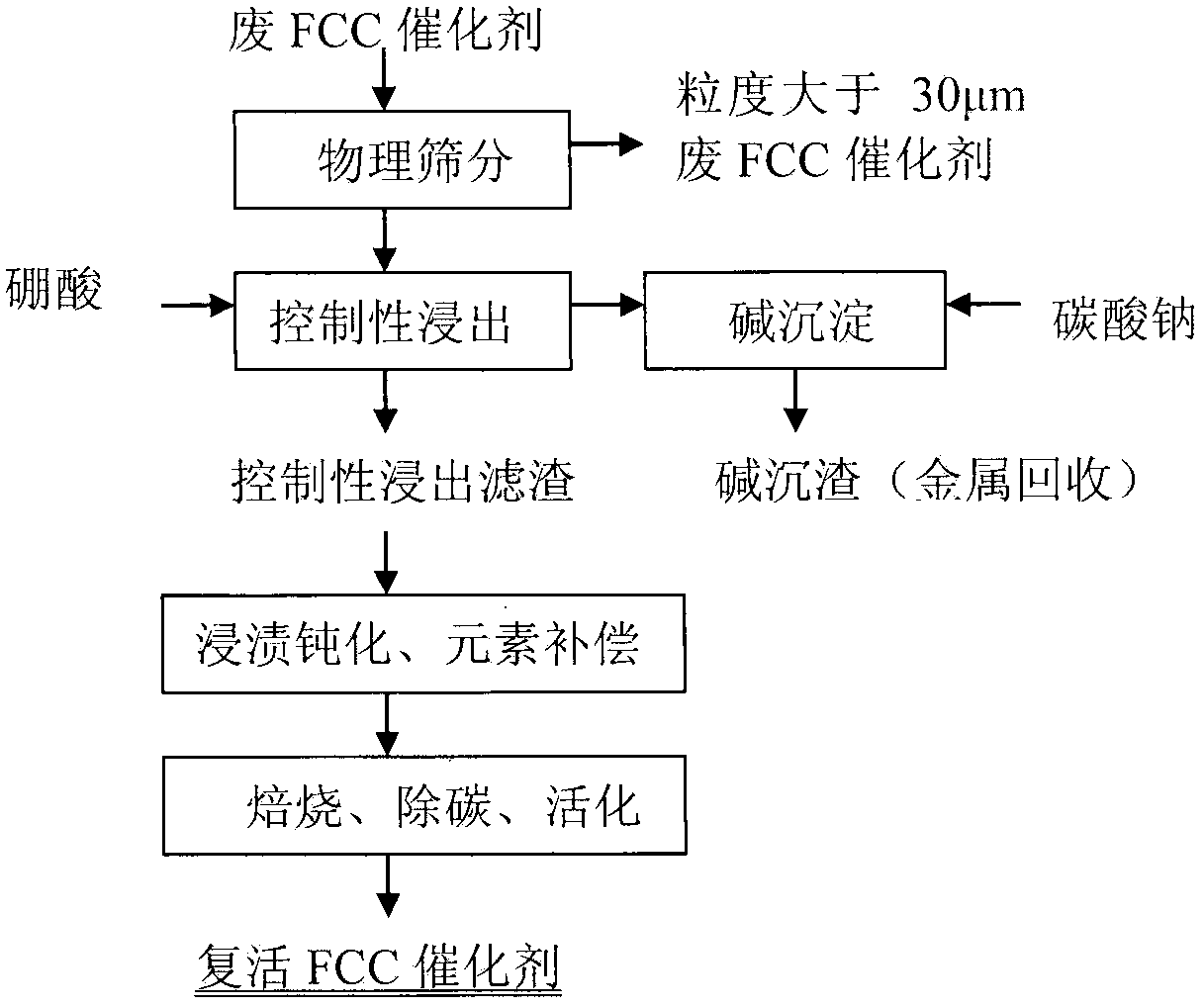
Waste FCC (fluid catalytic cracking) catalyst reactivation method based on controlled leaching, metal passivation and effective component compensation
A technology of spent catalysts and active ingredients, applied in the direction of catalyst regeneration/reactivation, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the loss of alumina and rare earth lanthanum oxide, short service time, catalyst skeleton collapse, etc. The problem is to overcome the loss of alumina, keep the acidity stable, and improve the catalytic performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
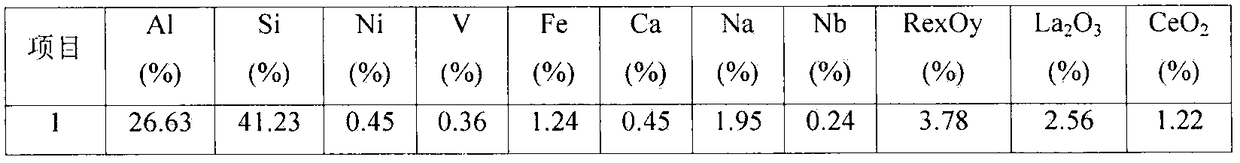
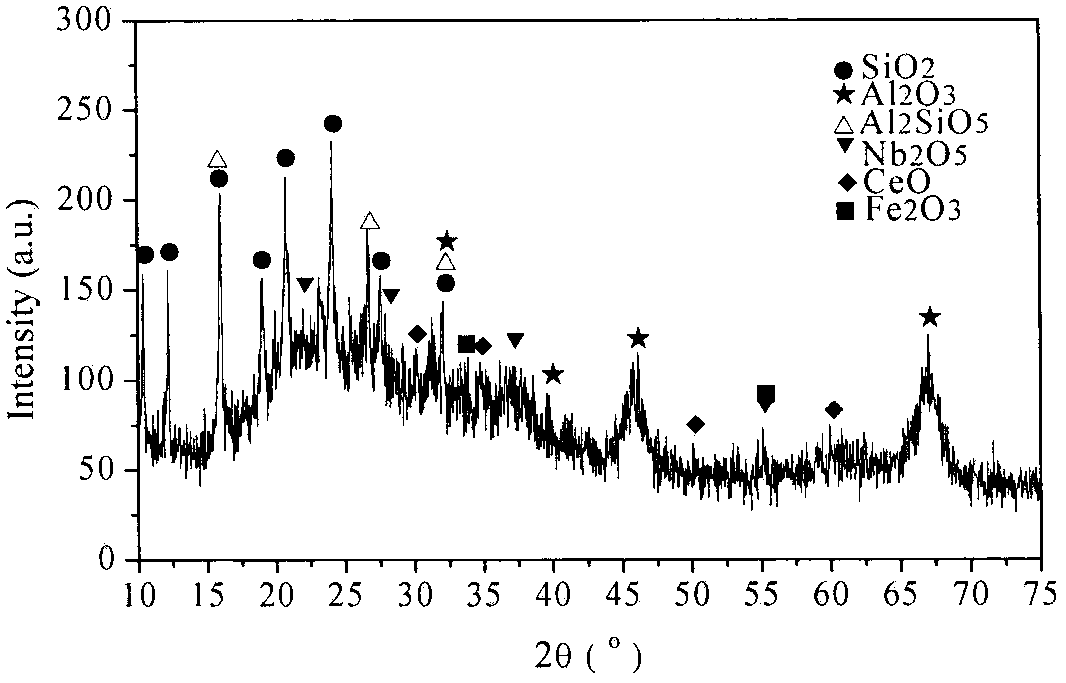
[0029] Embodiment 1: by sieving particle size greater than 30 μm waste catalyst (below the same), react with impurity-removing active agent, (in this embodiment waste FCC catalyst is recorded as former agent, and its test sample analysis data is as follows figure 1 As shown, the phase analysis is as follows figure 2 As shown, the following examples are the same), select 1% impurity removal activator and spent catalyst to control the impurity removal reaction, the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1, the reaction time is 3 hours, the process pH is controlled at ≮1, and the filter residue is deionized and washed for 2 After rinsing twice, the filter residue was impregnated in 0.03% boric acid and lanthanum nitrate (the amount of lanthanum nitrate added is based on the mass fraction of lanthanum oxide to control the loss of impurities, the same below), the immersion temperature was 45 ° C, the immersion time was 6 hours, and the Vacuum filtration, drying and dehydration at 120°C, calcinat...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Select 2% impurity removal agent and spent catalyst to carry out controlled impurity removal reaction, the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1, the reaction time is 4 hours, the process pH is controlled at ≮1, the filter residue is deionized, washed twice, and rinsed 2 times a kilogram, the filter residue was immersed in 0.04% boric acid and lanthanum nitrate solution, the immersion temperature was 45°C, the immersion time was 7 hours, vacuum filtered, dried and dehydrated at 120°C, roasted at 750°C for 3.5 hours, and the revived catalyst sample was obtained. Denoted as sample 2. The chemical element analysis, specific surface area and pore volume of the obtained revived catalyst were determined. See Figure 4 , Figure 5 .
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Select 3% impurity removal activator and spent catalyst to carry out controlled impurity removal reaction, the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1, the reaction time is 5 hours, the process pH is controlled at ≮1, the filter residue is deionized, pulp washed twice, and rinsed After 2 times, the filter residue was immersed in 0.05% boric acid and lanthanum nitrate solution, the immersion temperature was 45°C, the immersion time was 8 hours, vacuum filtered, dried and dehydrated at 120°C, and roasted at 760°C for 4 hours, the revived catalyst sample was obtained. Denoted as sample 3. The chemical element analysis, specific surface area and pore volume of the obtained revived catalyst were determined. See Figure 4 , Figure 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com