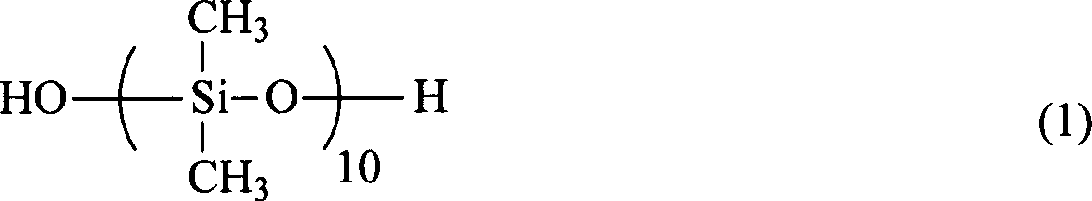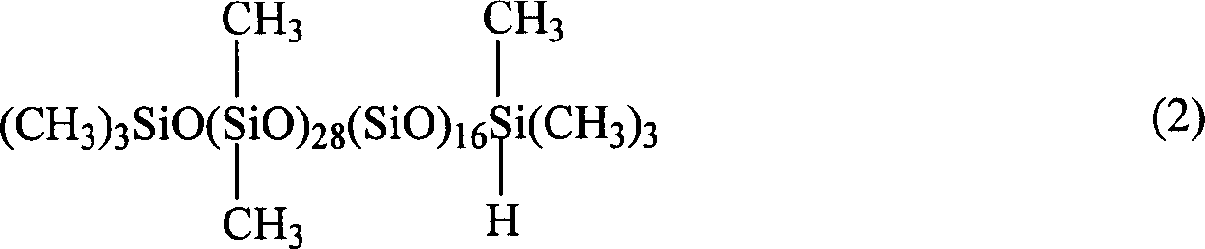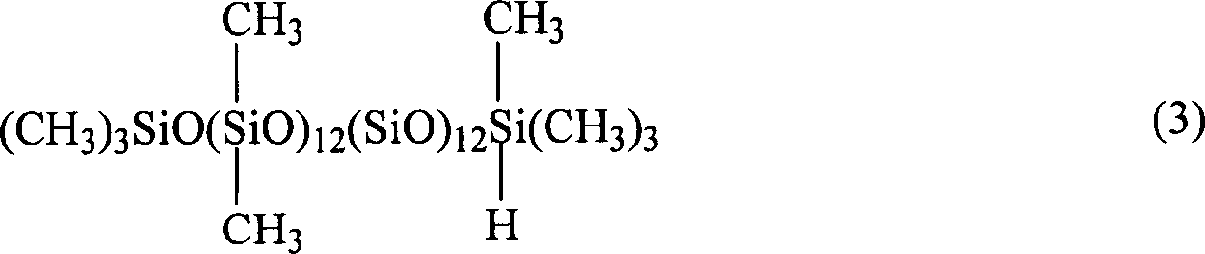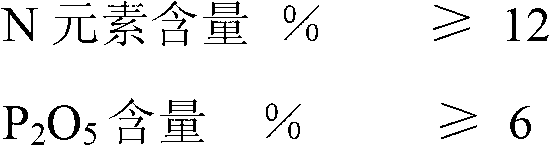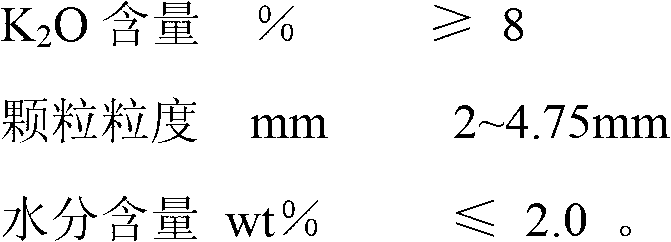Patents
Literature
180 results about "Dusting powders" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermal pressed silicon rubber sheets and manufacture thereof
InactiveCN1680506AAvoid bondingLow costFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsDusting powdersSilicon dioxide
The invention provides a silicone rubber sheet for thermocompression bonding which does not stick the periphery without dusting powder, does not adhere to an anisotropic electrically conductive adhesive, is excellent in surface releasing properties and durability, is provided with flexibility, and is inexpensive, and to provide a method for manufacturing the same. The silicone rubber sheet for thermocompression bonding is manufactured by providing the second silicone rubber layer prepared by molding and curing a composition comprising (F) an organopolysiloxane, (G) a silicone powder, preferably, (H) a carbon black with a volatile content of <=0.5 mass% or (I) a fine powder silica with a specific surface area of >=50 m2 / g, and (J) a curing agent, on one face or both faces of the first silicone rubber layer prepared by molding and curing a composition comprising (A) an organopolysiloxane with an average degree of polymerization of >=200, (B) a carbon black with a volatile content of <=0.5 mass%, (C) a fine powder silica with a specific surface area of >=50 m2 / g, (D) one or more selected from metals, metal oxides, metal nitrides, or metal carbides, and (E) a curing agent.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
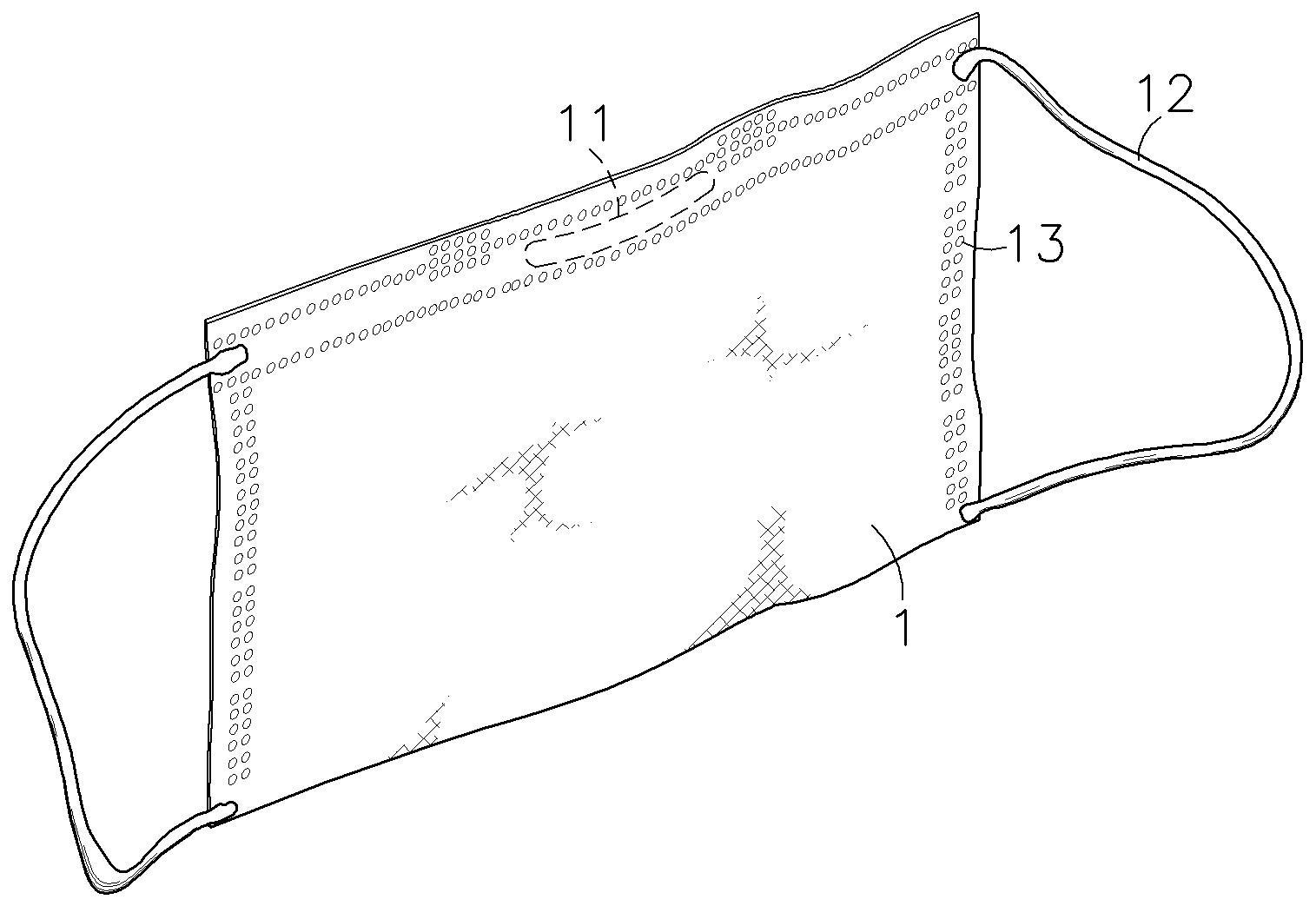
Face mask structure
InactiveUS20090084384A1Water absorptionEliminate odorBreathing filtersBreathing masksFiberDusting powders
A face mask structure, which includes an outer protective layer prepared from a water-repellent non-woven fabric; an inner protective layer prepared from a hydrophile non-woven fabric; a filter layer prepared from a static high-density fiber material for filtering microbes and dust powder, and sandwiched between the outer and inner protective layers; and a compound layer treated with a multiple functionalize carboxylic acid derivative that is a product from a chemical reaction between a cyclodextrin complex and a multiple functionalize carboxylic acid. The cyclodextrin complex can be a complex of cyclodextrin and an essential oil, antibiotic agent, or mosquito repellent agent.
Owner:CENT HEALTHCARE TECH
Nanometer silicon carbide-series infrared radiation coating and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of far infrared energy-saving coating used for a high-temperature industrial furnace, which particularly relates to a nanometer silicon carbide-series infrared radiation coating and a preparation method thereof. The coating is composed of a powder radiation material, a binding material, a slurry accessory ingredient and water, wherein the mass ratio of the waterto the powder radiation material is (0.5-2):1; the binding material is 10-30% of the total mass of powder radiation material; the slurry accessory ingredient is 0.1-3% of the total mass of powder radiation material; and the powder radiation material is composed of nanometer silicon carbide powder, zirconia powder, chromium hemitrioxide powder, ferric oxide powder, nickel oxide powder, bentonite powder and siliceous dust powder. The infrared energy-saving radiation coating disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high radiation coefficient and excellent thermal shock resistance. After high-temperature sintering, a sintering layer is formed on a refractory brick or cellucotton, the sintering layer can be firmly adhered on the surface of the lining of a kiln to perform the energy-saving effect on increasing radiant heat utilization and reducing heat loss.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method of producing forsterite refractory
A method for producing forsterite refractory is characterized by comprising: a. mixing the raw magnesite flotation tailing or magnesite shaft kiln dust removing powder, light burning magnesite powder and cabosil, wherein the weight ratio Mgo / SiO[2] is 1.342-1.476; b. according to the weight ratio, uniformly mixing 80-100 portions of mixed materials obtained in step a and 0-20 portions of burnable lost property, additionally with 30-70 portions of water, producing briquette; drying the briquette obtained in step b at 15-50 DEG C for 3-24 hours, drying at 110 DEG C for 12 hours, burning at the oxidative atmosphere; keeping warm at 500-650 DEG C for 2-3 hours, 1500 DEG C for 3-5 hours. The invention uses the industrial waste to produce the forsterite refractory, greatly reduces the production cost of the forsterite refractory, decreases the dust pollution and improves the ecologic environment.
Owner:海城华宇耐火材料有限公司
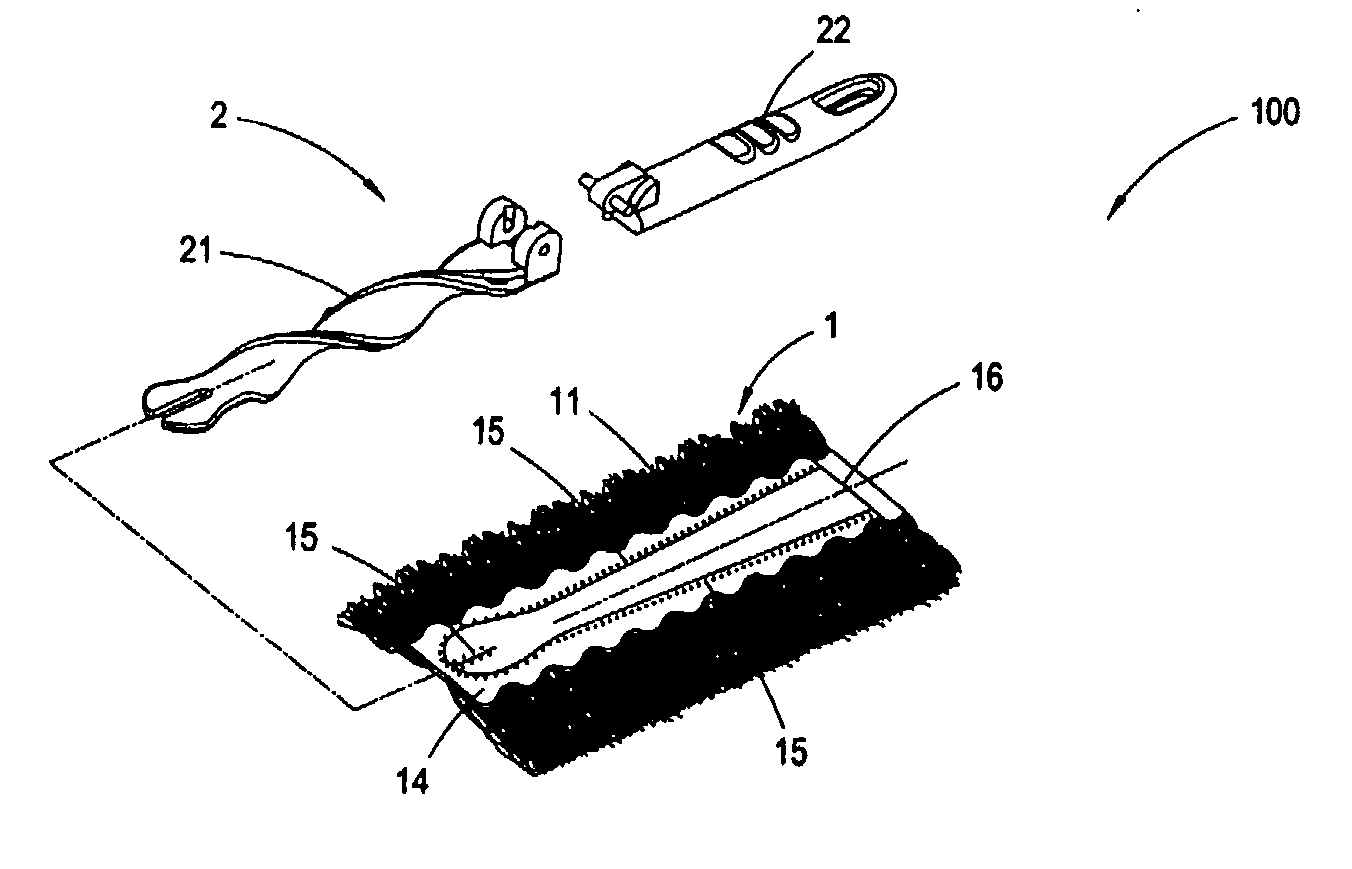
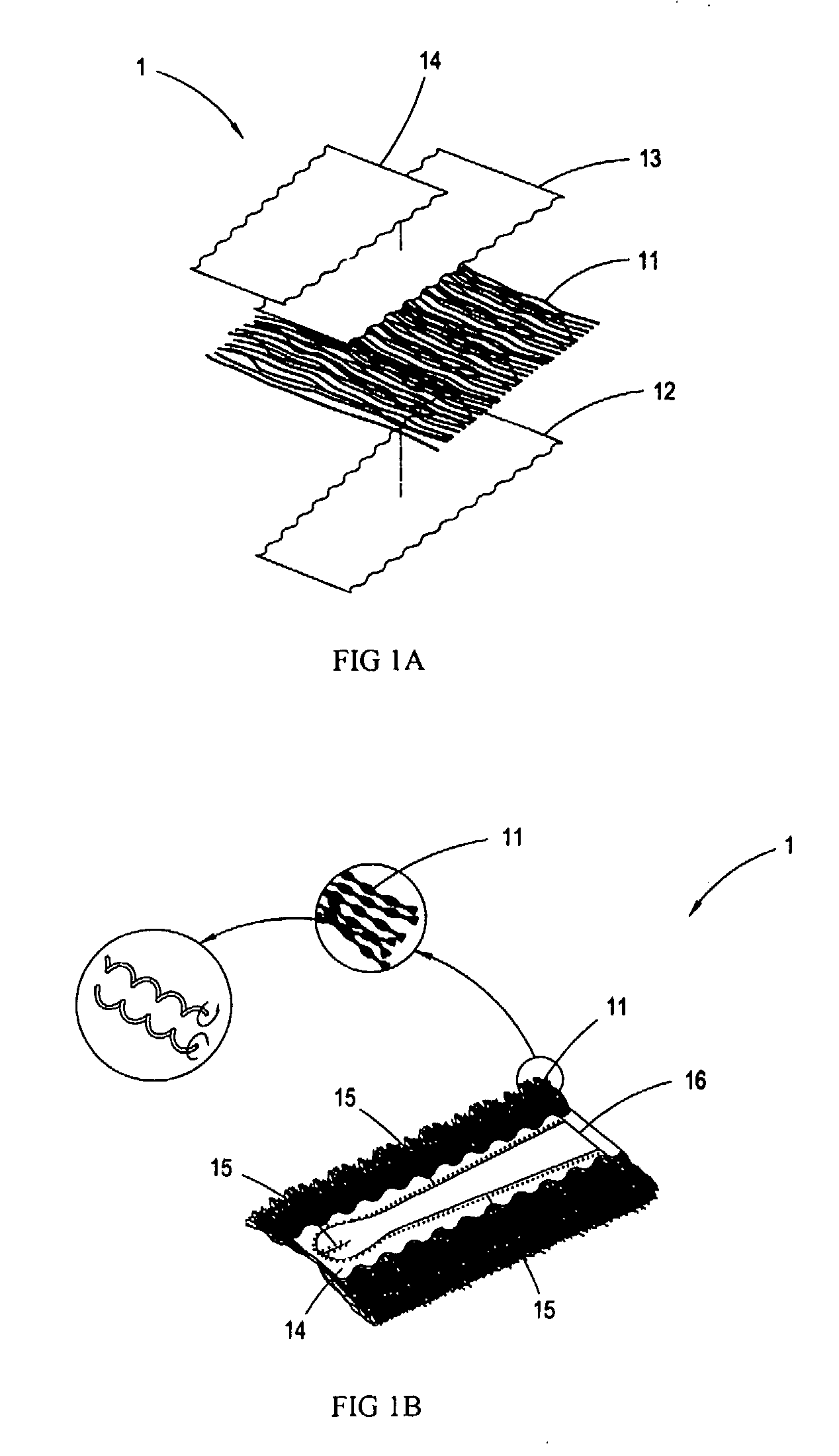
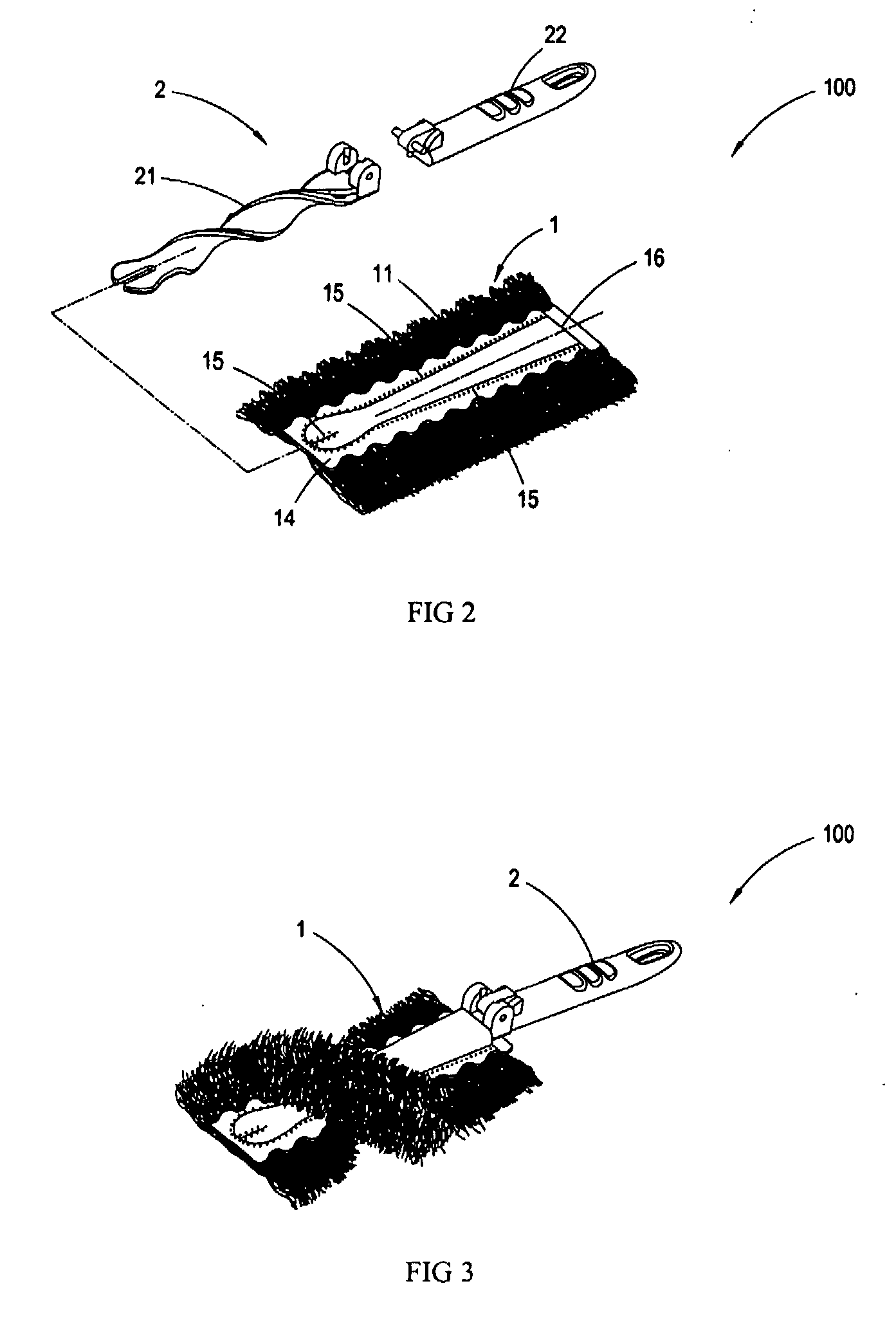
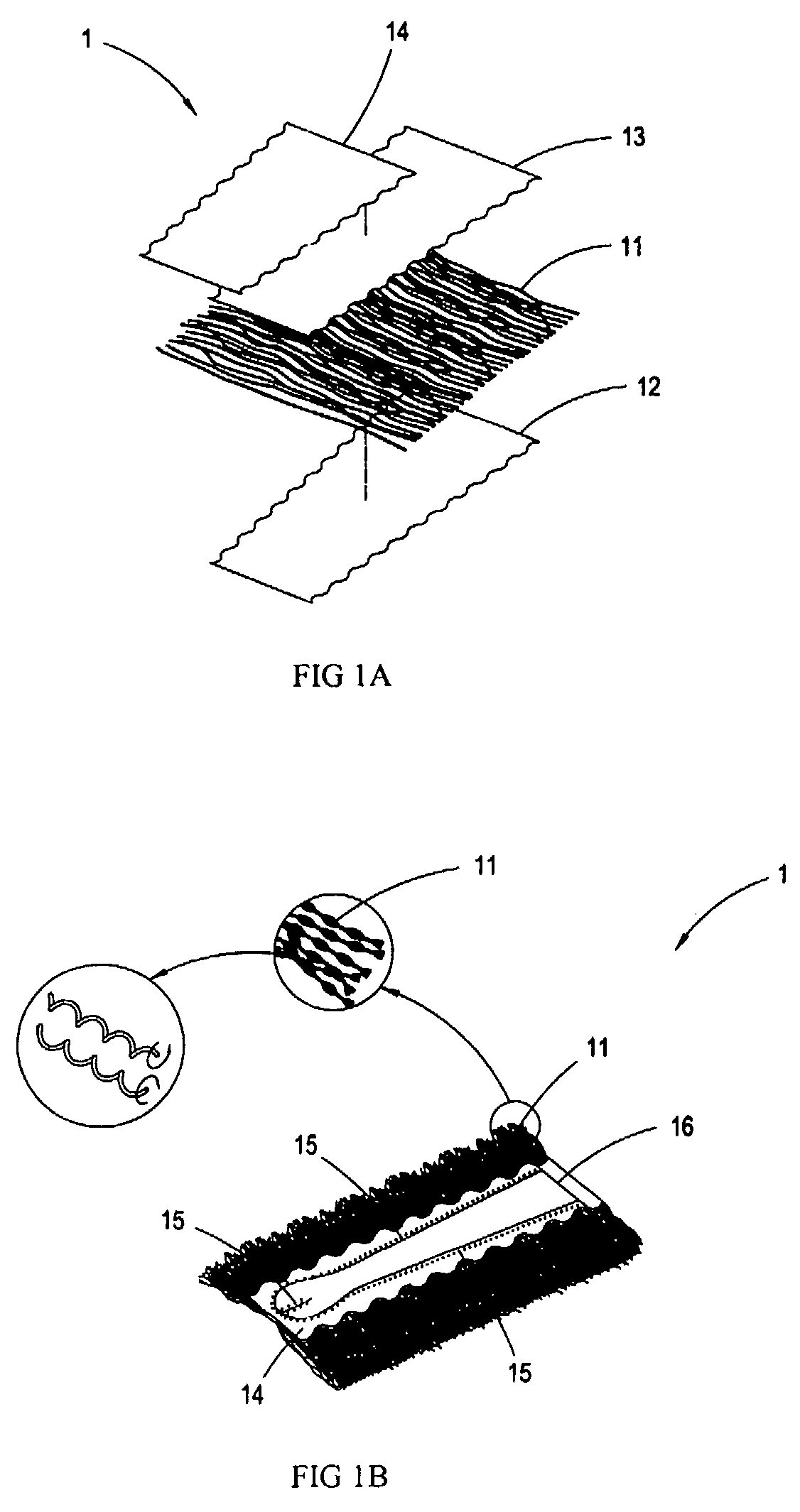
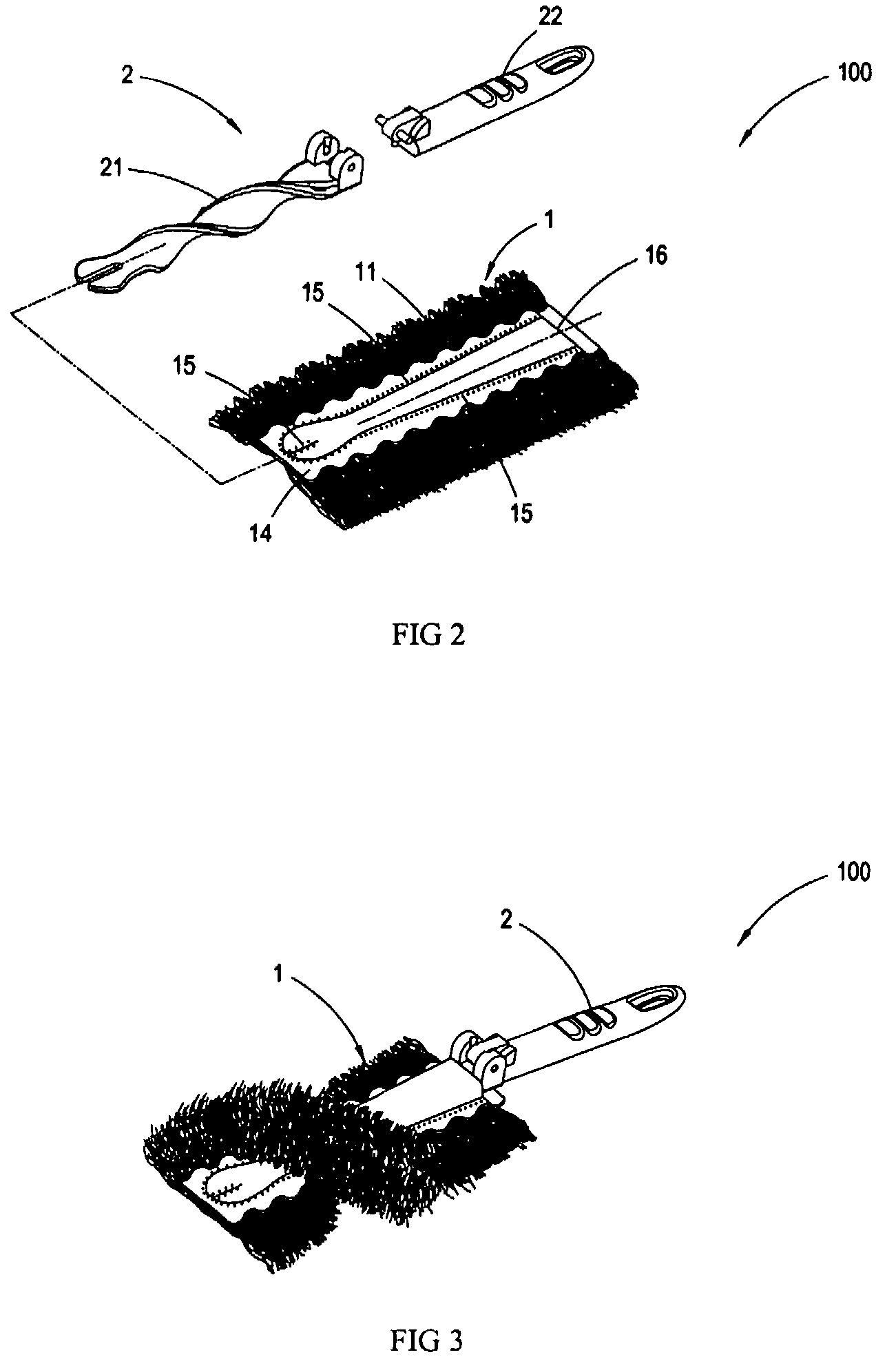
Standing duster article
InactiveUS20070033761A1Reduce raiseImprove dust resistanceBoard cleaning devicesCarpet cleanersYarnDusting powders
A standing duster article consisting of a dusting portion and a spiral handle, wherein the dusting portion is comprised of a segmented intermingled yarn layer, a hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer, a smooth nonwoven fabric layer, and a nonwoven / woven fabric layer; the segmented intermingled yarn layer is interleaved between the hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer and the smooth nonwoven fabric layer; the nonwoven / woven fabric layer is further superimposed on the smooth nonwoven fabric layer; a hot-pressing process is carried out to fuse the segmented intermingled yarn layer, the hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer, the smooth nonwoven fabric layer, and the nonwoven / woven fabric layer; the resulted lamination after fusion is cut by a cutting apparatus, so as to generate a slit in the middle to form the dusting portion which is easy to be folded to form two elongated openings; and a spiral end of the spiral handle is inserted into the openings to form the duster article with the spiral dusting portion. Since the intermingled yam of the segmented intermingled yam layer used in the present invention comprises alternate loose and tight segments, the fibers on the loose segments of the intermingled yarn are capable of capturing more dust powder. The alternate loose and tight segments are formed by twisting the intermingled yarn, such that each of the bundles of the intermingled yam is effectively bound and will not tangle with each other. Further, it is easy to install or remove the spiral handle in or from the dusting portion by such design.
Owner:YANG YA CHING
Dedusting dry powder recycling process
InactiveCN101224363ASimplify the recycling processNo spreading problemHuman health protectionDispersed particle filtrationDusting powdersMaterial scattering
The invention relates to a dust-removal dry powder recycling process. The process procedure consists of dust-removal ash hoppers, dust powder transferring devices, exhaust collecting cavities, wet ball machines and sealed transferring devices of each dust removal points of smelters or ironworks. The process includes three steps: dusts removing-transferring, dusts collecting and wet ball transferring, i.e. a set of dust powder air-transferring device is arranged below the dust-removal ash hopper of the dust catcher; compressed air is adopted for transferring the dust through a sealed transferring device into the dust collecting cavity far away, and then a ration feeding machine is adopted for transferring the dust to the wet ball machine; after wetting and balling by the wet ball machine, the finished small balls are finally transferred to a storing bin through a sealed transferring device as recycled materials for application. The invention adopts the novel dust disposal process of dust-removal dry powders to simplify the process procedure; a sealed state is guaranteed before wetting and balling and during the transferring process so as to avoid dust rising and material scattering; the recycling treatment is simple, thus saving investigation and manpower, and being environment-protective.
Owner:BAOSTEEL ENG & TECH GRP
Biomass fuel with good formability
InactiveCN103666620AStrong coagulationCompact structureSolid fuelsWaste based fuelFiberEnvironmental resistance
The invention relates to environment-friendly biomass fuel with good formability. The biomass fuel is renewable biomass fuel free of any harmful substance, which is prepared by mixing wood dust powder and an additive, wherein the additive is high clay having high viscosity and strong adsorptive power; and the biomass fuel is prepared by mixing the wood dust and the additive according to a ratio of 9:1. The high clay additive is beneficial to formation of wood dust particles, and the multiporous fiber-like structure of the high clay additive can adsorb tar in flue gas from a heating system in the biomass fuel processing course, thereby preventing the tar from being attached to a granulator and a chimney and further avoiding influencing the granulating effect. Besides, the additive also solves the problem that the tar is difficult to remove and clean.
Owner:广州金安源节能科技股份有限公司
Spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites
ActiveCN102515832AHigh strengthReduce energy consumptionCeramic materials productionCeramicwareDusting powdersExpanded clay aggregate
The invention discloses spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites. The key point of the technical scheme of the invention is that: the spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites consist of high-viscosity attapulgite clay powder, attapulgite clay tailing powder, fly ash, kaolin tailing powder, quartz sand tailing powder and wood dust powder. The spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites are prepared by mixing, pelletizing, baking, cooling, screening and packaging ingredients of the spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites. The spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites are spherical, are rough and firm on the surfaces, are provided with a large quantity of fine air holes, and are building ceramsites with light weight, high strength, low heat conduction coefficient, high refractability, high chemical stability, durability and high heat preserving and sound insulating performance. The spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites are produced by comprehensively utilizing fly ash and tailings. Resource utilization ratio is increased, waste is turned into valuable, and the environment is protected. The spherical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites are suitable for producing ceramsite concrete and heatpreserving and sound insulating materials.
Owner:NANGTONG HAODI ANTICORROSION EQUIP
Powder preparation method for induction heating and radio frequency plasma combined atomizing powder system
ActiveCN108161019AHigh purityPrevent purityAdditive manufacturing apparatusHigh pressureRadio frequency
The invention relates to a powder preparation method for an induction heating and radio frequency plasma combined atomizing powder system. The powder preparation method comprises the following steps that (1), raw materials are prepared and processed; (2), the system is pre-vacuumed and a protective atmosphere is established; (3), wire materials are straightened and conveyed; (4), high-frequency induction preheating is carried out; (5), radio frequency plasma melting is carried out; (6), powders are prepared by atomizing; (7), separation and dust removal are carried out; and (8), the powder size is graded. The powder preparation method for the induction heating and radiofrequency plasma combined atomizing powder system uses high purity metal wire material instead of the powders as the raw materials, so that the carrying of raw materials to adsorb gas and water is reduced; a technology of the high frequency induction heating combined with the radio frequency plasma smelting and gas atomization is adopted, during the whole process of heating, melting, and the gas atomization is free of pollution and impurities in the protective atmosphere, and the degree of superheat of liquid flow ordroplets is increased during the process of radio frequency plasma smelting; and high quality spherical powders can be obtained by adopting high pressure atomizing nozzles atomizing, and the yield ofmetal powders per unit time is increased.
Owner:北京金物科技发展有限公司
Method for manufacturing recombined tobacco leaves through paper-making mode
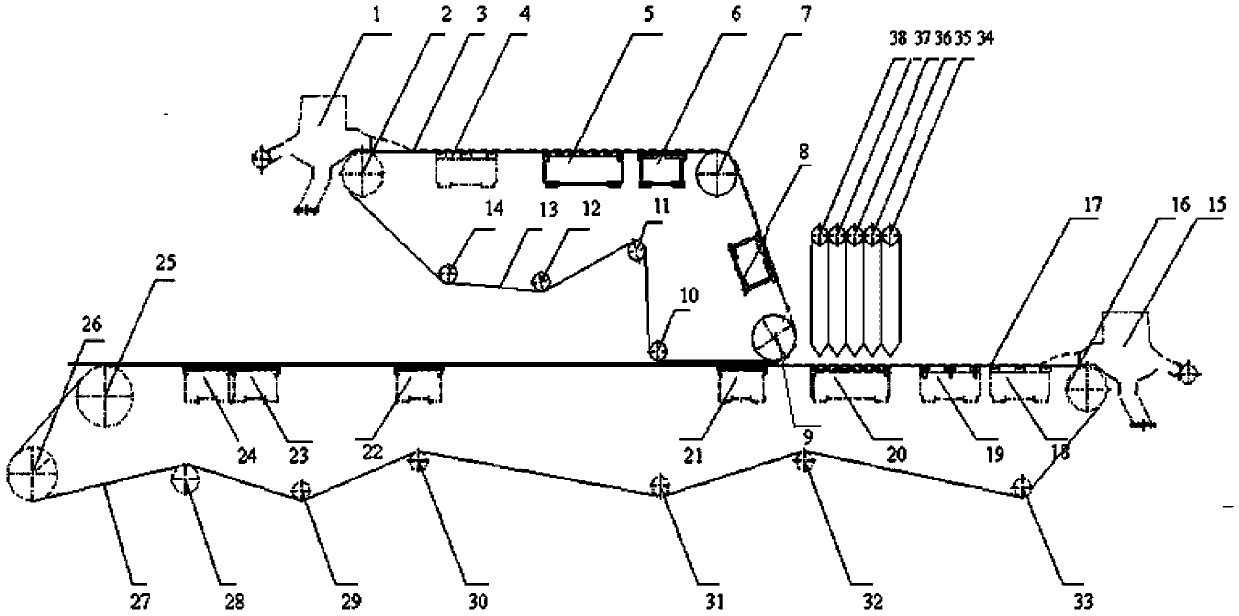
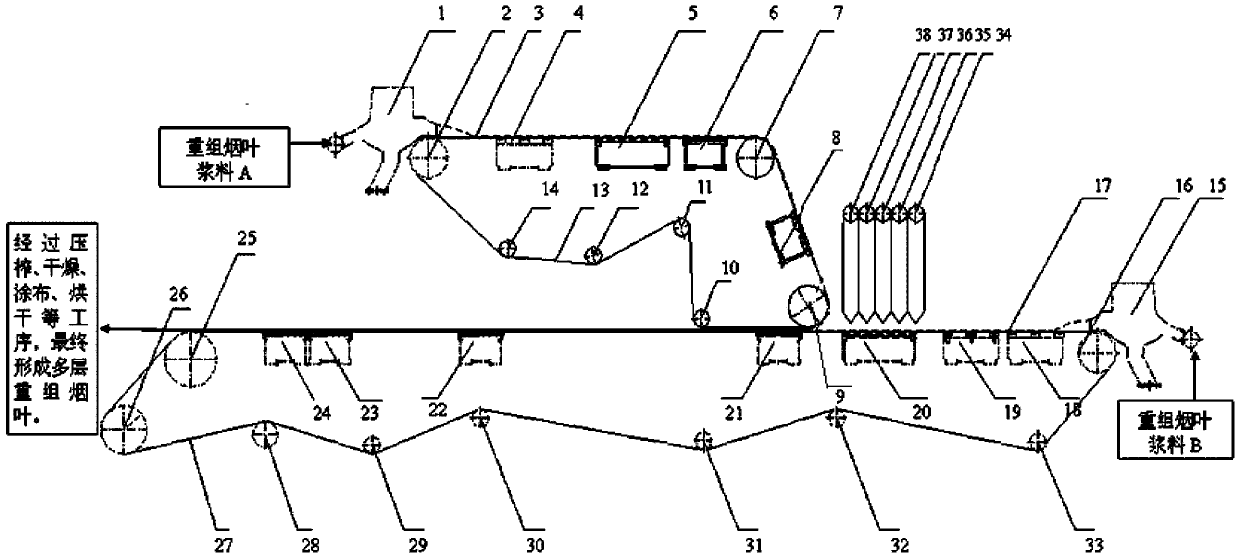
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing recombined tobacco leaves through a paper-making mode. The method is characterized in that two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices are adopted on a paper-making portion of a paper machine, namely, one is a bottom recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming device, and the other is a top recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming device, wherein the top recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming device is located on the top layer of the paper-making portion, the bottom recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming device is located on the bottom layer of the paper-making portion, and the two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices are arranged oppositely; a plurality of dusting devices with dusting powder quantity independently adjusted and controlled are arranged between the two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices, the dusting devices are successively arranged in the lengthwise direction of the paper-making portion on the bottom layer of a paper machine, the two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices convey recombined tobacco leaf pulp out in a flowing mode at the same time, the two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices are firstly independently formed in a flowing conveying mode to respectively form a wet substrate, and after the pulp flowing conveying substrates of the two recombined tobacco leaf substrate net portion forming devices are formed, the middle dusting devices are started. The method is scientific and reasonable, operation is convenient, and the bulk, the softness and the sensory quality of the recombined tobacco leaves through the paper-making mode can be adjusted according to requirements.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +1
Biological semi-organic fertilizer containing amino acid and making method thereof
InactiveCN105152781APromote growthGood physical propertiesFertilizer mixturesTrace element compositionDusting powders
The invention belongs to the technical field of fertilizer production and relates to biological semi-organic fertilizer containing amino acid and a making method thereof. Urea, monoammonium phosphate, potassium sulphate and bentonite are matched reasonably, amino acid mother liquor granules are adopted to form granulation master batch, aminated humic acid, medium trace element compositions, decomposed coal and amino acid mother liquor are blended to form a coating sizing agent used for primary coating of the granulation master batch, then a dusting powder agent is formed by microorganism bacterial liquid and calcium carbonate powder, a coating agent is formed by white oil, molasses and a mixture, and secondary coating is conducted in a coating machine to generate the biological semi-organic fertilizer containing amino acid. The biological semi-organic fertilizer containing amino acid has the efficiency of humic acid, amino acid, biological agents and the like and also has a slow-releasing function, effective constituents can be released slowly and orderly, fertilizer efficiency is remarkable, and production organization is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN DONGSHENGYANG COMPOUND FERTILIZER CO LTD
Powder filter device
InactiveCN102049402AAvoid pollutionDispersed particle filtrationDirt cleaningDusting powdersEngineering
The invention discloses a powder filter device for filtering the flying dust powder when a stereo forming mechanism runs. The powder filter device comprises a shell, a powder filter element, a reclaiming member and an air suction device, wherein the shell is provided with a suction port from which the dust powder is sucked; the powder filter element is arranged in the shell and used for partitioning the interior of the shell into a first space and a second space, wherein the suction port of the shell is communicated with the second space; the reclaiming member is arranged in the second space;and the air suction device is used for making the first space form a negative pressure state, guiding the dust powder sucked from the suction port into the second space, filtering the dust powder through the powder filter element and reclaiming the blocked powder in the reclaiming member.
Owner:MICROJET TECH
Coated Paper for Sheet-Fed Offset Printing
InactiveUS20080261021A1Simple printing processShorter reprinting time timeCylinder pressesNon-fibrous pulp additionDusting powdersPrinting press
The specification pertains to a single or multiple coated printing sheet in particular but not exclusively for sheet-fed offset printing with an image receptive coating layer on a paper substrate. The printing sheet has the property that it can be printed in an offset printing process without spraying a fine powder, usually called offset powder or dust powder, on the sheet as it comes off the press to prevent the ink from transferring to the back side of the next sheet. Also irradiative (UV or IR) drying on the sheet fed press is not necessary and / or the use of overprint varnish is not required. In addition to that, unexpectedly short times until reprinting and converting can be achieved. Furthermore methods for making such a printing sheet and uses of such a printing sheet are disclosed.
Owner:SAPPI NETHERLANDS SERVICES
Preparation method for special slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer for corn
ActiveCN103058751AMeet nutrient needsIncrease productionFertilizer mixturesDusting powdersStearic acid
The invention provides a preparation method for a corn-special slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer, and belongs to the preparation of a mixture of a plurality of fertilizers and components without special fertilizer efficiency. The corn-special slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer is prepared by taking compound fertilizer particles as fertilizer cores, then performing coating and dusting powder treatments. The compound fertilizer particles are prepared by the following raw materials by mass: 15 to 45 parts of urea, 5 to 40 parts of ammonium sulfate, 20 to 35 parts of potassium sulfate, 15 to 35 parts of a mixed phosphate fertilizer, 0.1 to 0.5 part of a zinc and iron additive, 7 to 10 parts of a granulating auxiliary agent and a proper amount of water. The preparation method for the compound fertilizer comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a compound of a potash fertilizer and a nitrogen fertilizer; (2) preparation of the mixed phosphate fertilizer; (3) preparation of mixed particles of the components of the compound fertilizer; (4) coating with stearic acid; (5) powder spreading of a modified zeolite powder material; and (6) screening, metering, quality inspection and packaging of qualified fertilizer. The invention provides the preparation method for the corn-special slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer which has overall nutrients and excellent slow releasing performance, improves both output and quality of corn, and saves resources and protects the environment.
Owner:SHIKEFENG CHEM IND
Method for producing antiseptic oriented strand board through full-eucalyptus leftover materials
InactiveCN106239689AWhite colorGood film formingWood veneer joiningDomestic articlesDusting powdersOptoelectronics
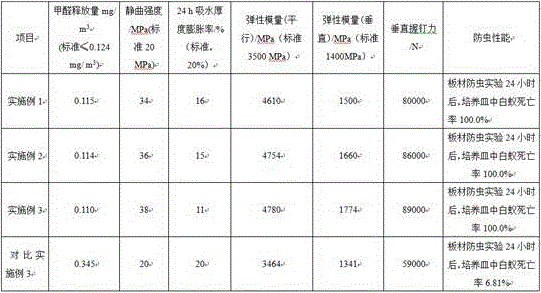
The invention provides a method for producing an antiseptic oriented strand board through full-eucalyptus leftover materials. The method comprises the procedures of material preparing, drying, peel and impurity removing, sorting and storing, surface layer and core layer gluing, classified paving, preheating press forming, sanding facing and the like. A surface layer is coated with an isocyanate wood dust powder composite adhesive, a core layer is coated with an antiseptic composite urea-formaldehyde resin adhesive, and core layer wood shavings are of three-layer structures including a core layer middle layer, a core layer upper surface layer and a core layer lower surface layer. The core layer middle layer is longitudinally laid, and the core layer upper surface layer, the core layer lower surface layer and the surface layer are transversely laid. According to the oriented strand board prepared through the method, the static bending intensity in the parallel direction ranges from 34 MPa to 38 MPa, and the parallel elasticity modulus ranges from 4,610 MPa to 4,780 MPa; and the vertical elasticity modulus ranges from 1,500 MPa to 1,774 MPa, the water absorption thickness swelling rate in 24 h ranges from 11% to 16%, and the vertical nail holding force reaches up to 89,000 N. Meanwhile, through adding of an antiseptic agent, the problem that panels are prone to suffering from corrosion of wood-destroying fungi, moulds and white ants is thoroughly solved, and the service life of the panels is prolonged.
Owner:广西横县新威林板业有限公司
Medical powder inhalation and application thereof
InactiveCN102058886AMeet the requirementsPromote healingAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDusting powdersMedical product
The invention relates to medical powder inhalation and application thereof. The medical dust powder inhalation mainly comprises a chitosan derivative, a latent solvent, a propellent and an inert substance as well as also possibly comprises optional functional substances of haemostatic, an antibacterial agent, analgesic and surfactant. The chitosan derivative powder, the latent solvent, the haemostatic powder, the antibacterial agent powder, the analgesic powder and the surfactant are placed into a reaction vessel, fully stirred at room temperature, uniformly mixed and dispersed to obtain a suspension; and the suspension, the propellent and the inert substance are simultaneously packed into subpackaged cans on an aerosol pressure excited filling and packing line to obtain the powder product. The invention also has obvious effects of stopping bleeding on a wound, relieving pain and speeding up repairing and healing of the wound besides the advantages of the traditional medical product, and has the advantages of stable quality, low cost, use convenience, no pollution to the atmosphere and high safety.
Owner:云南白药集团无锡药业有限公司
Standing duster article
InactiveUS7788759B2Reduce raiseImprove dust resistanceBoard cleaning devicesCarpet cleanersYarnDusting powders
A standing duster article consisting of a dusting portion and a spiral handle, wherein the dusting portion is comprised of a segmented intermingled yarn layer, a hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer, a smooth nonwoven fabric layer, and a nonwoven / woven fabric layer; the segmented intermingled yarn layer is interleaved between the hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer and the smooth nonwoven fabric layer; the nonwoven / woven fabric layer is further superimposed on the smooth nonwoven fabric layer; a hot-pressing process is carried out to fuse the segmented intermingled yarn layer, the hot-meltable nonwoven fabric layer, the smooth nonwoven fabric layer, and the nonwoven / woven fabric layer; the resulted lamination after fusion is cut by a cutting apparatus, so as to generate a slit in the middle to form the dusting portion which is easy to be folded to form two elongated openings; and a spiral end of the spiral handle is inserted into the openings to form the duster article with the spiral dusting portion. Since the intermingled yarn of the segmented intermingled yarn layer used in the present invention comprises alternate loose and tight segments, the fibers on the loose segments of the intermingled yarn are capable of capturing more dust powder. The alternate loose and tight segments are formed by twisting the intermingled yarn, such that each of the bundles of the intermingled yarn is effectively bound and will not tangle with each other. Further, it is easy to install or remove the spiral handle in or from the dusting portion by such design.
Owner:YANG YA CHING
Dam concrete and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101607808AIncreased durabilityImprove corrosion resistanceDusting powdersReinforced concrete
The invention discloses dam concrete and a preparation method thereof. The dam concrete is characterized by being prepared from the following materials: cement, water, sands, stones, siliceous dust powder, an air entraining agent rosinsoap and water reducing agent wooden-calcium, wherein the cement is selected from slag cement with 50-70 percent of slag mixing amount; the water is drinking water; the fineness modulus of the sands is greater than 2.5; the grain diameters of the stones are controlled within 150mm; the using amount of the siliceous dust powder is 5 percent of that of the cement; the mixing amount of the air entraining agent rosinsoap is 1 percent of the using amount of the cement; the mixing amount of the water reducing agent wooden-calcium is 0.5 percent of using amount of the cement; when the dam concrete is poured, a prefabricated reinforced concrete facing slab is used as a permanent moulding plate, and the dam concrete should prevent a construction gap from being arranged in a water level changing area, and the construction gap is sprayed with an epoxy adhesive. A high and large dam concrete structure member adopts layered water reducing for prepared concrete, 0.5 percent of the water is reduced by every 0.3m, and secondary vibration and secondary surface plastering measures are taken. The invention has the characteristics of high durability and strong corrosion resistance.
Owner:SINOHYDRO BUREAU 1 CO LTD
Powders having contact biocidal properties
ActiveUS20050250194A1Reduce solubilityLimited applicationBiocidePowder deliveryDusting powdersAqueous ethanol
Powders having contact biocidal properties comprise a polysacharide carrying atomic / metallic silver. The preferred polysaccharide is chitin, although other polysaccharides including chitosan, carboxymethyl celluloses and carrageenalls can be used. The chitin may be obtained from deproteinated crustacean shells without demineralisation, thus being admixed with calcium carbonate and other naturally occurring minerals present in the shells, and may be enzyme deacetylated. The powders of the invention can be used as biocidal dusting powders, formulated into pastes, gels, hydrogels, creams, foams and aerosol sprays for pharmaceutical applications, or dissolved to form solutions for coating substrates such as skin, fabrics, glass, leather and paper to give a bactericidal surface. A particular application of such a solution is as a protective, post-wash treatment for workwear in a laundering process. The powders of the invention may be prepared by slurrying a polysaccharide, which is capable of interacting with silver ions and which is in powder form, in a liquid in which the polymer is insoluble, which liquid contains silver ions, filtering off the powder, washing the powder, reducing the silver ions which have interacted with the polysaccharide to atomic / metallic silver, and drying the powder. According to the polysaccharide chosen, the liquid is suitably water or aqueous ethanol. The silver ions may derive from silver nitrate. The reduction of the silver ions which have interacted with the polysaccharide to atomic / metallic silver can be effected photochemically through exposure to light. To hasten the reduction, however, the washed powder is preferably slurried in a solution of an alkali metal halide, irradiated under stirring with natural or artificial light containing an ultraviolet component, and again filtered off and washed, before drying it.
Owner:HYDRODYNE SYST
Cylindrical attapulgite fly ash ceramsites
ActiveCN102515833AImprove resource utilizationReduce land occupationCeramic materials productionCeramicwareDusting powdersExpanded clay aggregate
Owner:南通沪联航海设备有限公司
Method for carrying out cutting seedling by Rosa multiflora Thunb seedling clods
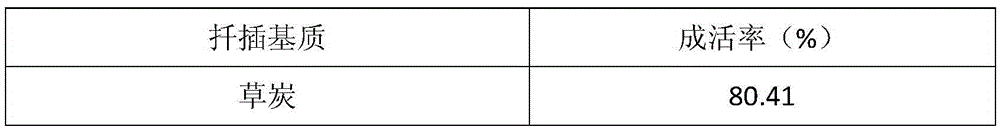
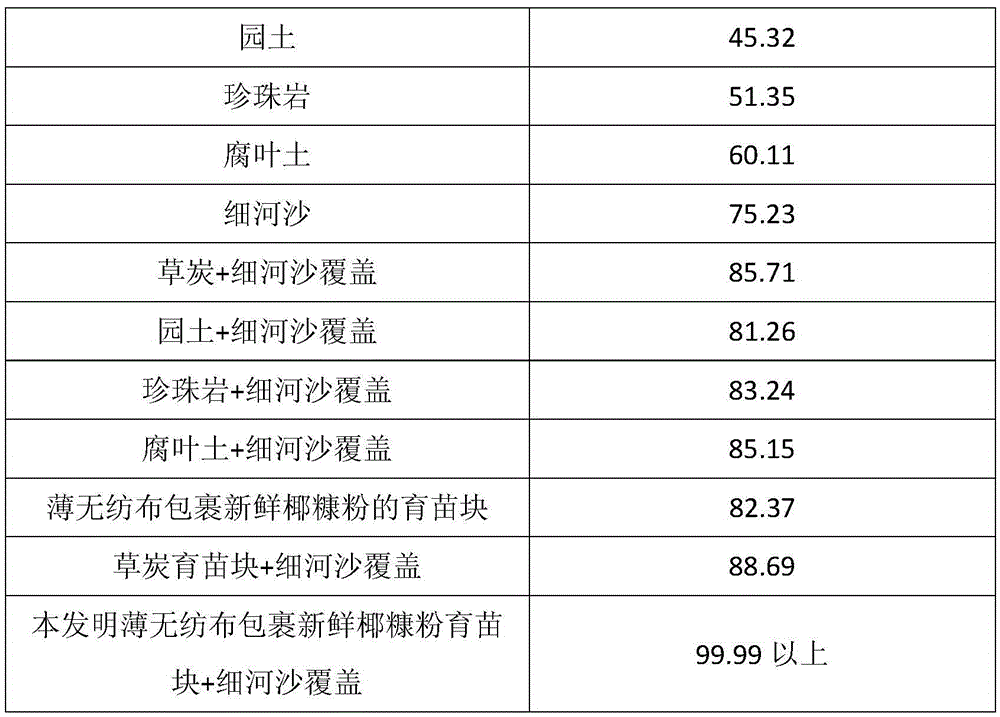
InactiveCN105494065AEffective protectionSimple processGrowth substratesCulture mediaFresh coconutDusting powders
The invention discloses a method for carrying out cutting seedling by Rosa multiflora Thunb seedling clods. The method mainly comprises: (1) cutting preparation, i.e., selecting 5 to 10cm of underyearling semi-lignified branches of Rosa multiflora Thunb; (2) preparation of the cutting seedling clods, i.e., shearing thin non-woven fabrics to coat fresh coconut dust powder so as to form the cylindrical seedling clods with diameters of 3cm and heights of 4cm; (3) cutting, i.e., removing leaves from the sheared branches and inserting the branches into the seedling clods; (4) coverage of thin fine river sand; (5) watering; (6) film mulching, wherein rooting occurs about 30 to 40 days after film mulching. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to operate, is hormone treatment-free, is short in rooting time, is suitable for large-scale Rosa multiflora Thunb industrial breeding, and has broad-spectrum adaptability.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Slow release compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of wheat
ActiveCN103058761AIncrease productionQuality improvementFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesDusting powdersManganese
The invention provides a slow release compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of wheat. The slow release compound fertilizer is a mixture of a plurality of fertilizers and components with no special fertilizer efficiency. The slow release compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of wheat uses compound fertilizer as the core of fertilizer and is prepared by filming and dusting powder processing; and the slow release compound fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials by mass: 21 to 47 parts of urea, 8 to 15 parts of ammonium sulfate, 10 to 30 parts of potassium sulfate, 20 to 35 parts of a mixed phosphate fertilizer, 0.1 to 0.5 part of an iron, manganese, boron, copper, zinc and molybdenum additive, 6 to 12 parts of a granulating auxiliary agent and a proper amount of water. A preparation method for the slow release compound fertilizer comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a compound of a potash fertilizer and a nitrogen fertilizer; (2) preparation of the mixed phosphate fertilizer; (3) preparation of mixed particles of the components of the compound fertilizer; (4) coating with stearic acid; (5) powder spreading of a modified zeolite powder material; and (6) screening, metering, quality inspection and packaging. The slow release compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of wheat provided by the invention has overall nutrients and excellent slow releasing performance, improves both output and quality of wheat, saves resources and protects the environment.
Owner:SHIKEFENG CHEM IND
Slow-release compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of corn
ActiveCN103058754AMeet nutrient needsIncrease productionDi-calcium phosphate fertilisersFertilising methodsDusting powdersStearic acid
The invention provides a corn-special slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer and belongs to the preparation of a mixture of a plurality of fertilizers and components with no special fertilizer efficiency. The invention is characterized in that the compound fertilizer is prepared by taking compound fertilizer particles as fertilizer cores, then performing coating and dusting powder treatment; the compound fertilizer particles are prepared by the following raw materials by the mass: 15 to 45 parts of urea, 5 to 40 parts of ammonium sulfate, 20 to 35 parts of potassium sulfate, 15 to 35 parts of a mixed phosphate fertilizer, 0.1 to 0.5 part of a zinc and iron additive, 7 to 10 parts of a granulating auxiliary agent and a proper amount of water. A preparation method for the compound fertilizer comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a compound of a potash fertilizer and a nitrogen fertilizer; (2) preparation of the mixed phosphate fertilizer; (3) preparation of mixed particles of the components of the compound fertilizer; (4) coating with stearic acid; (5) powder spreading of a modified zeolite powder material; and (6) screening, metering, quality inspection and packaging of qualified fertilizer. The scorn-pecial slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer applicable to plantation of corn provided by the invention has overall nutrients and excellent slow releasing performance, improves both output and quality of corn, and saves resources and protects the environment.
Owner:甘肃施可丰生态科技有限公司
Dust removing method and device of cantilever-type comprehensive mechanized development machine
The invention discloses a dust removing method and a device of cantilever-type comprehensive mechanized development machine; limited sealing space is formed among the external space of the cutting head of the development machine, the development machine body and the coal rock body; the dust powder produced in the process of cutting and smashing the coal rock through the cutting head of the development machine is sealed in the sealing space; the dust powder in the sealing space is removed through the spraying dust removing device; the dust powder in the sealing space is pumped out through the dust removing fan and purified. The invention can greatly reduce the dust powder produced in the cutting process of the development machine, prevent the dust powder dispersing in the working environment and effectively intercept the dust powder flying so as to purify the air and prevent the operator suffering from pneumoconiosis. The device has higher economic and social benefits.
Owner:陈中跃
Tea-dust glaze and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses tea-dust glaze and a preparation method thereof. The tea-dust glaze is prepared from albite, ferric oxide, silica, kaolin, talcum, calcium carbonate and tea dust powder. The preparation method comprises the steps that the raw materials are fully mixed, wet ball milling is conducted, and after screening is conducted, glaze slip is obtained; a green body is immersed into the glaze slip to be uniformly coated with the glaze slip, the glaze-coated green body is taken out and dried at a ventilation place, and a green body to be sintered is obtained; the green body to be sintered is placed in a furnace, heated to 900 DEG C, heated to 1,280 DEG through medium reduction sintering, heated to 1,300 DEG C through oxidation sintering, cooled to room temperature along with furnace cooling and then taken out to obtain a tea-dust glaze porcelain. Accordingly, the practicability of the tea-dust glaze is improved, and the glaze quality of the tea-dust glaze porcelain is greatly promoted.
Owner:德化县新君诚陶瓷工艺有限公司
An apparatus and method for beating and rolling a food doughbelt
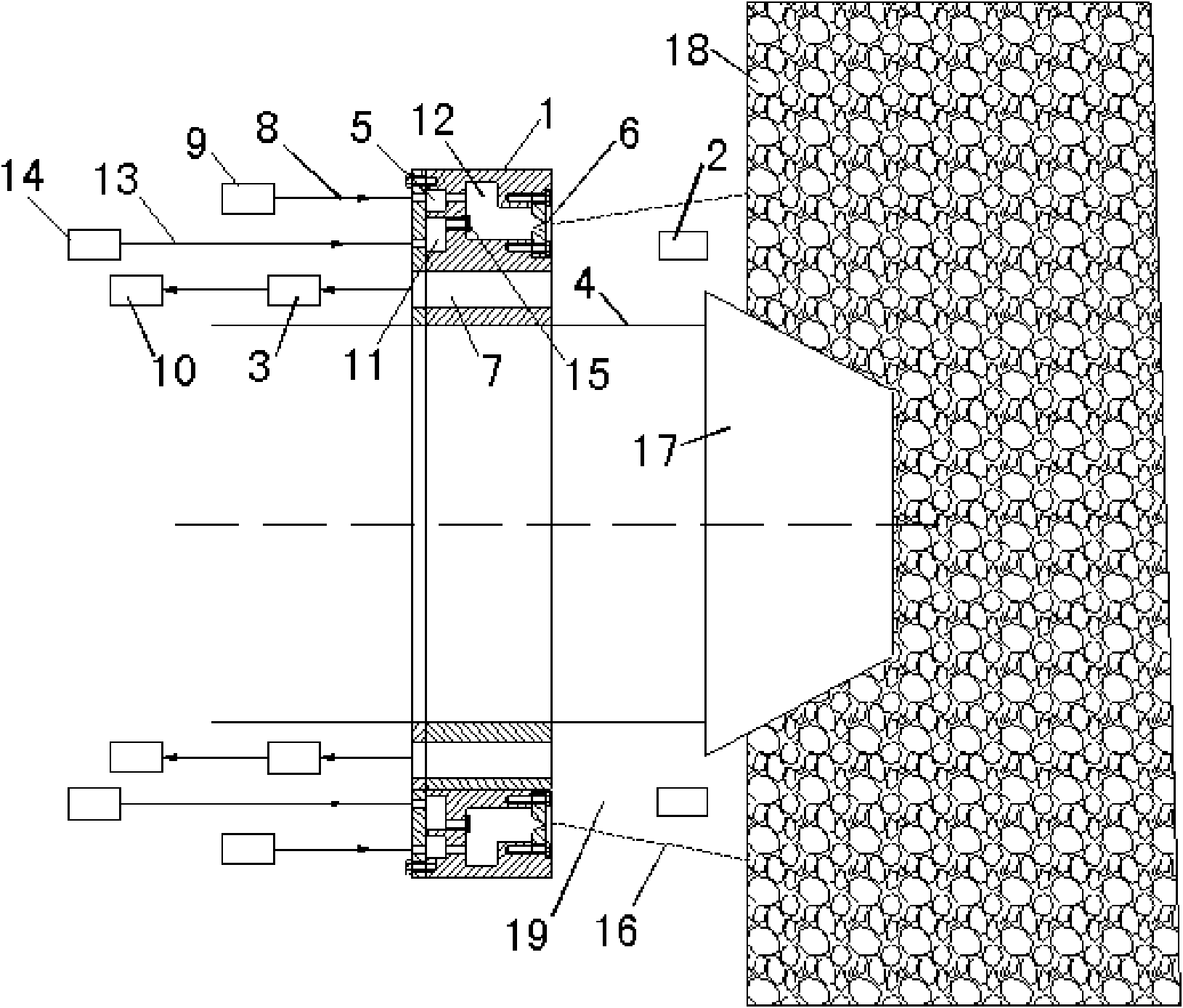
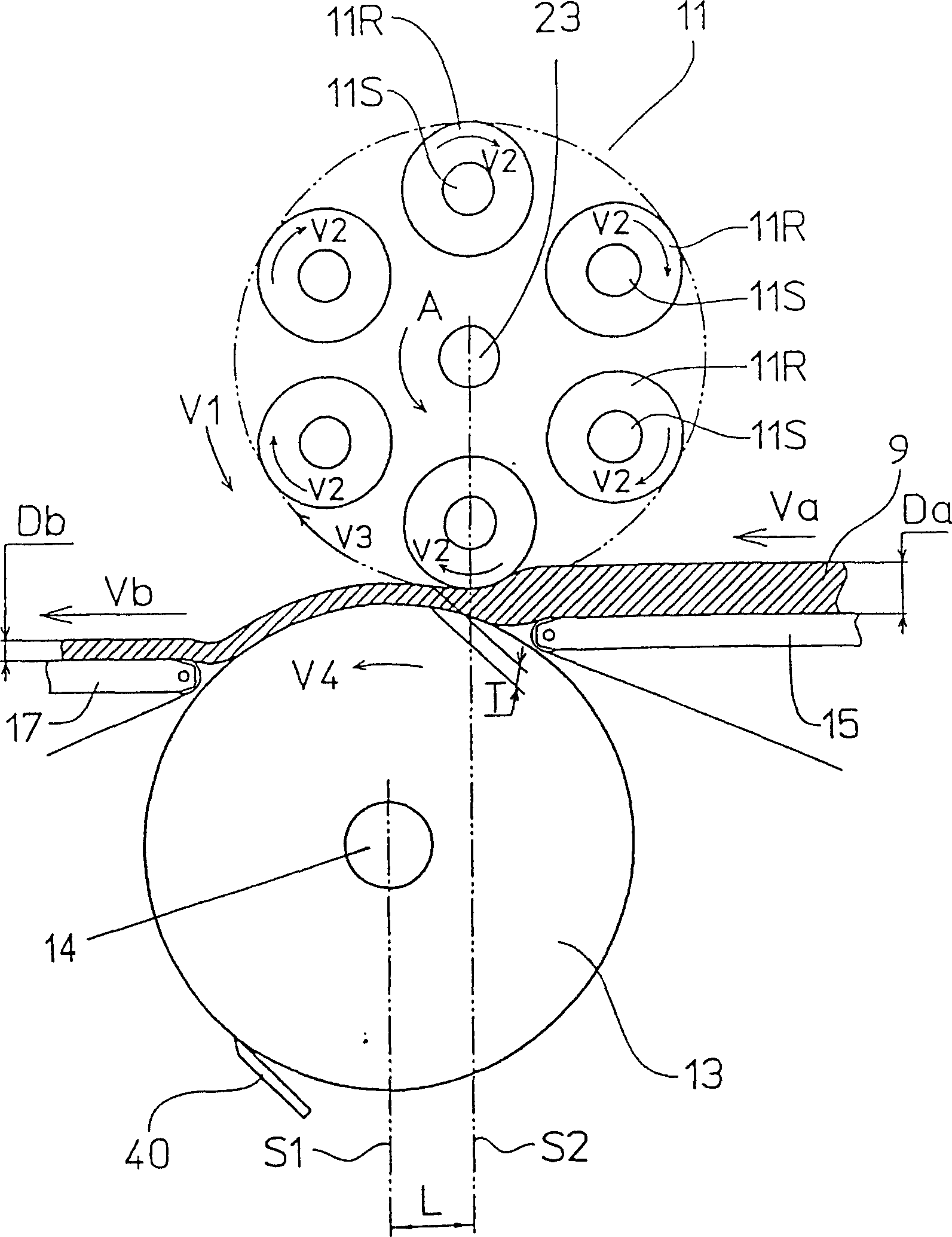
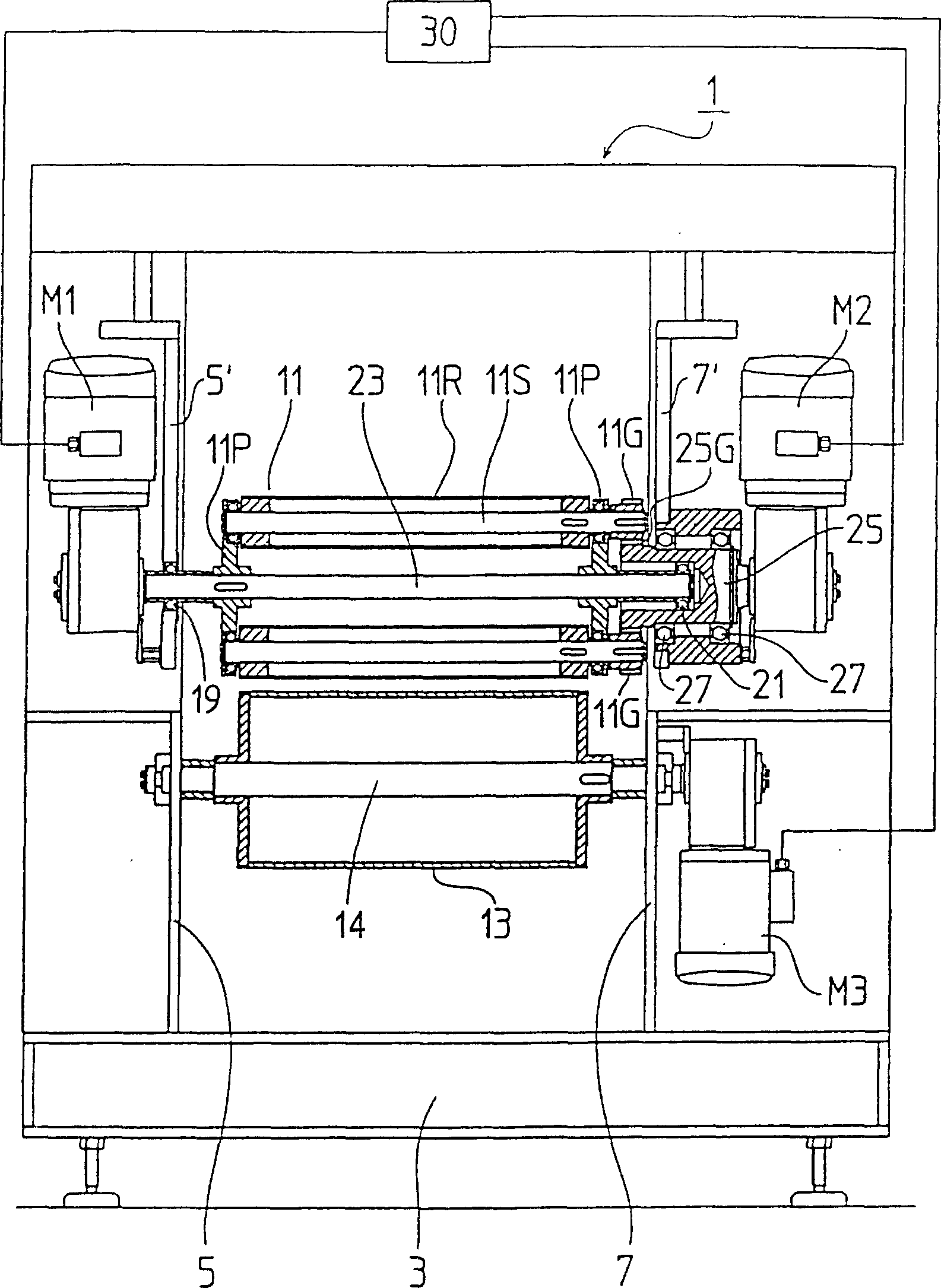
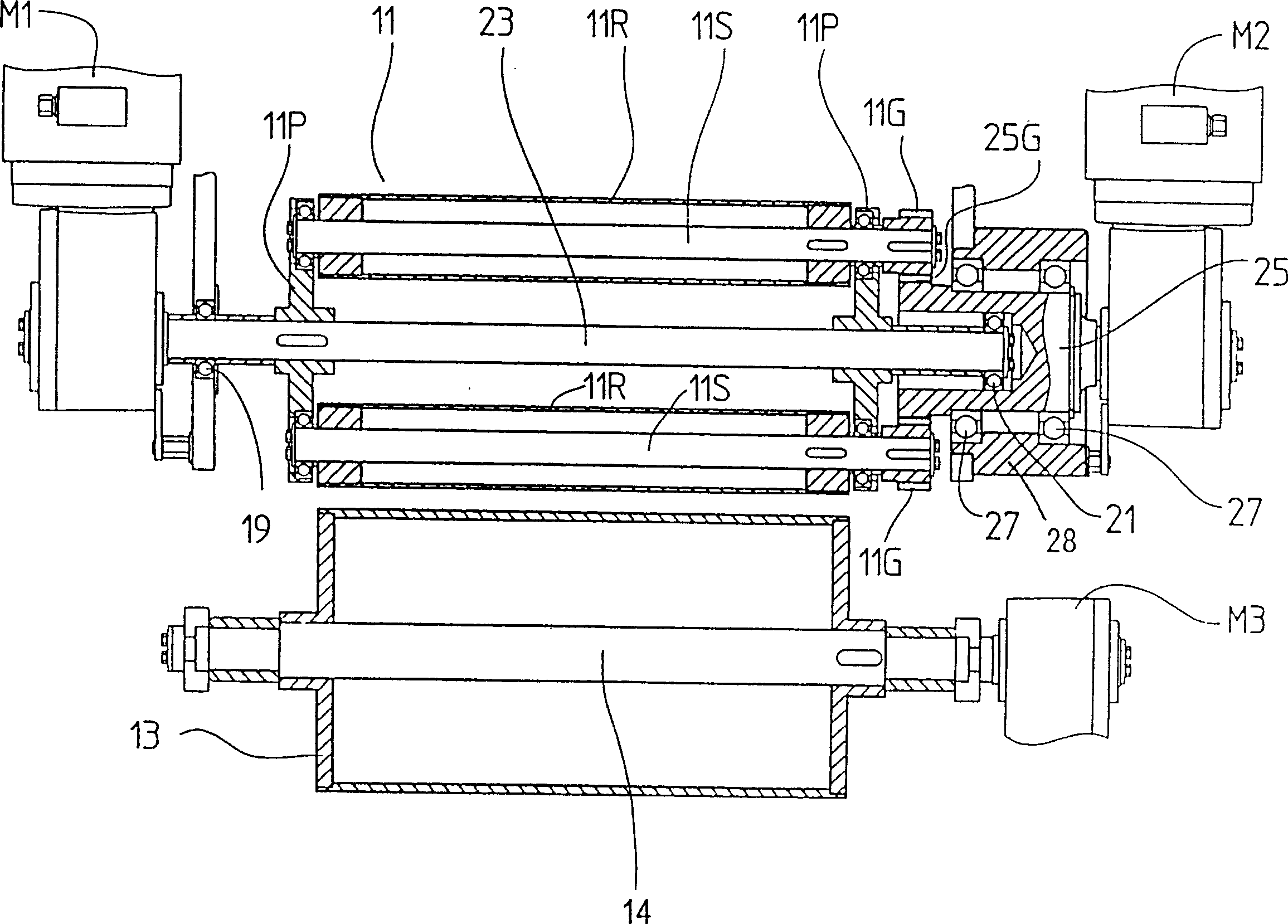
Conventionally, it has been necessary to use abundant dusting powder to prevent food dough from adhering to a rolling apparatus. A plurality of rolling rollers move sequentially upstream from downstream or downstream from upstream along the food dough belt, while each rolling roller rotates on its own axis. The moving direction of the rolling roller is changed according to technical requirements. The number of beats is regulated by changing the moving speed V1 of the rolling roller. Further, the peripheral speed of the rolling roller is made to be equal to or almost equal to the surface speed of the food dough belt by changing the rotating speed V2 of the rolling roller. Therefore, according to the invention, it is possible to reduce the amount of dusting powder and also to make the internal phase of bread dough uniform.
Owner:RHEON AUTOMATIC MASCH CO LTD
Power spraying spray coating automatic production line
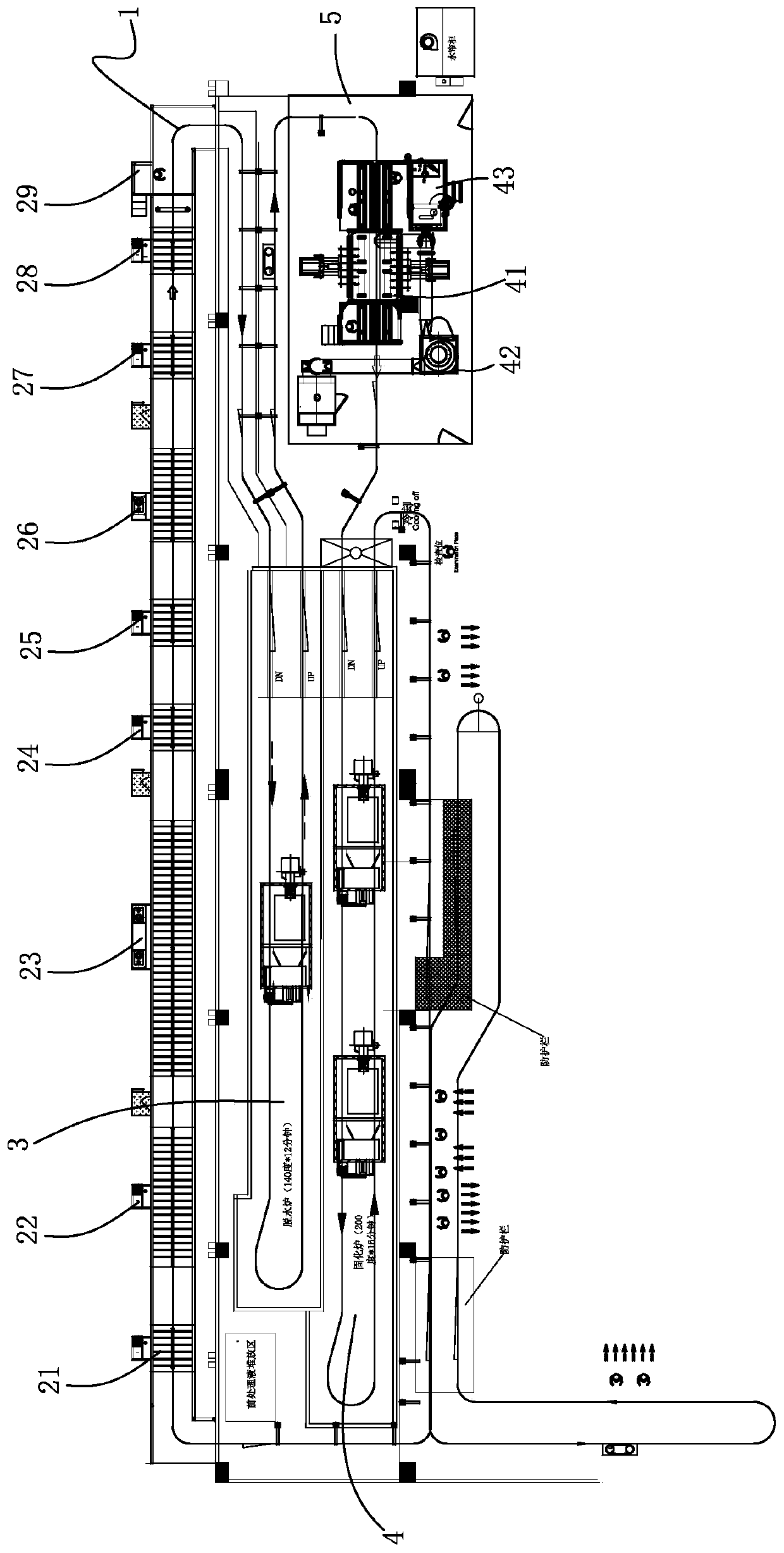
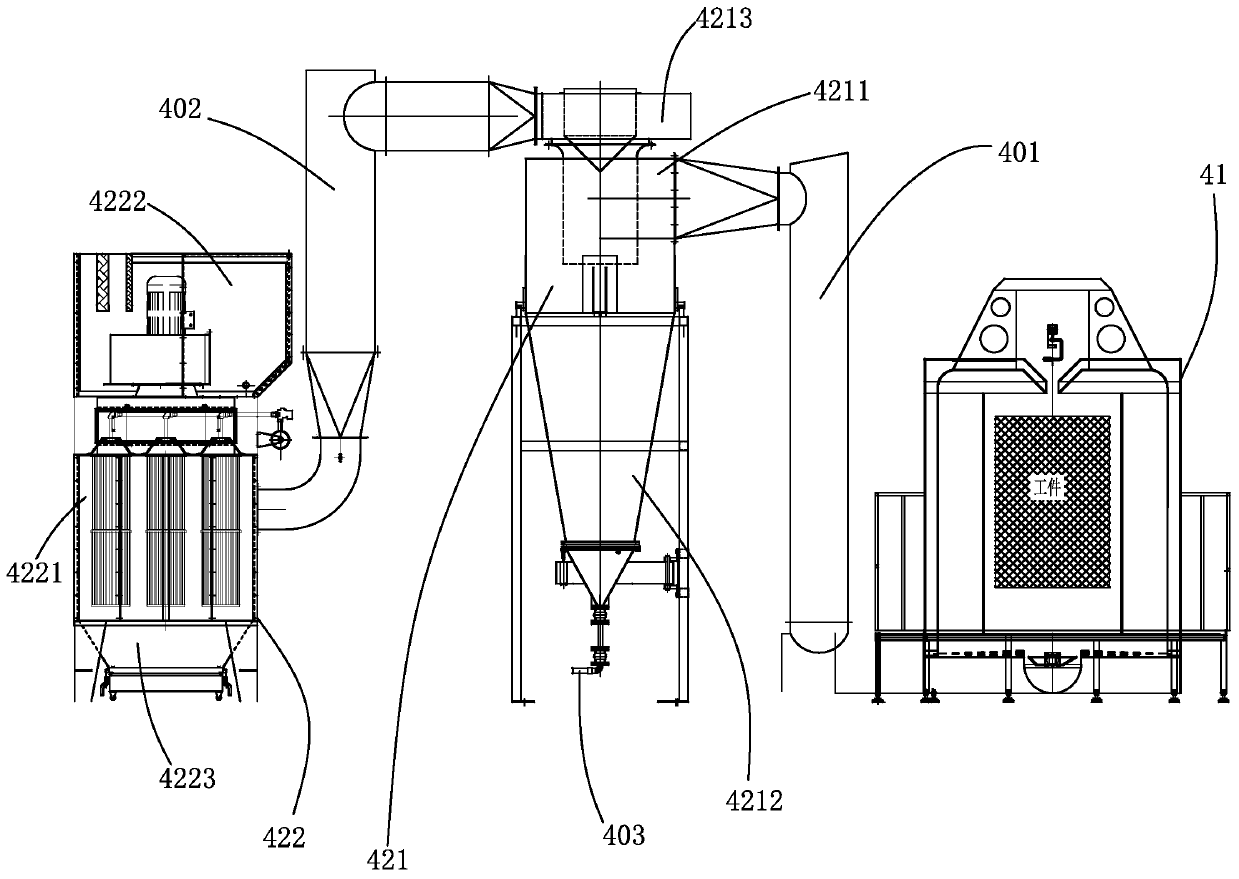
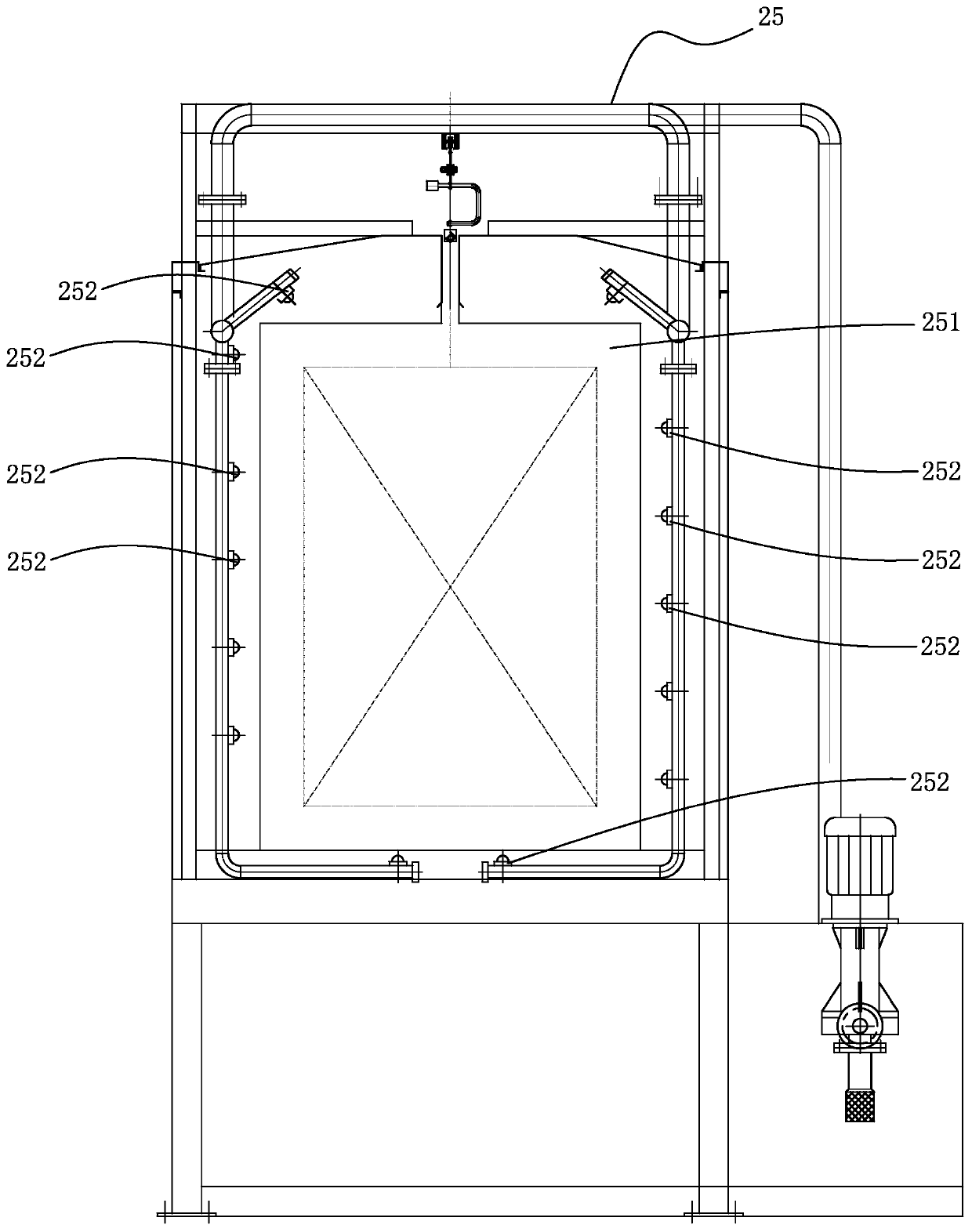
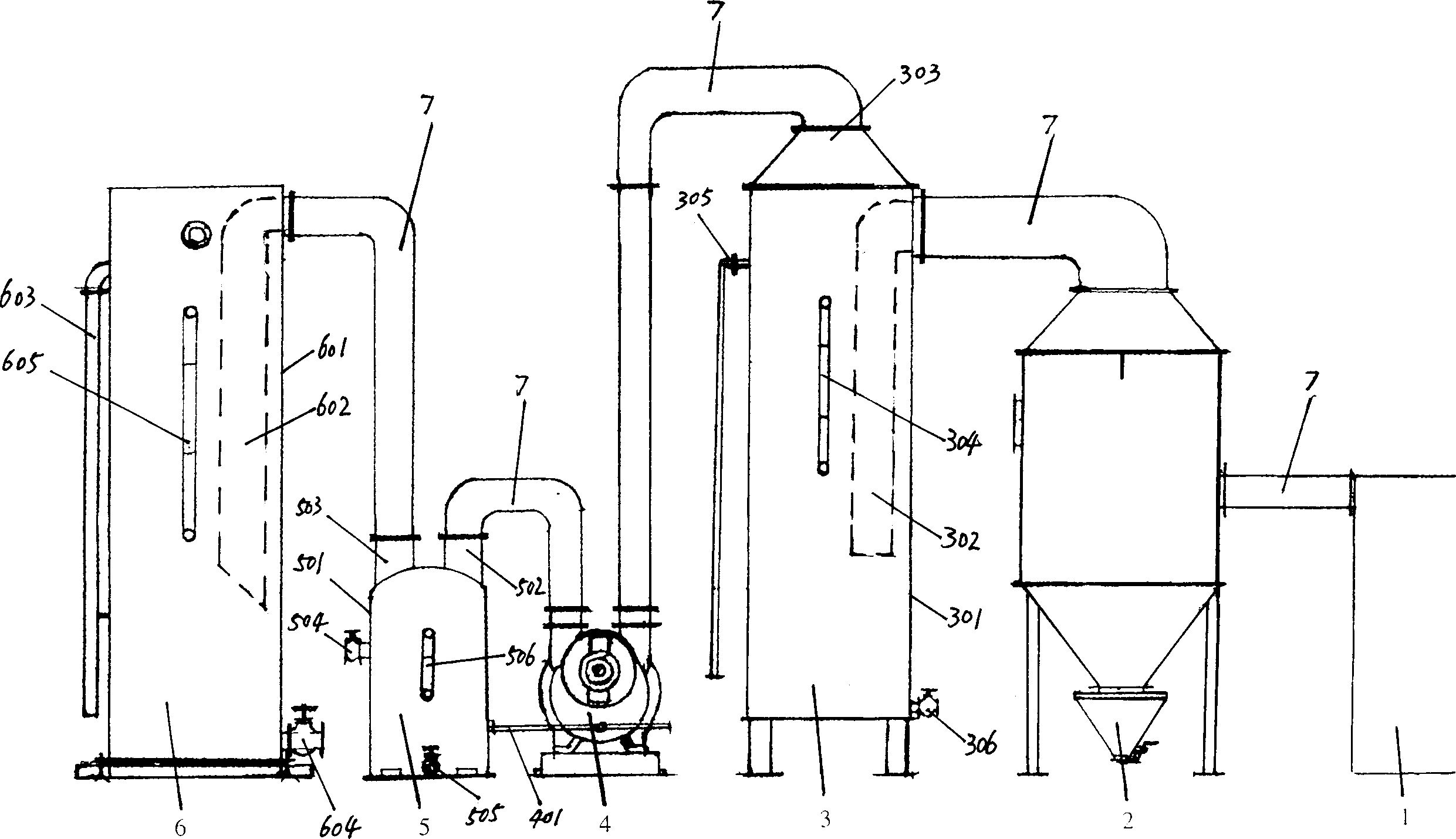
PendingCN111558486AImprove efficiencyReduce or even eliminate cleaningSpray boothsDusting powdersMetallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of an automatic production line of powder spraying on the surface of a workpiece, and particularly relates to a power spraying spray coating automatic production line. The power spraying spray coating automatic production line comprises a workpiece circulation conveying line, a spraying pretreatment system, a dewatering drying system, a powder sprayingsystem and a powder solidification system. By integrating the integral automatic production of pre-treatment, drying, powder spraying and solidification forming on the workpiece, the power spraying spray coating automatic production line has the advantages that the automation degree is high; and the production efficiency is greatly improved. In addition, a recovery filtering device for powder recovery and dust filtration and a power supply center are added to a spraying room; through the recovery filtering device, dust powder inside the spraying room is recovered; a part of the dust powder iscollected and treated through filtration; a part of the dust powder returns to the powder supply center to be directly and repeatedly used; the cost is reduced; and the dust utilization rate is improved.
Owner:中山方圆谷涂装科技有限公司
Stainless steel dusting powder reduced pellet containing photovoltaic material and production method thereof
InactiveCN102433444APromote reductionImprove dynamic conditionsProcess efficiency improvementDusting powdersMolten slag
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and particularly relates to a stainless steel dusting powder reduced pellet containing a photovoltaic material and a production method thereof. The photovoltaic cutting waste material and stainless steel dusting powder are mixed in a certain ratio and the mixture is pressed to obtain the reduced pellet. When stainless steel mother liquor is smelted in an electric furnace, the reduced pellet is directly added in the furnace and then returned back to the electric furnace along with scrap steel. The method has the breakthrough that chromium oxides and nickel oxides are combined with high-purity reducing metal silicon, thus the dynamical conditions for the reduction of chromium and nickel are optimized; and a lot of heat is generated when the metal silicon and silicon carbide in the stainless steel dusting powder reduced pellet are oxidized, thus slag is molten faster, the liquidity of the molten slag is improved and chromium and nickel can be reduced more easily.
Owner:上海盛宝冶金科技有限公司
Preparation method of special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer
ActiveCN103113153ASuitable for growthIncrease productionDi-calcium phosphate fertilisersAmmonium salt fertilisersDusting powdersStearic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of a special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer. The special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer belongs to mixtures of a plurality of fertilizers containing a material affecting nitrification of urea in soil and an un-specificness fertilizer component. The special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 20-45 parts of the urea, 10-20 parts of ammonium sulfate, 20-40 parts of potassium sulfate, 10-30 parts of mixed phosphatic fertilizer, 0.1-0.5 part of zinc, copper, boron and molybdenum additive, 6-12 parts of granulation addition agent and a right amount of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a mixture of a potash fertilizer and a nitrogenous fertilizer; (2) preparing the mixed phosphatic fertilizer; (3) preparing mixed particles of each component of the compound fertilizer; (4) filming stearic acid; (5) dusting powder on a modified zeolite powder body material; and (6) screening. By utilizing the preparation method, conventional prejudices are overcome, the production cost is reduced, and environmental protection is facilitated. The invention provides the preparation method of the special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer which is comprehensive in nutrition, excellent in slow-release performance and high in fertilizer using efficiency. By utilizing the special tobacco slow-release long-acting compound fertilizer, requirements on nutrient by tobacco can be fully met, the output of the tobacco can be improved, and the quality of the tobacco can be improved.
Owner:SHIKEFENG CHEM IND
Apparatus and method for removing smoke of boiler
InactiveCN1395979AExtended service lifeEasy to discharge ashCombination devicesImpellerChemical reaction
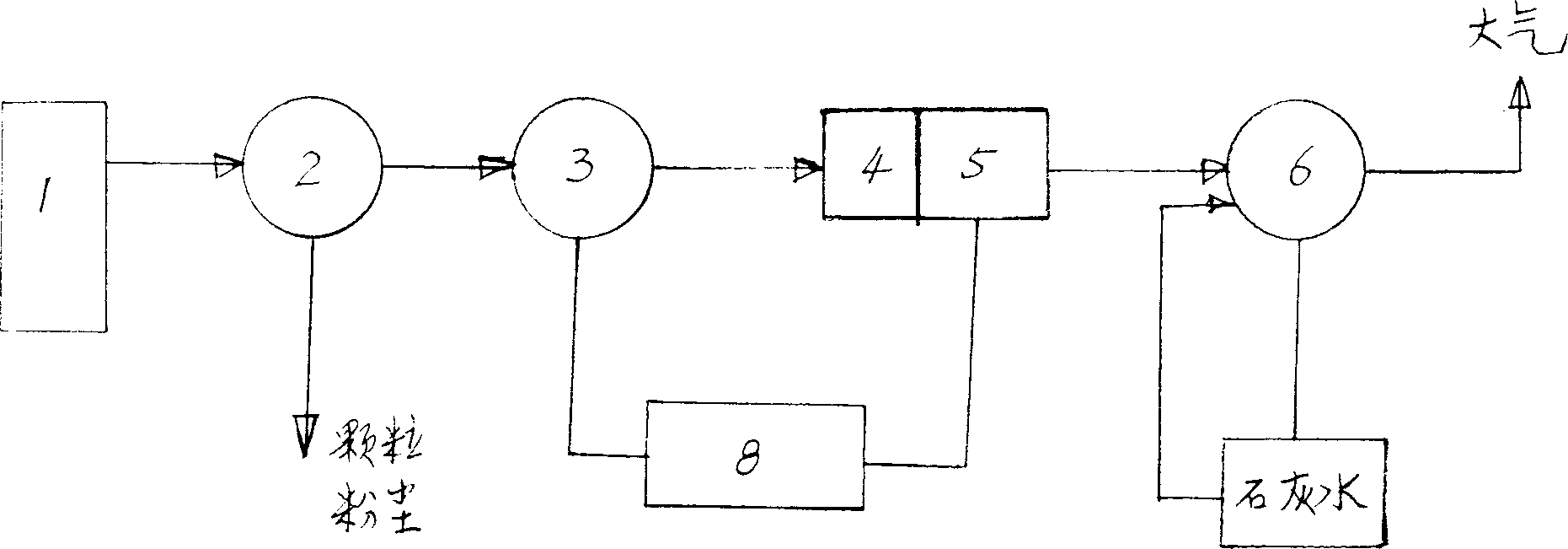
A smoke cleaner for boiler and its cleaning method are discloosed. The smoke from boiler flows through cyclone dust collector for removing dust, hydraulic draught fan, wet dust for further removing dust and sulfuride, and gas-water separator for separating water from gas. The water containing dust powder flows in depositing pool. The gas flows into lime milk in desulfurizer to obtain chean gas for exhausting. Its advantages are high effect and low corrosion to equipment.
Owner:张福生
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com