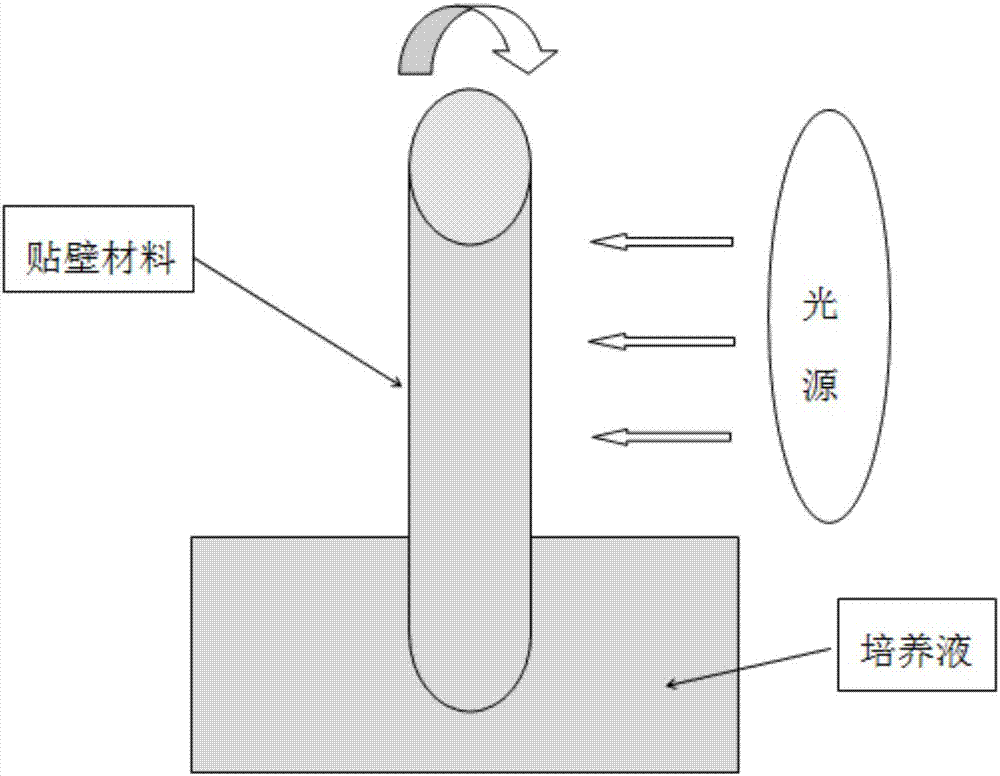
Method of subjecting Haematococcus pluvialis to attachment culture with rotary biomembrane reactor to produce astaxanthin
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and membrane reactor, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effect of simple biomass harvesting, small footprint, and increased algae biomass
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Effect of Nitrogen Deficiency Stress on Astaxanthin Accumulation at Different Times in Batch Culture Mode in Example 1
[0022] 1) Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis species into BG11 culture solution (sodium nitrate 1500mg / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 40mg / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 75mg / L, calcium chloride dihydrate 36mg / L L, citric acid 6mg / L, ferric ammonium citrate 6mg / L, disodium edetate 1mg / L, sodium carbonate 20mg / L, boric acid 2.86mg / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 1.86mg / L, seven Zinc sulfate water 0.22mg / L, sodium molybdate dihydrate 0.39mg / L, copper sulfate pentahydrate 0.08mg / L, cobalt nitrate hexahydrate 0.05mg / L) in the triangular flask, under light intensity 1000-4000lx, room temperature ( 20-30°C, the same below), cultivate for 5-7 days, and obtain a higher density algae liquid as the seed liquid;
[0023] 2) Adhesive culture: take the seed liquid in step 1), transfer it to a rotating biofilm reactor containing...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The impact of different light intensity stress on the accumulation of astaxanthin under the batch culture mode of embodiment 2
[0029] 1) Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis species into BG11 culture solution (sodium nitrate 1500mg / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 40mg / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 75mg / L, calcium chloride dihydrate 36mg / L L, citric acid 6mg / L, ferric ammonium citrate 6mg / L, disodium edetate 1mg / L, sodium carbonate 20mg / L, boric acid 2.86mg / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 1.86mg / L, seven Zinc sulfate water 0.22mg / L, sodium molybdate dihydrate 0.39mg / L, copper sulfate pentahydrate 0.08mg / L, cobalt nitrate hexahydrate 0.05mg / L) in a conical flask, under light intensity 1000-4000lx, room temperature , cultured for 5-7d, to obtain higher density algae liquid as seed liquid;
[0030] 2) Adhesive culture: take the seed liquid in step 1), transfer it to a rotating biofilm reactor containing BG11 culture liquid, and carry out...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Simultaneously performing nitrogen deficiency stress and high light intensity stress on Haematococcus pluvialis in batch culture mode to induce astaxanthin accumulation
[0036] 1) Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis species into BG11 culture solution (sodium nitrate 1500mg / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 40mg / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 75mg / L, calcium chloride dihydrate 36mg / L L, citric acid 6mg / L, ferric ammonium citrate 6mg / L, disodium edetate 1mg / L, sodium carbonate 20mg / L, boric acid 2.86mg / L, manganese chloride tetrahydrate 1.86mg / L, seven Zinc sulfate water 0.22mg / L, sodium molybdate dihydrate 0.39mg / L, copper sulfate pentahydrate 0.08mg / L, cobalt nitrate hexahydrate 0.05mg / L) in a conical flask, under light intensity 1000-4000lx, room temperature , cultured for 5-7d, to obtain higher density algae liquid as seed liquid;
[0037] 2) Adhesive culture: take the seed liquid in step 1), transfer it to a rotating biofilm r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com