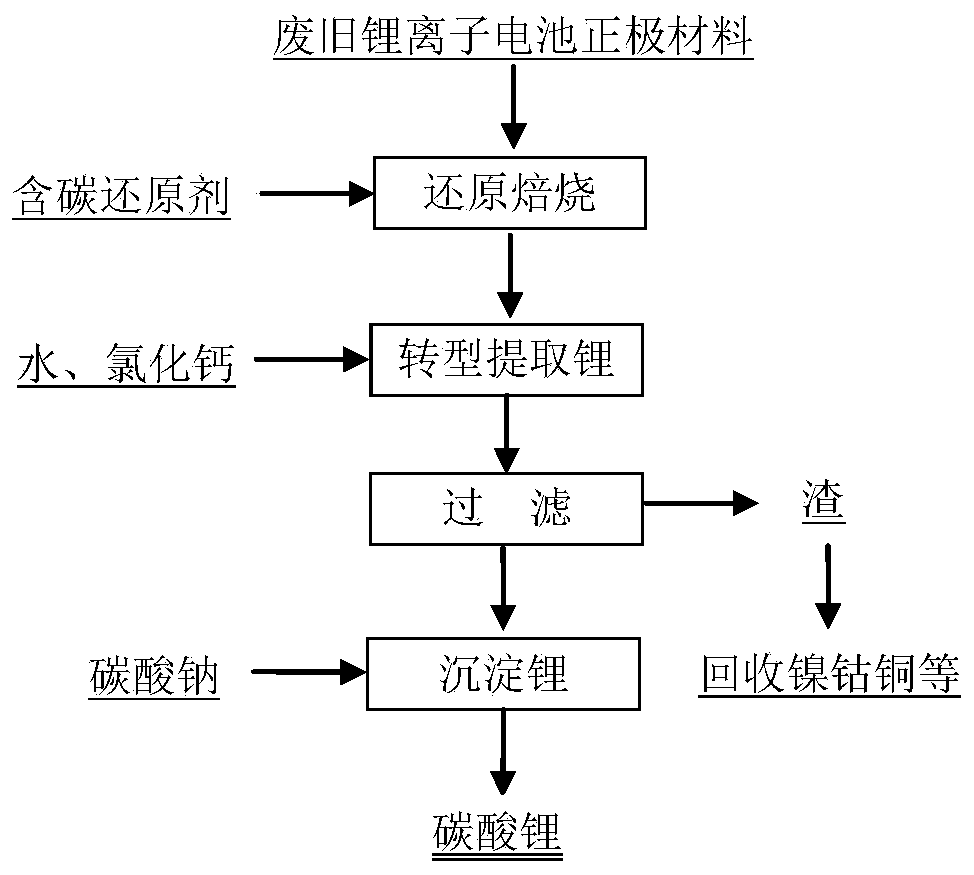
Method for extracting lithium and nickel cobalt from waste lithium ion battery step by step
A lithium-ion battery and lithium extraction technology, which is applied in battery recycling, process efficiency improvement, recycling technology, etc., can solve problems such as the difficulty in completely removing nickel, cobalt, iron, manganese and aluminum impurities, affecting the purity of lithium salt products, and high concentration of sodium ions , achieve the effect of avoiding disposal and environmental problems, shortening the lithium recovery process, and simplifying the recovery process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
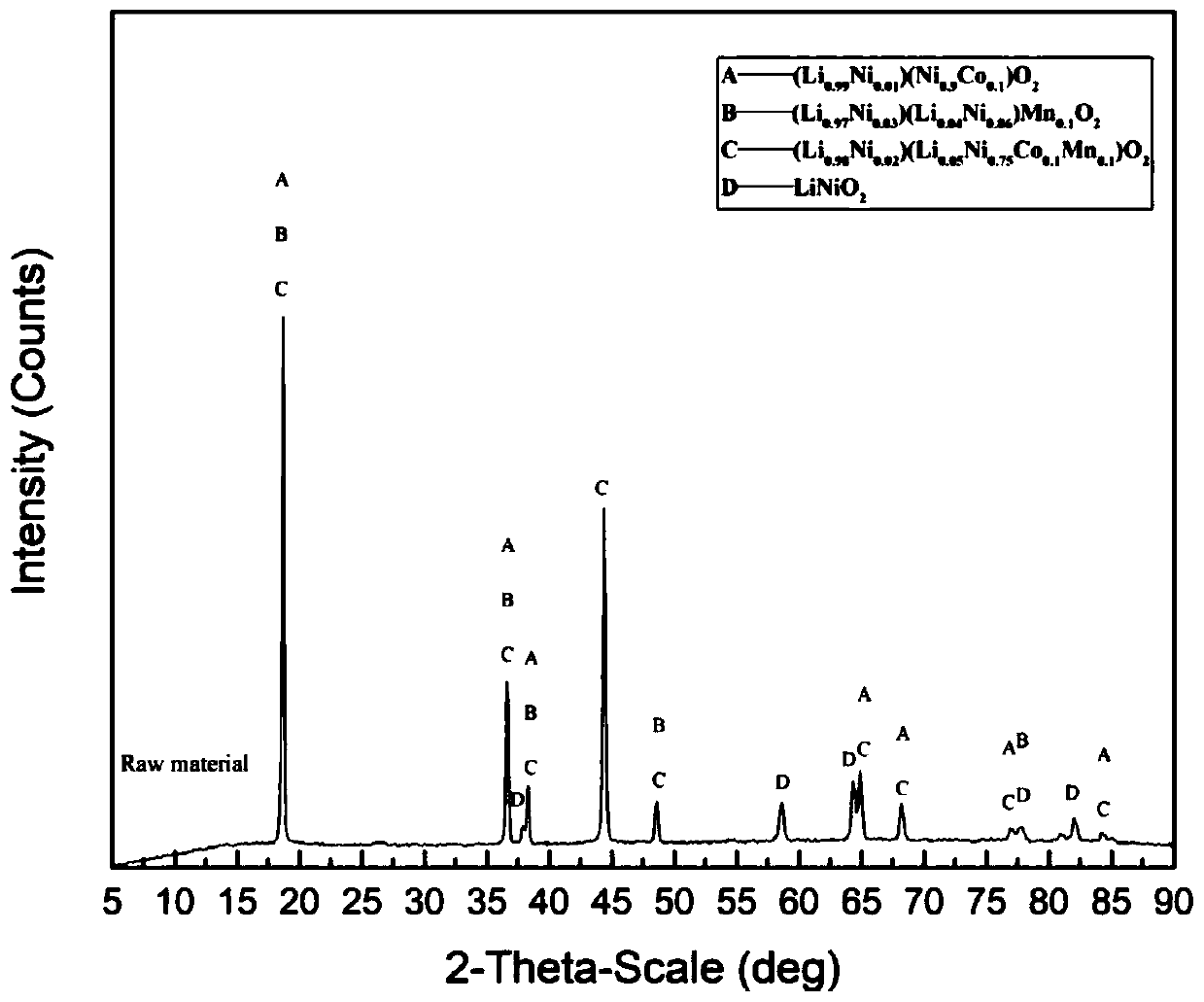
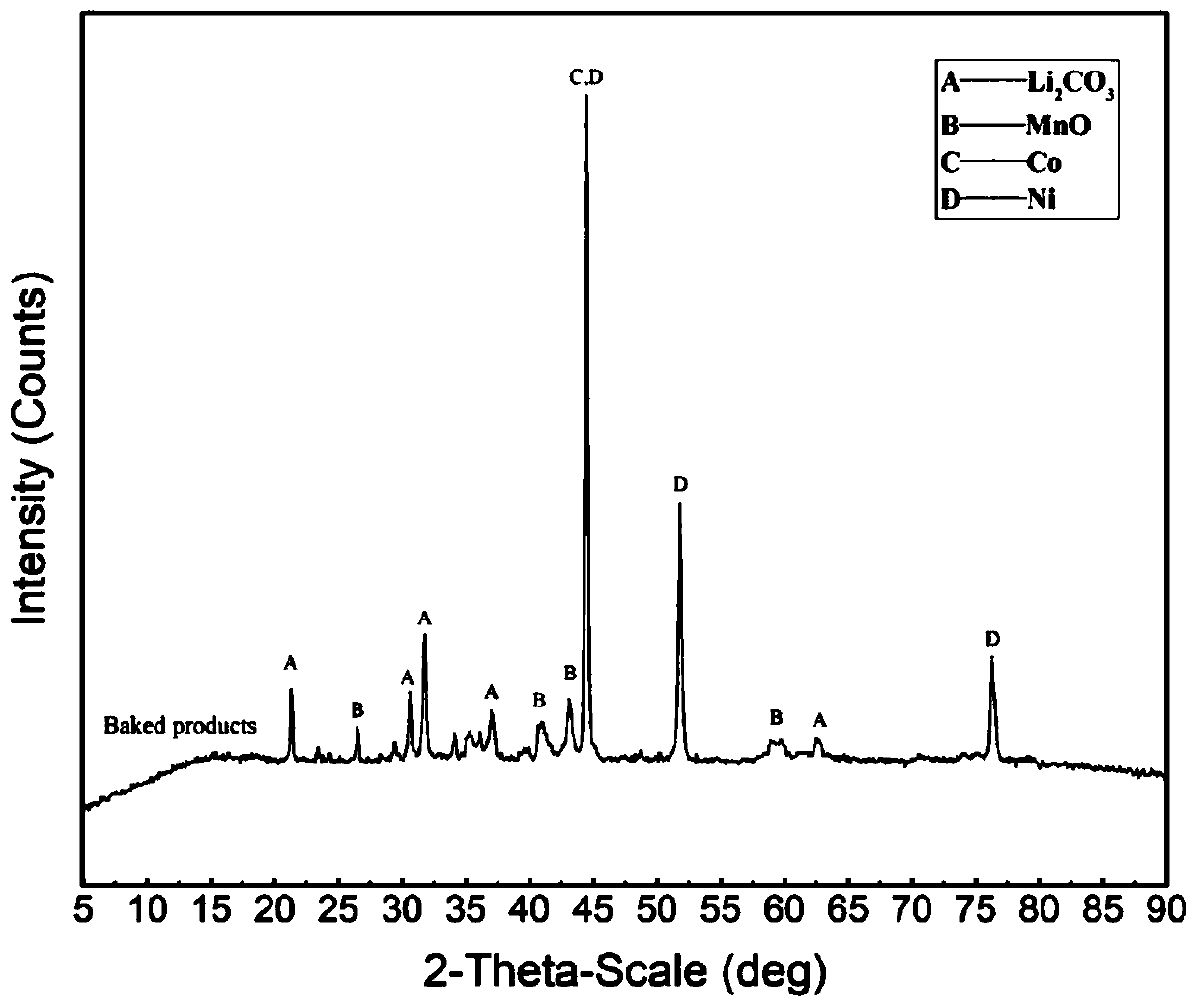
[0050] The nickel-manganese-manganese-cobaltate lithium positive electrode material obtained from dismantling, crushing and screening of waste lithium-ion batteries is reduced and roasted with carbon monoxide at 500-1000°C to obtain calcined sand; the calcined sand is added to a dissolution mill, mixed with water and mixed An appropriate amount of calcium chloride is added as a transformation agent, so that the lithium carbonate in the calcined sand is transformed into calcium carbonate, and the lithium is extracted into the solution. The amount of calcium chloride added is 0.8 times the molar number of lithium in the calcine, the amount of water added is 1 to 4 times the mass of the calcine, the temperature for lithium transformation is 20-100°C, and the slurry is separated from solid and liquid , to obtain lithium-containing solution and transformation slag. figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 They are the XRD patterns of positive electrode material, calcined sand, and transi...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The lithium cobalt oxide positive electrode material obtained from the dismantling, crushing and screening of waste lithium-ion batteries is reduced and roasted with coke powder at 850°C to obtain calcined sand; the calcined sand is added to the stirring mill, and water and an appropriate amount of milk of lime are added Carry out transformation to extract lithium, the amount of calcium chloride is added according to 0.6 times the molar number of lithium in the calcine, the amount of water is added according to 2 times the mass of calcine, the temperature of transformation and extraction of lithium is 25 ° C, and the slurry is solid-liquid Separate to obtain lithium-containing solution and transformation slag.
Embodiment 3
[0054] The nickel cobalt lithium manganese oxide positive electrode material obtained from dismantling, crushing and screening of waste lithium-ion batteries is reduced and roasted with coal powder at 800°C to obtain calcined sand; add calcined sand to the dissolution mill, and add appropriate amount of water and lime Carry out grinding transformation, the amount of lime added is 0.6 times the molar number of lithium in the calcine, the amount of water is added according to 2 times the mass of the calcine, the temperature for transforming and extracting lithium is 25°C, and the transformed slurry is solidified liquid separation to obtain lithium-containing solution and transformation slag. An appropriate amount of lithium phosphate is added to the obtained lithium-containing solution, stirred and reacted for a period of time, and filtered to obtain a pure lithium solution. Then add an appropriate amount of sodium carbonate solution into the pure lithium solution, stir and filt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com