A method for extracting tungsten by acid decomposition wolframite
A wolframite and acid decomposition technology, applied in the field of chemical production, can solve the problems of polluting the environment, high price, increase tungsten smelting cost, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing decomposition cost, increasing product added value, and reducing environmental protection costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
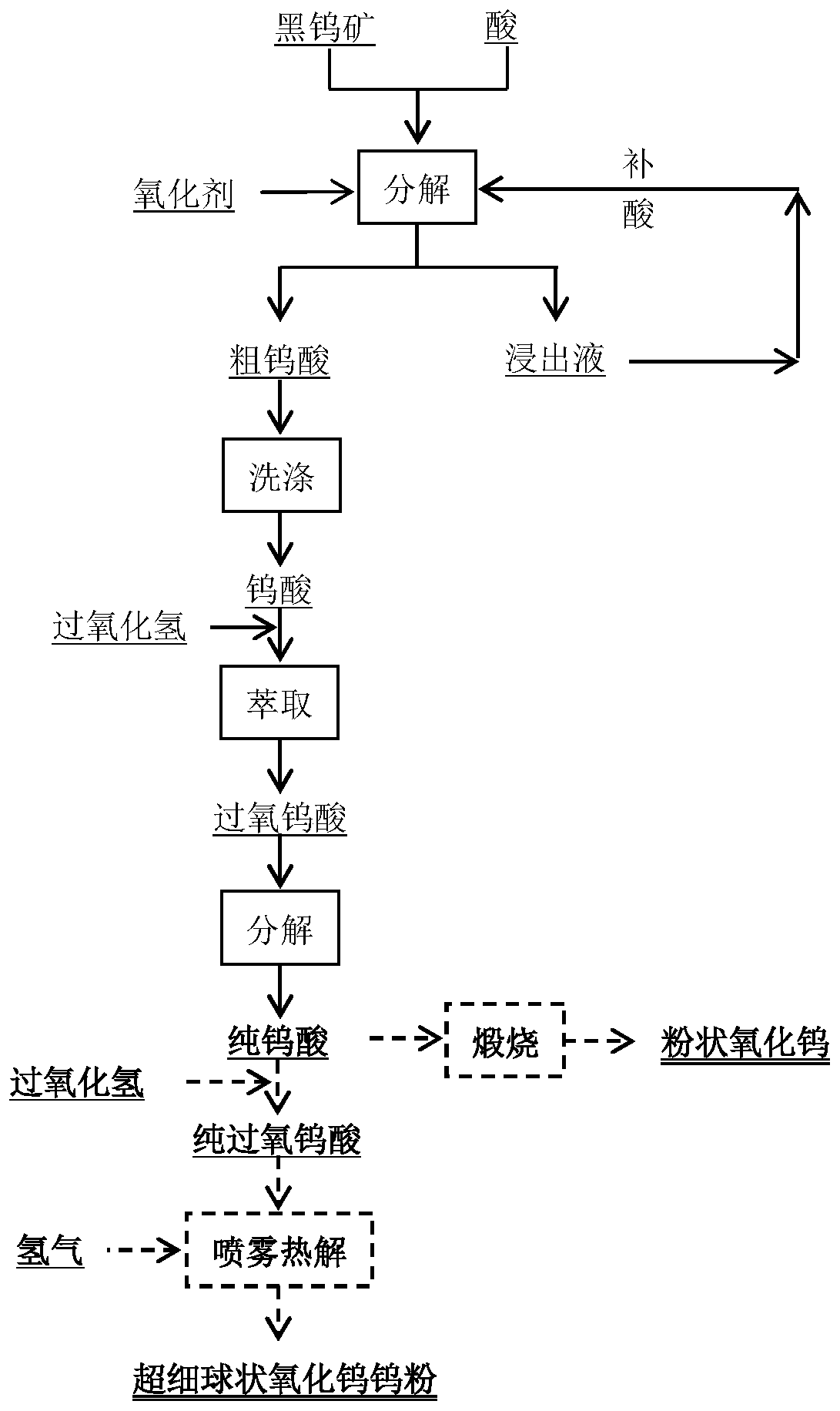
[0036] This embodiment provides a method for acid-decomposing wolframite to extract tungsten. The raw material used in this method is wolframite with a grade of 40% and a particle size of 100 μm. The method is specifically as follows:
[0037] (1) Leaching reaction: adding wolframite to the sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 200g / L, adding sodium hypochlorite equivalent to 1.5 times the total molar amount of iron and manganese in the wolframite, and the liquid-solid ratio of the system is 6:1. The leaching reaction was carried out at 90°C for 3 hours, and 99.2% of tungsten was converted into tungstic acid;
[0038] (2) Filtration and washing: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition residue and leaching solution; add sulfuric acid to the leaching solution and return to step (1) as a raw material for leaching reaction;
[0039] (3) hydrogen peroxide extraction-decomposition and extraction of tungsten: wash the decomposed slag obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0042] This embodiment provides a method for acid-decomposing wolframite to extract tungsten. The raw material used in this method is wolframite with a grade of 10% and a particle size of 200 μm. The method is specifically:
[0043] (1) Leaching reaction: Add wolframite to a nitric acid solution with a concentration of 120g / L, the liquid-solid ratio of the system is 7:1, and carry out the leaching reaction under the conditions of 200°C and controlled oxygen pressure of 2.5Mpa by introducing oxygen 1 Hours, 99.4% of tungsten is converted into tungstic acid;
[0044] (2) Filtration and washing: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition slag and leachate; add nitric acid in the leachate and return to step (1) as raw material for leaching reaction;
[0045] (3) hydrogen peroxide extraction-decomposition and extraction of tungsten: wash the decomposed slag obtained in step (2) and mix it with a hydrogen peroxide solution with a mass concentration of 3...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment provides a method for acid-decomposing wolframite to extract tungsten. The raw material used in this method is wolframite with a grade of 65% and a particle size of 50 μm. The method is specifically as follows:
[0051] (1) Leaching reaction: Add wolframite to a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 200g / L, and then add solid tungstic acid accounting for 10% of the wolframite mass. The liquid-solid ratio of the system is 3:1. 、The leaching reaction was carried out under the condition of 1.25Mpa for 6 hours, and 99.3% of tungsten was converted into tungstic acid;
[0052] (2) Filtration and washing: filter the reaction product obtained in step (1) to obtain decomposition residue and leaching solution; add sulfuric acid to the leaching solution and return to step (1) as a raw material for leaching reaction;
[0053] (3) hydrogen peroxide extraction-decomposition and extraction of tungsten: wash the decomposed slag obtained in step (2) and mix it w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com