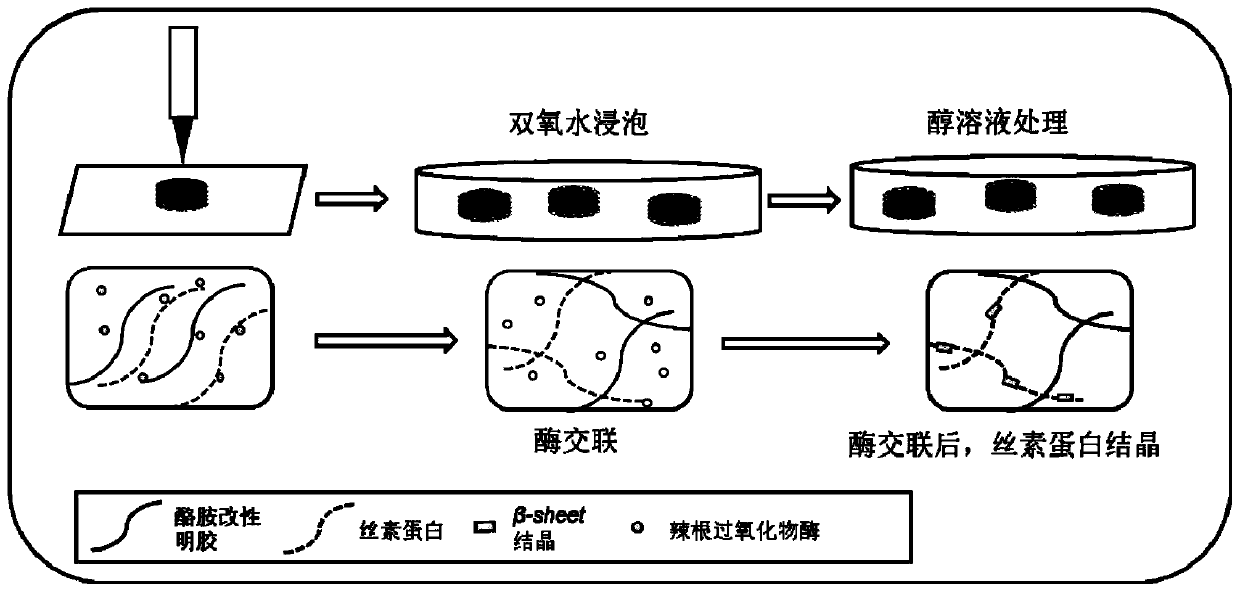
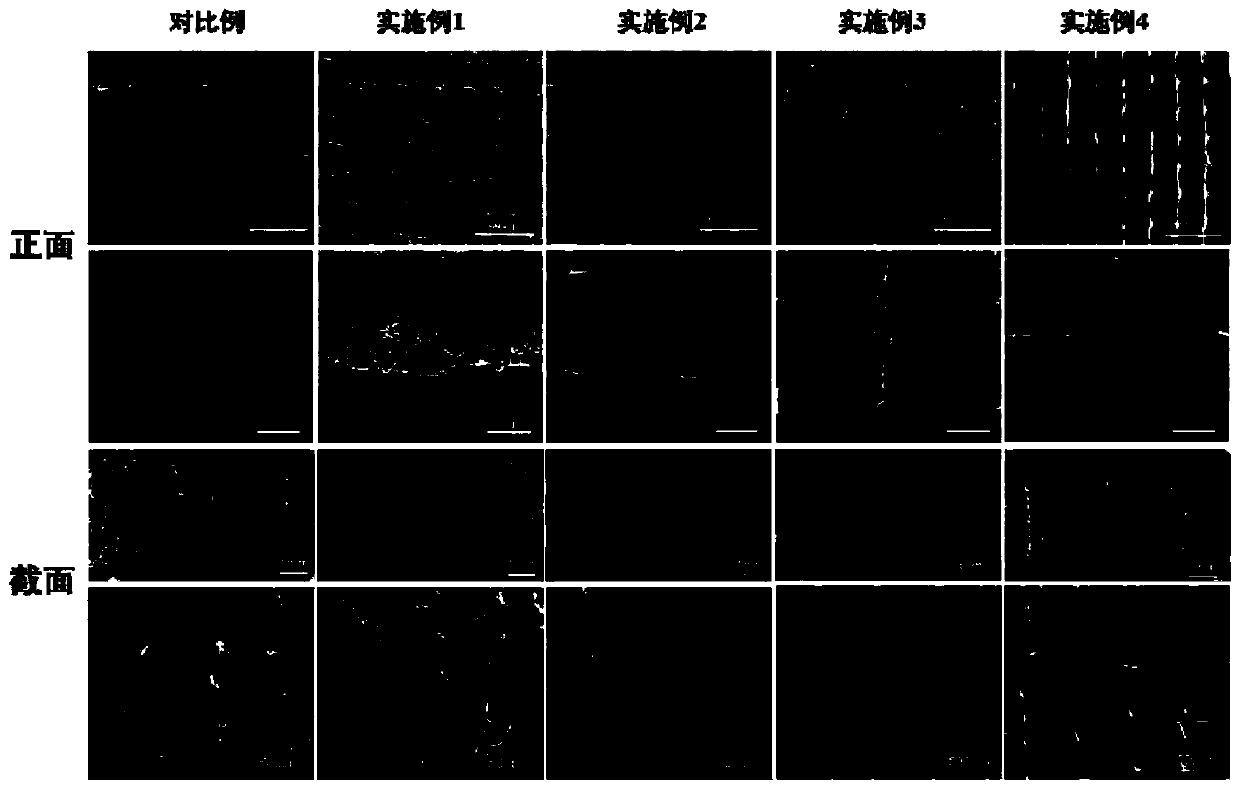
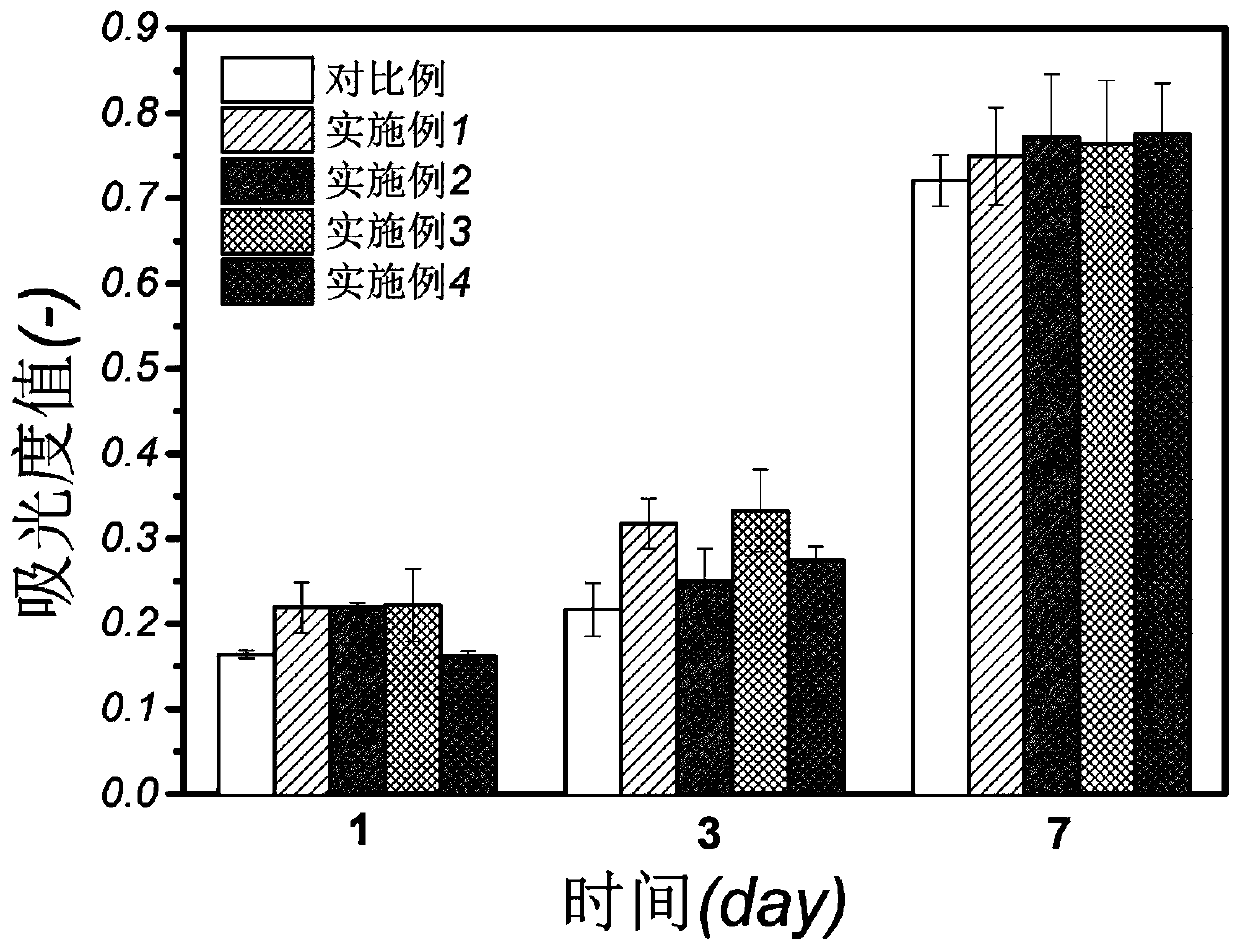
3D printing fibroin/gelatin support used for cartilage repairing, and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and cartilage repair technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of unfavorable cell migration, adhesion and growth, no cell adhesion sites, poor mechanical properties of gelatin, etc., to achieve The effect of simple preparation process, easy source, high compressive modulus and compressive fatigue resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1) Printing material preparation
[0034] 1.1) Preparation of tyramide-grafted modified gelatin: prepare 500ml of 50mM morpholineethanesulfonic acid buffer, add 10g of gelatin powder, stir at 50°C, and fully dissolve. Add 5g of tyramine hydrochloride, stir and dissolve fully; after the solution is cooled to room temperature, add carboxyl activator N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodi Imine hydrochloride 0.37g / 0.11g, to activate the carboxyl group on the gelatin molecular chain, react at room temperature for 12h; put the reaction product into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10000-12000, and dialyze for 4 days under a deionized water environment. Finally, the water was removed by a freeze dryer to obtain a white spongy modified product, which was stored in a moisture-proof cabinet for future use.
[0035] 1.2) Preparation of silk fibroin solution: add 4g of degummed silk to a beaker, then add 20ml of 9.3mol / l lithium bromide...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1) Printing material preparation
[0042]1.1) Preparation of tyramide-grafted modified gelatin: prepare 500ml of 50mM morpholineethanesulfonic acid buffer, add 10g of gelatin powder, stir at 50°C, and fully dissolve. Add 5g of tyramine hydrochloride, stir and dissolve fully; after the solution is cooled to room temperature, add carboxyl activator N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodi Imine hydrochloride 0.37g / 0.11g, to activate the carboxyl group on the gelatin molecular chain, react at room temperature for 12h; put the reaction product into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10000-12000, and dialyze for 4 days under a deionized water environment. Finally, the water was removed by a freeze dryer to obtain a white spongy modified product, which was stored in a moisture-proof cabinet for future use.
[0043] 1.2) Preparation of silk fibroin solution: add 4g of degummed silk to a beaker, then add 20ml of 9.3mol / l lithium bromide ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] 1) Printing material preparation
[0050] 1.1) Preparation of tyramide-grafted modified gelatin: prepare 500ml of 50mM morpholineethanesulfonic acid buffer, add 10g of gelatin powder, stir at 50°C, and fully dissolve. Add 5g of tyramine hydrochloride, stir and dissolve fully; after the solution is cooled to room temperature, add carboxyl activator N-hydroxysuccinimide and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodi Imine hydrochloride 0.37g / 0.11g, to activate the carboxyl group on the gelatin molecular chain, react at room temperature for 12h; put the reaction product into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 10000-12000, and dialyze for 4 days under a deionized water environment. Finally, the water was removed by a freeze dryer to obtain a white spongy modified product, which was stored in a moisture-proof cabinet for future use.
[0051] 1.2) Preparation of silk fibroin solution: add 4g of degummed silk to a beaker, then add 20ml of 9.3mol / l lithium bromide...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com