A group of synthetic methods of natural and unnatural protopanaxatriol-type ginsenosides
A technology of protopanaxatriol and ginsenoside, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and botany, can solve the problems of many side reactions, large pollution, poor stereoselectivity of chemical methods and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
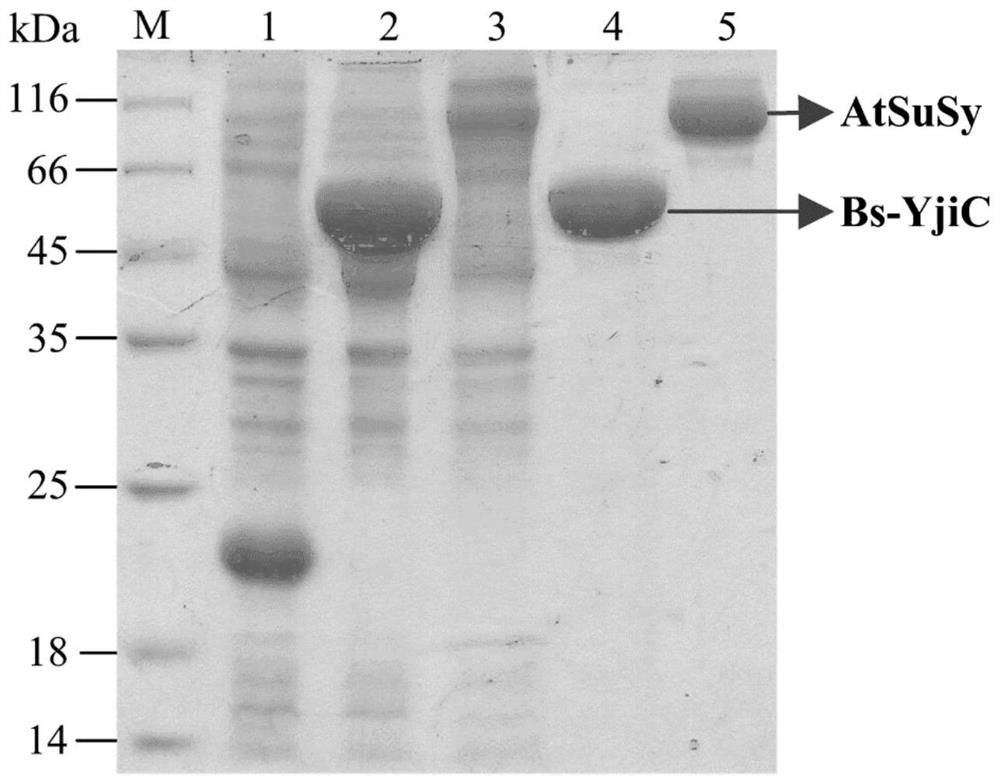
[0056] Example 1. Cloning, expression and purification of glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC and sucrose synthase AtSuSy
[0057] The gene accession numbers of glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC and sucrose synthase AtSuSy in NCBI (https: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ) are NP_389104 and NM_001036838, respectively, with the genomic DNA of Bacillus subtilis 168 As the template, the Bs-YjiC-F and Bs-YjiC-R primer pairs were used to amplify the glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC gene; the Arabidopsis cDNA was used as the template, and the At-SuSy-F and AtSuSy-R primer pairs were used to amplify the gene. Increase the sucrose synthase AtSuSy. The nucleotide sequences of the primers used are as follows (restriction enzyme sites are underlined):
[0058] Bs-YjiC-F: 5′-CGCGGATCCATGAAAAAGTACCATATTTCGAT-3′ (BamHI restriction site)
[0059] Bs-YjiC-R: 5′-CGCGTCGACTTACTGCGGGACAGCGGATTTT-3′ (SalI restriction site)
[0060]AtSuSy-F: 5′-GCGTCGACAAATGGCAAACGCTGAACGTATGATAA-3′ (SalI restriction site)
[0061] AtSuSy-...
Embodiment 2
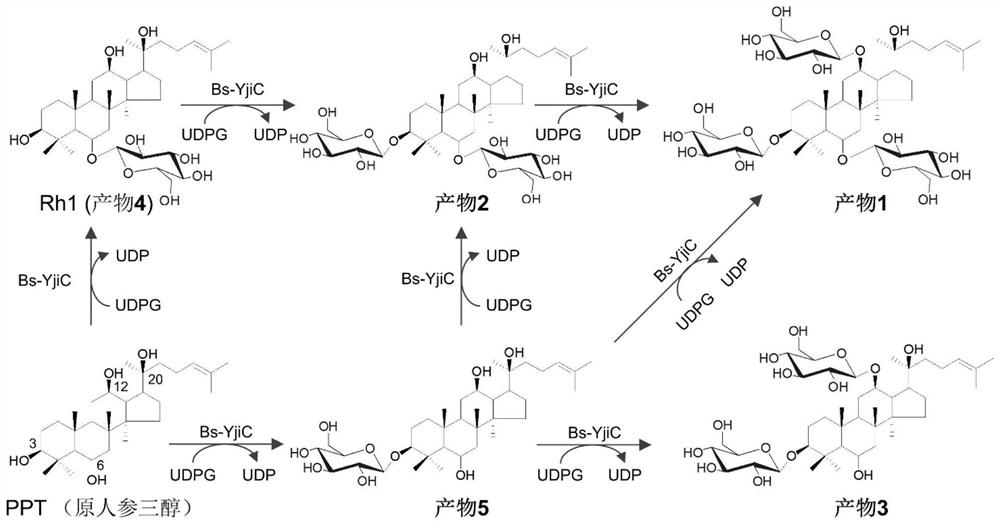
[0063] Example 2. Glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC catalyzes the glycosylation of protopanaxatriol
[0064] According to the steps described in Example 1, the glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC was isolated and purified. The reaction system for the glycosylation of protopanaxatriol catalyzed by the glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC included: 2mM protopanaxatriol, 10mM uridine diphosphate glucose, 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10mM MgCl 2 , and 5mU / mL glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC at 35°C for 0.5h.
[0065] After the reaction was completed, an equal volume of methanol was added to terminate the reaction, and then centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, added to a liquid bottle, and passed through high performance liquid chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry Analysis and identification of glycosylation products. The analytical conditions of high performance liquid chromatography were: mobile phase A was ...
Embodiment 3
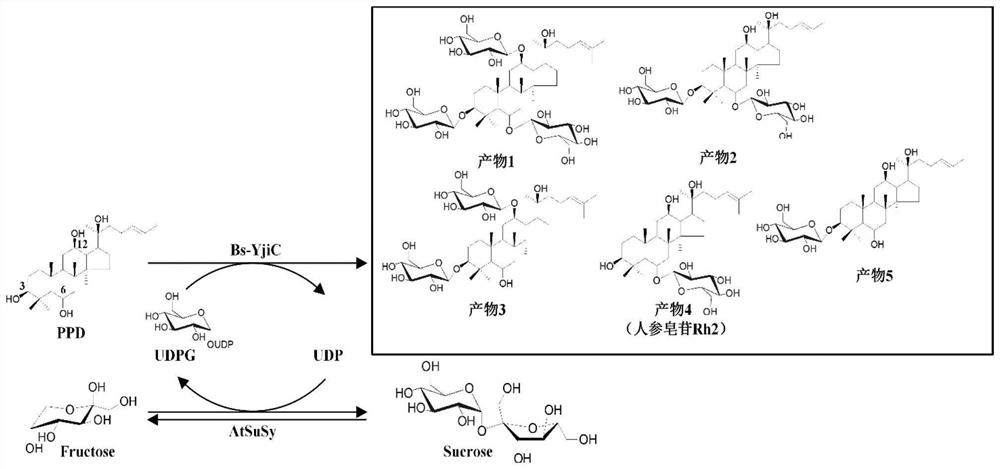
[0068] Example 3. Coupling reaction of glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC and sucrose synthase AtSuSy to catalyze the glycosylation of protopanaxatriol
[0069] Glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC coupled with sucrose synthase AtSuSy to catalyze the glycosylation of protopanaxatriol. The reaction system is: 3mM protopanaxatriol, 0.5mM uridine diphosphate, 50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.5) , 10mM MgCl 2 , 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (v / v), 160mU / mL glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC, 200mU / mL sucrose synthase AtSuSy, 35°C reaction, 200rpm for 1h. After the reaction, the reaction product was identified according to the reaction conditions in Example 2 and the high-performance liquid chromatography detection method. like Figure 5 As shown, the double-enzyme coupling reaction system composed of glycosyltransferase Bs-YjiC and sucrose synthase AtSuSy can use cheap sucrose as the glycosyl group, just like the reaction system using expensive uridine diphosphate glucose as the glycosyl donor. Donor, Efficiently catalyz...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com