Automatic extraction method of cell components
An automatic extraction and cell technology, which is applied to the device for automatic separation of protein and subcellular structure in animal and plant cells, and in the field of multi-sample batch processing, can solve the problems of subcellular structure destruction, excessive homogenization, and manual operation. Achieve the effect of uniform cell crushing, avoiding differences, and saving manpower
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
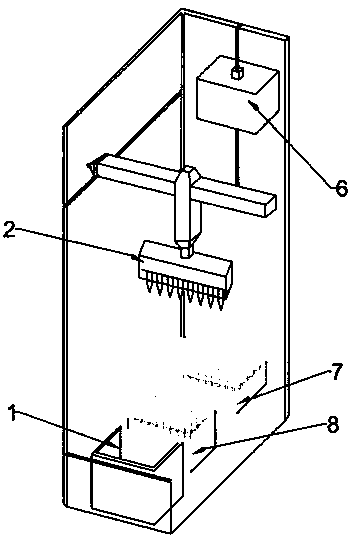
[0041] Such as Figure 1~3 As shown, a method for automatic extraction of cell components, the instrument used in the method includes an automatic extraction device for cell components, and the reagents used include sensitizers and a series of cell protein extracts;
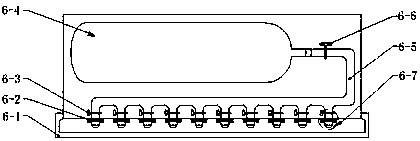
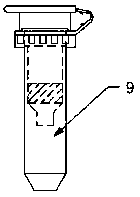
[0042] The automatic cell component extraction device includes: a pipetting system, a filtration system, a cooling system, and an automatic control system. The cooling system provides a low temperature of 0-4°C for the pipetting system and / or the filtration system, wherein the automatic control system is respectively Connect with pipetting system, filter system, cooling system; Described filter system includes: include filter tube placement box 7, ventilation pressure supply system 6, filter tube 9, wherein filter tube 9 includes filter column 9-3, collection tube 9- 1. The filter column 9-3 includes a filter element 9-2. The filter element 9-2 breaks up the cells with cell membrane sensitization and filters out ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2 Extraction of human liver cancer cell total protein
[0057] Collect 5×10 per well 6 HepG2 cells were washed with cold PBS. Add about 200 μL of cell sensitization solution to each well, add it to the cell sample, mix well, and add it to the sample tank. Put the corresponding filter tube in the hole of the filter tube placement box. The filter element is made of sintered polytetrafluoroethylene particles with an average particle size of 50 μm, a porosity of 45%, and an average pore size of 30 μm. Select the gas injection port and the sample tank.
[0058] Start the automatic extraction program, and after 5 minutes of low-temperature incubation at 0-4°C, the row-type pipette moves to the top of the pipette tip placement box, and moves down to insert the pipette tip. Move to the sampling tank, draw 200 μL of cell suspension, then move to the filter tube placement box, add to the filter tube, and return the pipette to its original position. The ventilation an...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3: Extraction of human liver cancer membrane protein
[0061] Collect 5×10 per well 6 HepG2 cells were washed with cold PBS. Add about 200 μL of membrane protein sensitization solution to each well, add it to the cell sample, mix well, and add it to the sample tank. Put the corresponding filter tube in the hole of the filter tube placement box. Select the air nozzle and the sample tank.
[0062] Start the automatic extraction program, and after 10 minutes of low-temperature incubation at 0-4°C, the row-type pipette moves to the top of the pipette tip placement box, and moves down to insert the tip. Move to the sampling tank, draw 200 μl of the mixed sample, then move to the filter tube placement box, add the sample to the filter tube, and return the pipette to its original position. The ventilation and pressure supply system moves down, the air nozzle and the filter column are closed, and the air nozzle ejects pressurized gas, so that the cell suspension tre...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com