Pseudoalteromonas polysaccharide degrading bacteria as well as culture method and application thereof
A kind of pseudoalteromonas, expanded culture technology, applied in the field of pseudoalteromonas polysaccharide degrading bacteria and its culture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Embodiment 1, separation and purification of coastal sediment microorganisms
[0069] Take the coastal sediments near the trestle bridge in Qingdao, take 1g sample, put it in the only carbon source medium of agarose, alginate or carrageenan with a volume of 100mL, under the conditions of the temperature of 28°C and the number of revolutions of 200 rpm, Cultivate until the solution is turbid; take 1 mL of the solution and add it to 9 mL of sterile water, and dilute to a concentration of 10 -1 、10 -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 、10 -5 5 concentration gradients. Spread the diluted bacterial suspension on the primary screening medium, make two parallels for each concentration, and culture at 28°C for 7 days. Pick out the single colony that can make the plate sink, and after 3 times of streaking on the plate to separate and purify, pick the single colony in the liquid medium for primary screening, culture at 28°C and 200 rpm for 3 days, take 1.6 mL of the culture and add 400 μL of gl...
Embodiment 2
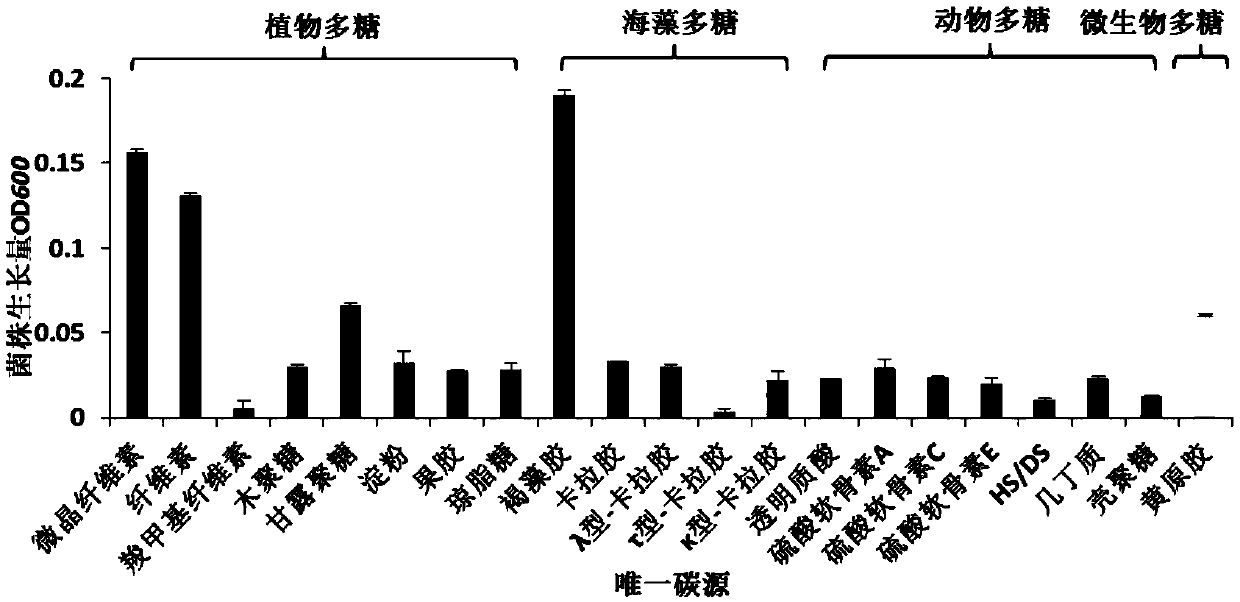
[0075] Embodiment 2, the screening of polysaccharide degrading bacteria
[0076] The single clones of the strains obtained in Example 1 were inoculated into the sole carbon source liquid medium, cultured at 200 rpm and 30°C for 72 hours, and the turbidity of the bacterial solution and the change of the viscosity of the culture solution were observed. The enzyme-producing strains were selected according to the above two indicators. Pick the strains with large changes in the turbidity and viscosity of the bacteria in each unique carbon source medium, and pick them on the solid medium for primary screening and culture them, keep the strains and record them with numbers, such as Q01, Q02, Q03, ... etc.; after culturing a single colony for 24 hours, stain with modified Lugol's iodine solution;
[0077] The preparation method of the above-mentioned sole carbon source medium is:
[0078] Add polysaccharide substrates to the artificial seawater to a final concentration of 0.10% (w / v...
Embodiment 3
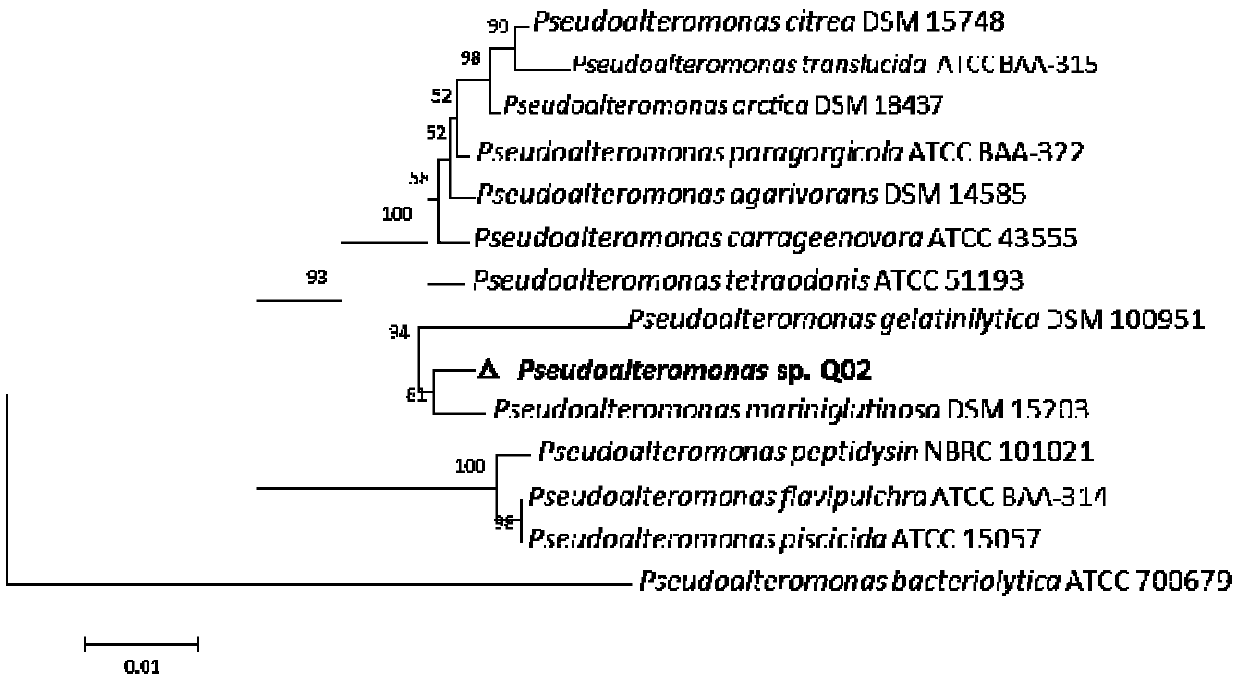
[0087] Example 3, Molecular identification of Pseudoalteromonas sp.Q02 strain based on 16S rRNA gene cloning
[0088] Genomic DNA of bacterial strain Q02 was prepared with a bacterial genome extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical) and used as a template, amplified with universal primers (27f and 1492r) of bacterial 16S rRNA gene, and subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis, and then gel The recovery kit (Tiangen) purified the PCR amplification product, and after electrophoresis verification, it was connected to pEASY-Blunt Simple CloningVector and transformed into E.coli Trans1 T1 competent cells. After ampicillin resistance screening, positive clones were obtained. The obtained 16S rRNA gene sequencing was completed by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The sequence was compared with the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the standard strain collected by the National Center for Biological Information (NCBI) in the United States, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using ME...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com