Double-gradient artificial vertebral lamina and preparation method thereof
A dual-gradient, artificial technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of insufficient compatibility and anti-adhesion, poor new bone formation ability, no osteoinductivity, etc., and achieve good osteoconduction and osteoinduction ability, Good soft tissue compatibility and anti-adhesion ability, excellent osteoinductive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1. A dual-gradient artificial vertebral plate
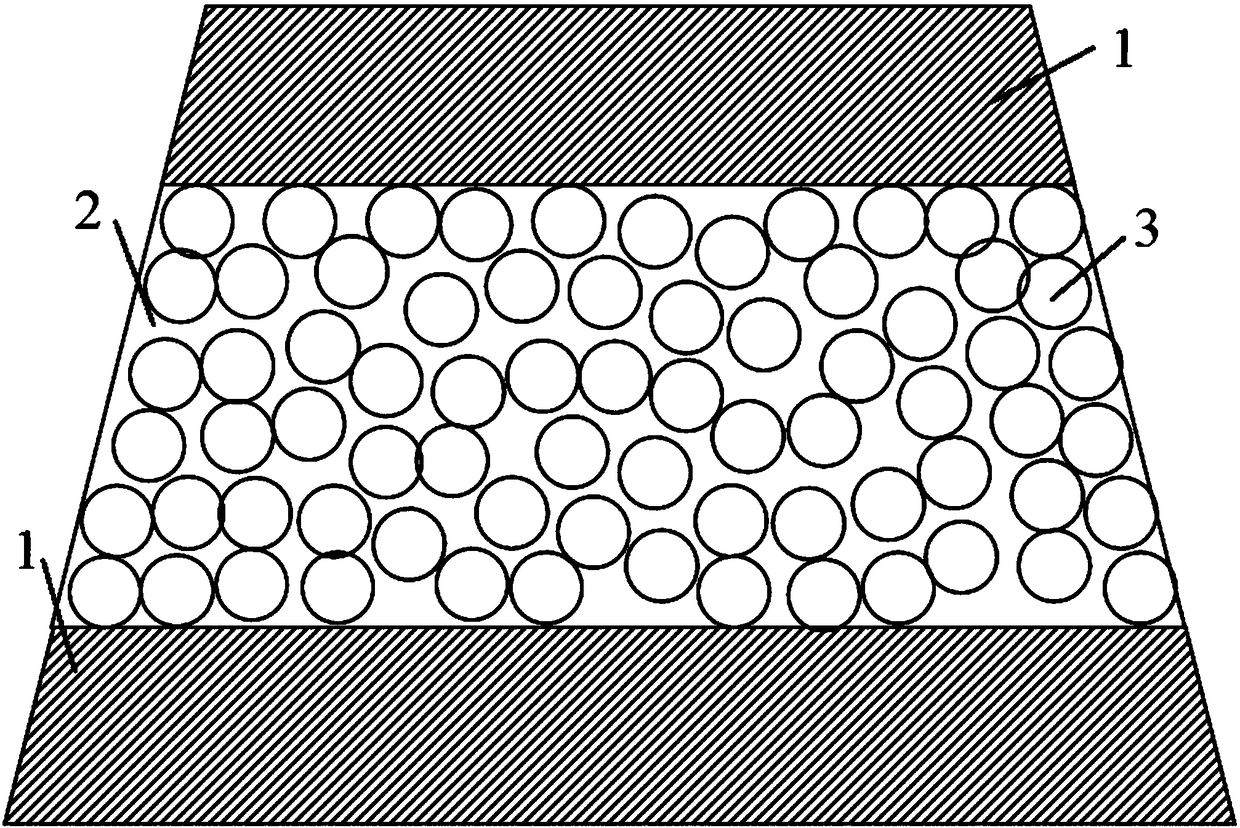
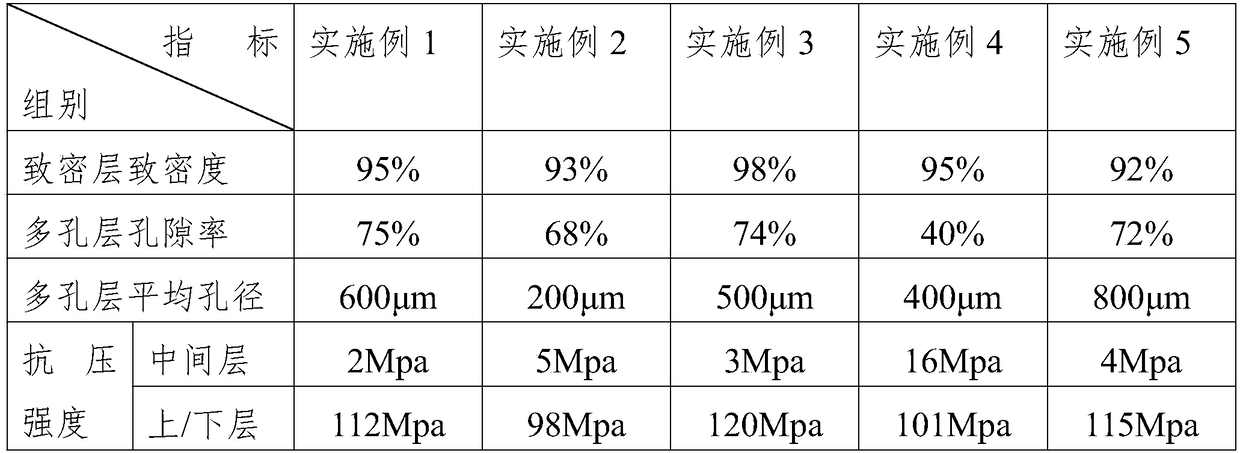
[0029] The artificial vertebral plate described in Example 1 is a matrix with a trapezoidal cross-section and an axial length. The matrix is composed of an upper layer, a middle layer and a lower layer. The upper and lower layers are hydroxyapatite ceramic layers 1. The middle layer is a two-phase calcium phosphate ceramic layer 2, and the upper and lower layers are dense structure layers with a thickness of 1 mm. The middle layer is a porous structure layer with a porosity of 75%.
[0030] Preparation:
[0031] A) Raw material preparation:
[0032] Preparation of nano-hydroxyapatite powder or slurry: mix 0.835mol / L calcium nitrate aqueous solution and 0.5mol / L diammonium hydrogen phosphate aqueous solution in equal volume, the ratio of calcium to phosphorus is 1.67, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 11.0 with ammonia water. Stir the reaction for 12h, then aging at 60℃ for 24h, wash with deionized water to obta...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2. A dual-gradient artificial vertebral plate
[0039] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that in steps B) and C), the binder is polyethylene glycol, the dispersant is citric acid, and the pore former is polymethyl methacrylate. The step D ) The isostatic pressure is 300 MPa, and the step E) is: placing the green body in the cavity of the muffle furnace sintering furnace, sintering in the muffle furnace, and increasing the temperature at a temperature rise rate of 0.5°C / min To 150℃, keep for 10min; then increase the temperature to 500℃ at a heating rate of 0.5℃ / min and keep it for 10minh; then increase the temperature to 600℃ at a heating rate of 0.5℃ / min, keep it for 30min to decompose organic matter; continue to use Muffle furnace sintering, heating up to 1000°C at a heating rate of 10°C / min, holding time 1h, and reducing the temperature to room temperature at a cooling rate of 20°C / min, cutting to obtain an artificial lamina with double gradients...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3. A dual-gradient artificial vertebral plate
[0041] The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that in steps B) and C), the binder is polyethylene glycol, the dispersant is ammonium citrate, and the pore former is polystyrene. The step D) The isostatic pressure is 500 MPa, and the step E) is: placing the green body in the cavity of the muffle furnace sintering furnace, sintering in the muffle furnace, and raising the temperature to 250 at a heating rate of 20°C / min ℃ for 2h; then increase the temperature to 500℃ at a heating rate of 3℃ / min and keep it for 4h; then increase the temperature to 800℃ at a heating rate of 20℃ / min and keep it for 4h to decompose organic matter; continue to use muffle Furnace sintering, heating up to 1200°C at a heating rate of 20°C / min, holding time 4h, and lowering the temperature to room temperature at a cooling rate of 100°C / min; cutting to obtain a double-gradient artificial lamina with a porosity of 74% .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com