Method for extracting tungsten and molybdenum through acid decomposition of high-molybdenum scheelite
A technology of scheelite and acid decomposition, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of increasing tungsten smelting costs, hydrogen sulfide harming production and environment, and polluting the environment, so as to reduce production and operation costs and increase product added value , The effect of reducing the decomposition cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
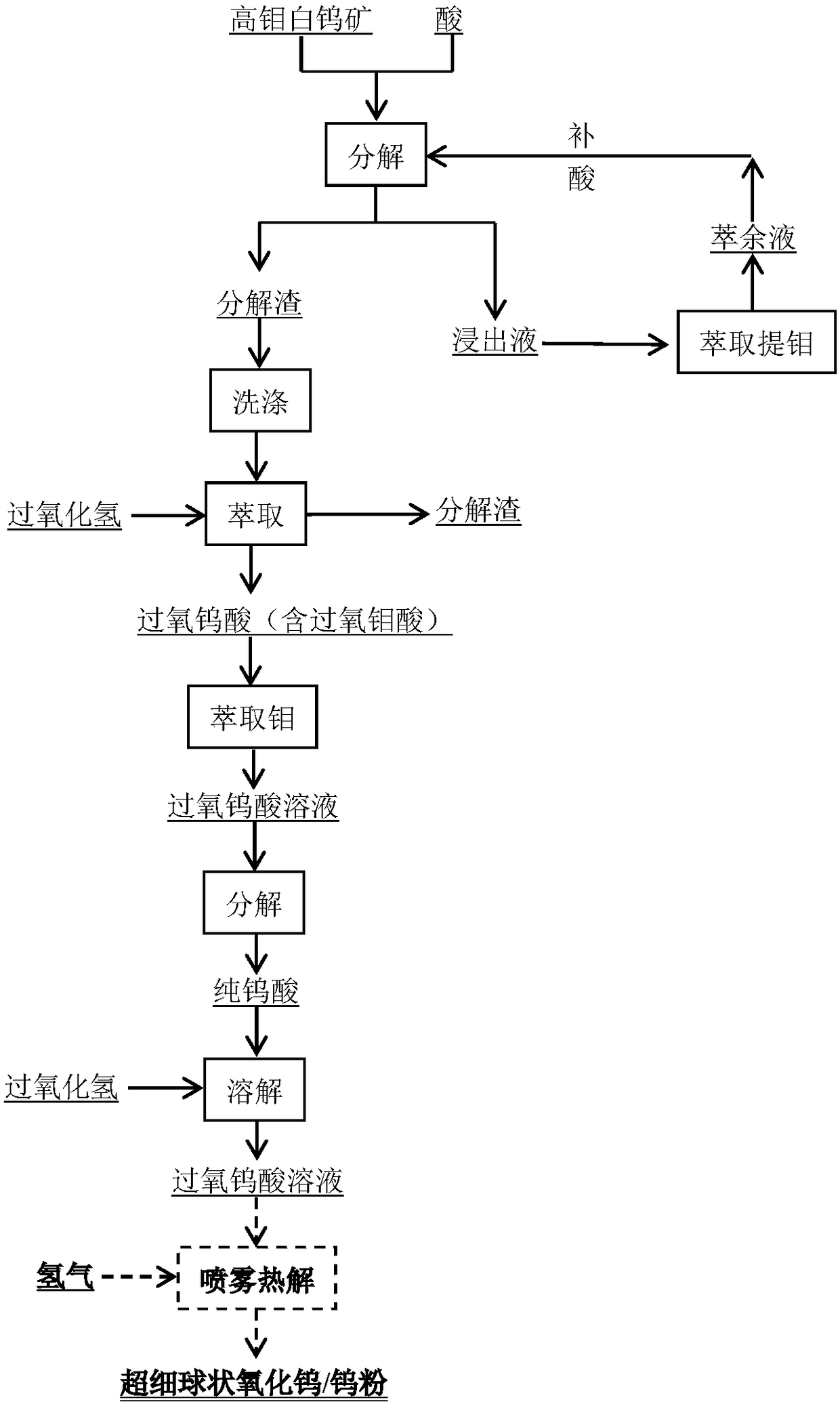
[0055] The raw material that this embodiment adopts is WO 3 High-molybdenum scheelite with a grade of 40%, a Mo grade of 5%, and a particle size of 120 μm.
[0056] A method for acid-decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite to extract tungsten and molybdenum, comprising the following steps:
[0057] (1) Leaching reaction: Add high-molybdenum scheelite into a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 150g / L. The liquid-solid ratio of the system is 5:1. The leaching reaction is carried out at 150°C and 0.5Mpa for 3 hours; 99.5% Tungsten is converted into tungstic acid, 10.5% of molybdenum is converted into molybdenum acid, and the leaching rate of molybdenum is 89.1%;
[0058] (2) extracting molybdenum in the leachate: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition residue and leachate; add extractant (30% P204+10%TBP+kerosene) to the gained leachate to control the volume of the organic phase and the water phase The ratio is 1:1, mixed, and the extr...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The raw material that this embodiment adopts is WO 3 High-molybdenum scheelite with a grade of 30%, a Mo grade of 25%, and a particle size of 50 μm.
[0066] A method for acid-decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite to extract tungsten and molybdenum, comprising the following steps:
[0067] (1) Leaching reaction: Add high-molybdenum scheelite into hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 200g / L, the liquid-solid ratio of the system is 5:1, and carry out leaching reaction at 200°C and 2.5Mpa for 3 hours; 99.5% Tungsten is converted into tungstic acid, 2.5% of molybdenum is converted into molybdenum acid, and the leaching rate of molybdenum is 97.2%;
[0068] (2) Molybdenum extraction in the leachate: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition residue and leachate;
[0069] Add sulfuric acid to the leaching solution, the molar ratio of the amount of sulfuric acid to the calcium ion content in the leaching solution is 1:1, and perfo...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The raw material that this embodiment adopts is WO 3 High-molybdenum scheelite with a grade of 55%, a Mo grade of 2.5%, and a particle size of 150 μm.
[0076] A method for acid-decomposing high-molybdenum scheelite to extract tungsten and molybdenum, comprising the following steps:
[0077](1) Leaching reaction: Add high-molybdenum scheelite into a nitric acid solution with a concentration of 200g / L, and at the same time add tungstic acid with 10% tungsten ore mass. The liquid-solid ratio of the system is 7:1. Carry out leaching reaction for 4 hours; 99.5% of tungsten is converted into tungstic acid, 1.2% of molybdenum is converted into molybdenum acid, and the leaching rate of molybdenum is 98.2%;
[0078] (2) Molybdenum extraction in the leachate: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition residue and leachate;
[0079] Add sulfuric acid to the leaching solution, the molar ratio of the amount of sulfuric acid to the calcium ion content...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com