Method for extracting beta-chitin from squid cartilage
A squid cartilage and chitin technology, applied in the field of biomaterials, can solve the problems of imperfect preparation conditions, unclear product parameters, easy configuration changes, etc., achieve superior moisture absorption performance, avoid product degradation, and reduce preparation costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] A method for extracting β-chitin from squid cartilage, comprising: using alkali boiling and ultrasonic waves to perform a protein removal process on the above squid cartilage, using acid leaching to perform a calcium removal process on the above squid cartilage after protein removal, and, further A process of providing concentrated alkali and porogen to solubilize the material obtained from calcium removal; the deacetylation degree of the soluble β-chitin product obtained from the above soluble treatment is 92-96%, and the nitrogen content is 6-10%. The method is to prepare soluble β-chitin through deproteinization and inorganic salt removal process of squid cartilage under the action of ultrasonic-assisted extraction, and then deacetylation reaction with concentrated alkali. The extraction process is simple and easy to operate, and the time is short. The amount of reagents is small, the raw materials are cheap and easy to obtain, the finished product has a high degree o...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for extracting β-chitin from squid cartilage, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0035] (1) After washing and drying the squid cartilage, crush it to 150 mesh fibrous powder;
[0036] (2) Add a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 8wt% to the fibrous powder at a ratio of 1:6.5 to the ratio of solid to liquid, and keep it warm for 120 minutes at a temperature of 100 ° C. During this period, an ultrasonic wave with a power of 800 W is introduced every 20 minutes. , the single introduction time is 20min, until the alkali boiling is completed, then remove the solvent, wash the precipitate with water until neutral, and set aside;
[0037] (3) Add a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 5.5wt% to the precipitate obtained in step (2) at a ratio of 1:10, soak for 5.5 hours at a temperature of 35°C, and wash with distilled water after soaking to neutral, then repeat the acid leaching operation once, and the decalcified product is...
Embodiment 3
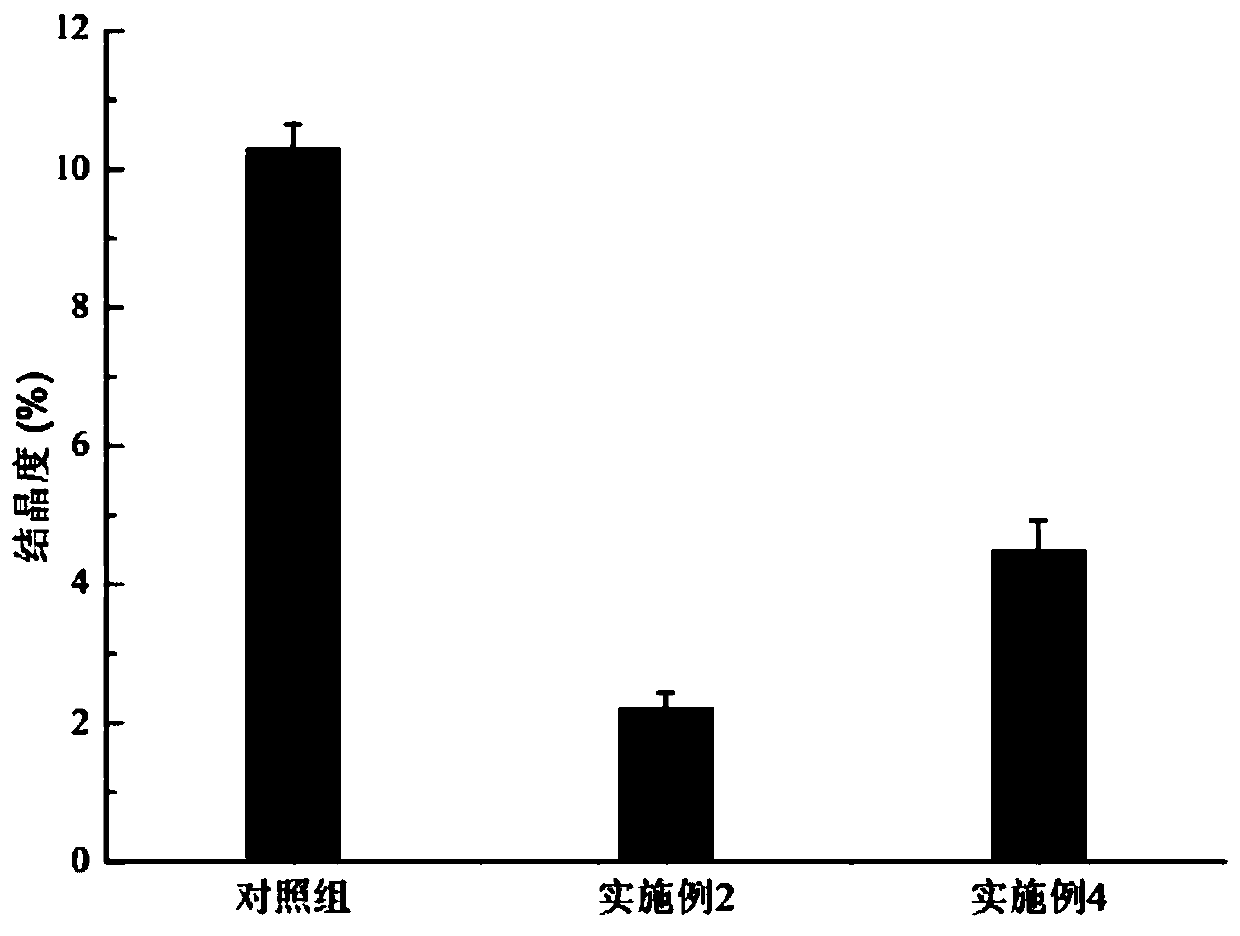
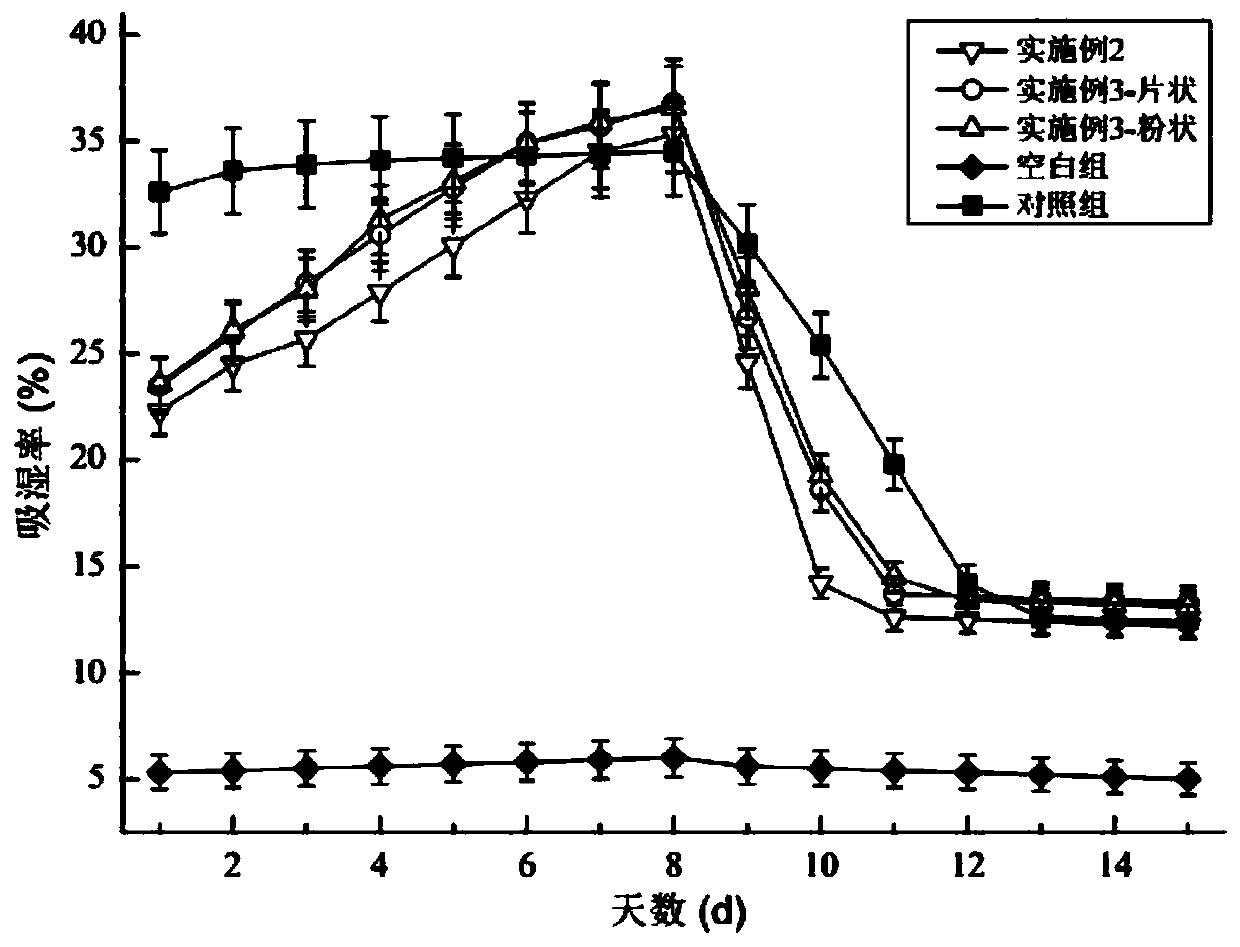
[0040] The difference between this embodiment and Example 2 is only that the lye used in the protein removal process is a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 8wt%, and the solid-liquid ratio of squid cartilage and lye is 1:4; the sodium hydroxide solution used 0.02-0.08 wt% of barbituric acid and 0.05-0.15 wt% of 4-methylguaiacol are also dispersed in it. The above-mentioned barbituric acid and 4-methylguaiacol can combine and remove the hydration electrons generated in the system under the action of ultrasonic waves, avoiding the recombination of hydration electrons and hydroxyl radicals, so as to improve the attack of chitin by hydroxyl radicals. The binding bond with protein makes the binding site between chitin and protein loose, can accelerate the degradation and separation of chitin and protein, can not only reduce the consumption of alkali, but also increase the purity of chitin, and the other two can be combined with The sugar rings connected to carbon at...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com