 180nm-250nm
[0036] (1) Disperse 0.029g CTAB and 0.96g F127 in ethanol / water (7mL / 14mL) solution, and magnetically stir at room temperature for 20min to form a colorless transparent solution.
[0037] (2) Add 0.093g (30mmoL) of resorcinol and 0.171mL of ammonia water (mass concentration: 25%) to step (1), and stir electromagnetically at 60°C.
[0038] (3) After half an hour, 0.126 μL of formaldehyde was added to step (2), and electromagnetic stirring was continued for 16 hours.
[0039] (4) Centrifuge the reaction solution obtained in step (3), wash with water three times, and wash with ethanol twice. Vacuum dried overnight to obtain a khaki carbon sphere precursor.
[0040](5) The khaki carbon sphere precursor obtained in step (4) was carbonized at 600° C. for 4 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere, and cooled naturally to obtain carbon spheres with an outer diameter of 180 nm-250 nm.
[0041] (6) ...
Embodiment 2
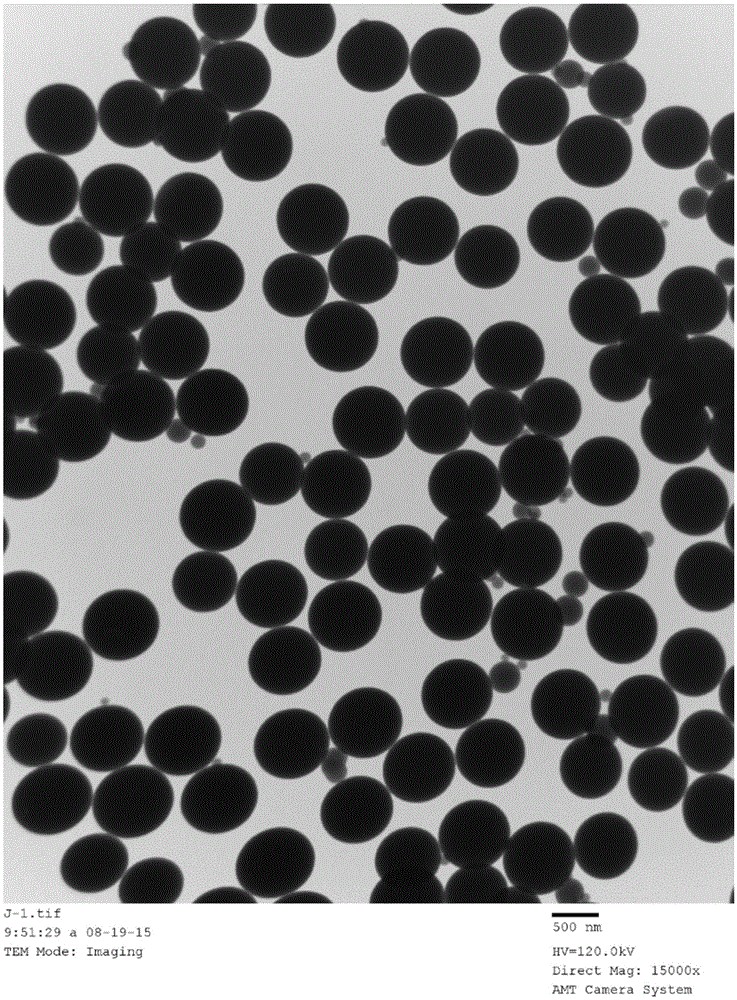
[0043] Embodiment 2: the preparation of the carbon oxide sphere that diameter is 600nm-800nm
[0044] The experimental operation steps are the same as those described in steps (1)-(6) in Example 1, except for the following special instructions.
[0045] The amount of CTAB used in step (1) is 0.232g.
[0046] In step (5), the temperature is naturally lowered to obtain carbon spheres with an outer diameter of 600nm-800nm.
[0047] Vacuum drying in step (6) to obtain carbon oxide spheres with an outer diameter of 600nm-800nm.
[0048] figure 2 It is the transmission electron micrograph of carbon oxide spheres with a diameter of 600nm-800nm obtained in Example 2;
[0049] The preparation method of the submicron carbon oxide spheres involved in the present invention is simple, the raw materials used are cheap, and the prepared materials are spherical with regular appearance, and the particle diameter can be adjusted between 70nm and 1000nm. The obtained carbon oxide spheres ...
Embodiment 3
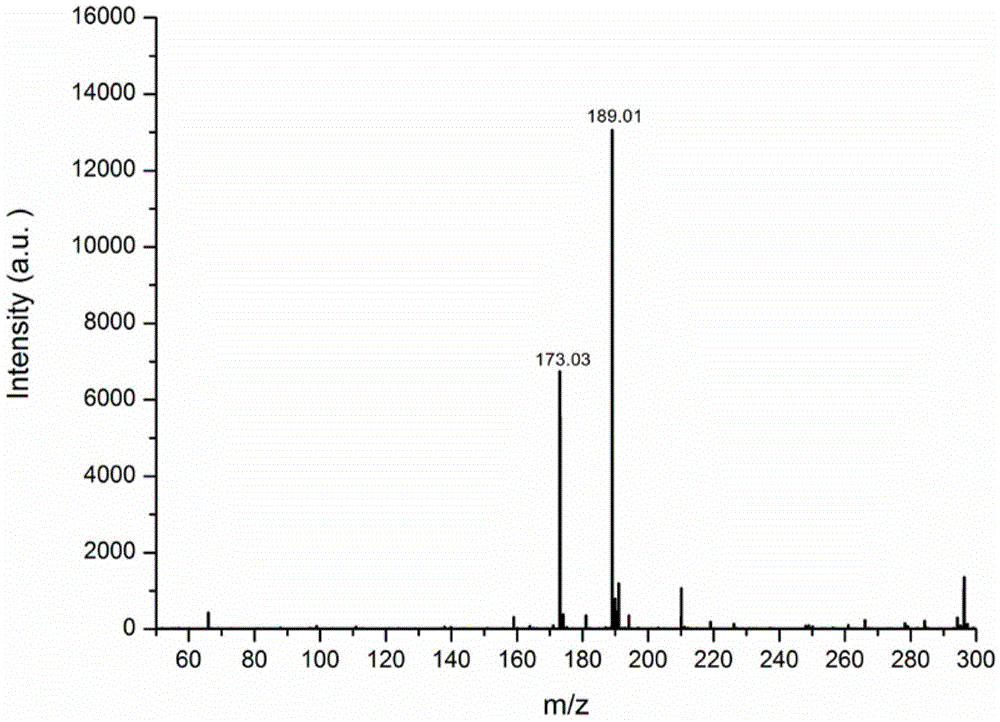
[0052] Example 3: 180nm-250nm carbon oxide spheres as a matrix MALDI-TOF MS detection of sugar compounds D-xylose (MW=150.13), a sugar compound that is not easily ionized, was used as the detection object.
[0053] 1. Prepare 10Mm of D-xylose mother solution (aqueous solution), and obtain a 1Mm dilution by gradient dilution. It can be stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0054] 2, the carbon dioxide sphere matrix solution of 180nm-250nm in the preparation 2mg / Ml embodiment 1 (solvent used is ethanol water mixed solution, V 乙醇 :V 水 =1:1). Ultrasound for 5 minutes to disperse evenly. It can be stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0055] 3. Take 0.5 μL of the 1 Mm diluent in step 1, drop it on the 384-well stainless steel MALDI sample target, and let it dry naturally to form a uniform sample layer.
[0056] 4. Take 0.5 μL of the matrix solution in step 2, apply it on the sample layer, and let it dry naturally.
[0057] 5. Send to MALDI-TOF MS for analysis. Mass spectrometry da...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com