Method for extracting microbial DNA in water body
An extraction method and microbial technology, applied in the field of molecular ecology, can solve the problems of low cell lysis rate, interfere with the extraction reaction, DNA loss, etc., and achieve the effects of high purity, improved elution efficiency, and single DNA band.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
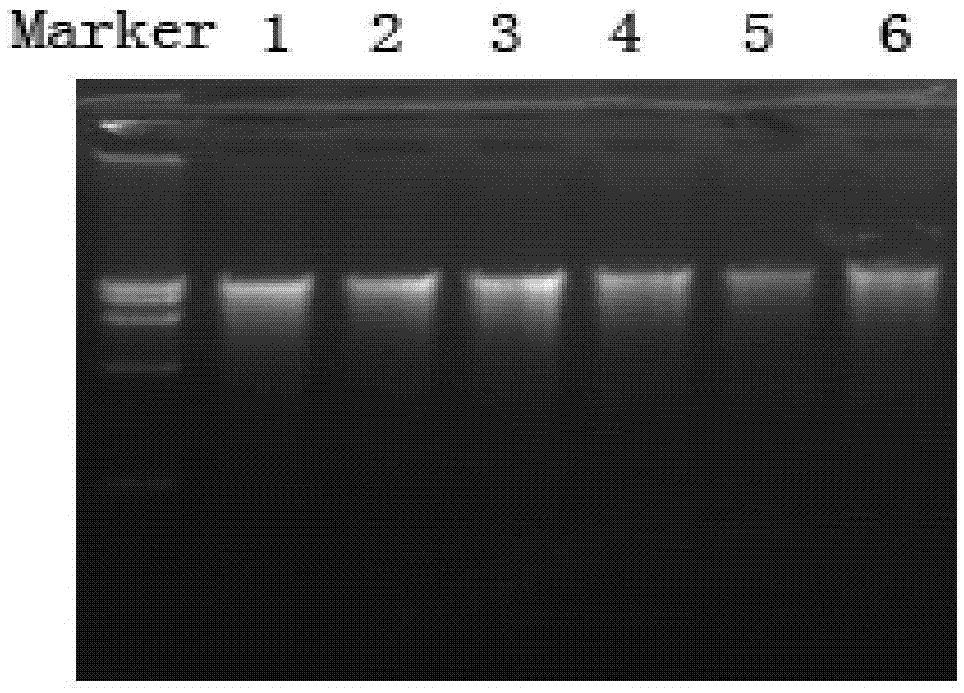
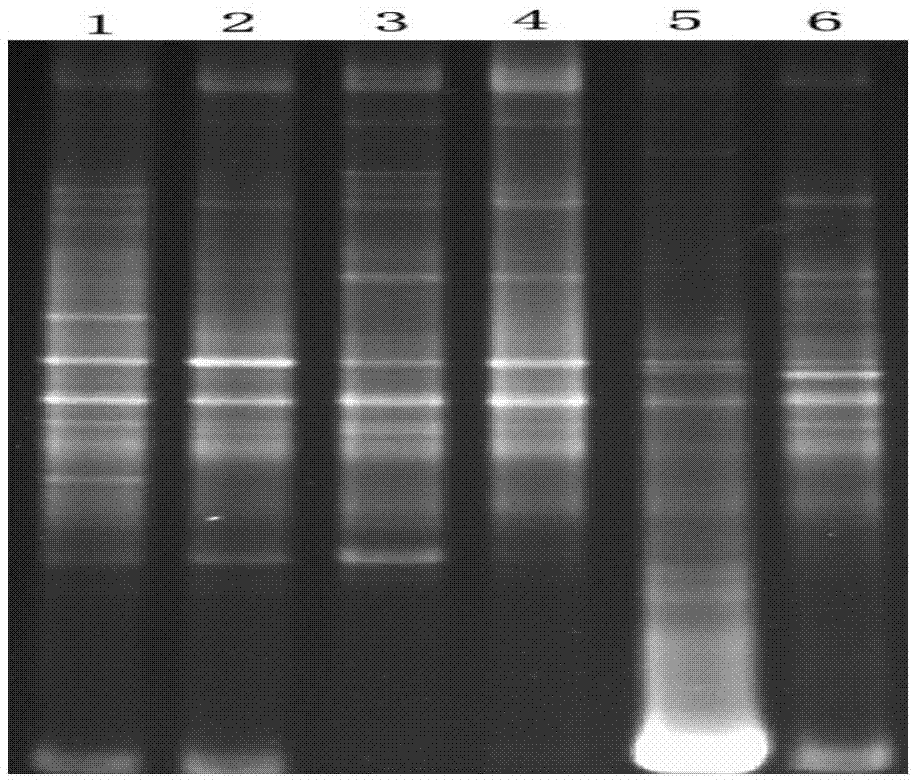
[0045] 1. Utilize the method of the present invention to extract the microbial DNA of 6 different water body samples (river water, lake water, each 2 sampling points that seawater position is different), sample is respectively taken from the Huangpu River fresh water of 2 different positions, 2 different positions The eutrophic water of Taihu Lake and seawater from the Yangtze River estuary of Chongming Island in two different locations, the extraction steps are as follows:
[0046] 1) Using the five-point sampling method, use plexiglass samplers to collect water bodies 0.5 meters below the water surface at two different locations (10-20 meters apart from the water surface), put them into sterilized bottles, store the samples at 4 degrees, and transport them back to In the laboratory, extract DNA immediately, take 50ml of water sample and filter it through a 0.22μm microporous membrane, cut the filter membrane and the filtrate into 1-2mm debris under sterile conditions, put it ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] In this example, reagent I is: 0.3M phosphate buffer solution, pH=8.0; the content of each component in reagent II is: 2wt% SDS, 60mM Tris-HCl, 200mM NaCl, 100mM EDTA, 1wt.%PVPP, pH=8.0 ; Reagent III is: 120mM aluminum sulfate; the content of each component of reagent IV is: 5M potassium acetate, 6wt.% glacial acetic acid, pH=5.0; the content of each component of reagent V is: 10M guanidine isothiocyanate, 0.6M potassium acetate The contents of each component of the reagent VI are: 10M guanidine isothiocyanate, 23mM sodium citrate; the reagent VII is: 75% ethanol.
[0070] Other operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the DNA concentration and purity results of the extracted water body samples are shown in Table 2.
[0071] Table 2
[0072]
[0073]
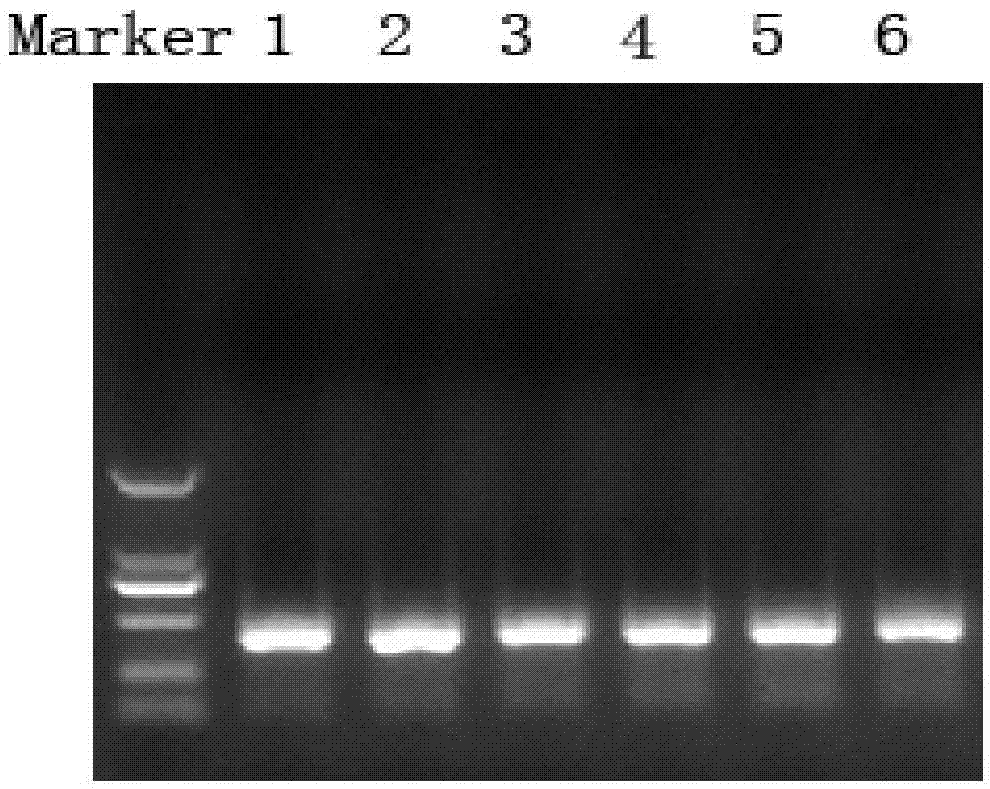
[0074] Utilize the microbial DNA of 6 different water body samples (river water, lake water, the different sampling points of seawater position) that this embodiment extracts, PCR amplifies 18S rRNA gene, ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] In this example, the reagent I is: 0.25M phosphate buffer, pH=7.5; the content of each component in the reagent II is: 1.5wt% SDS, 40mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, 70mM EDTA, 0.5%PVPP, pH=8.0 ; Reagent III is: 100mM aluminum sulfate; the content of each component of reagent IV is: 3M potassium acetate, 4wt.% glacial acetic acid, pH=4.8; the content of each component of reagent V is: 8M guanidine isothiocyanate, 0.4M potassium acetate The content of each component of the reagent VI is: 8M guanidine isothiocyanate, 22mM sodium citrate; the reagent VII is: 73% ethanol.
[0077] Other operating steps are the same as in Example 1, and the results of DNA concentration and purity of the extracted water samples are shown in Table 3.
[0078] table 3
[0079] sample
[0080] Utilize the microbial DNA of 6 different water body samples (river water, lake water, the different sampling points of seawater position) that this embodiment extracts, PCR amplifies 18S rRNA gene, agar...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com