Epitope identification method of thallus antibody
A technology of antigenic epitopes and bacterial antibodies, applied in chemical instruments and methods, specific peptides, anti-bacterial immunoglobulins, etc., to achieve the effects of improving research efficiency, reducing the number of synthesis, and reducing workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
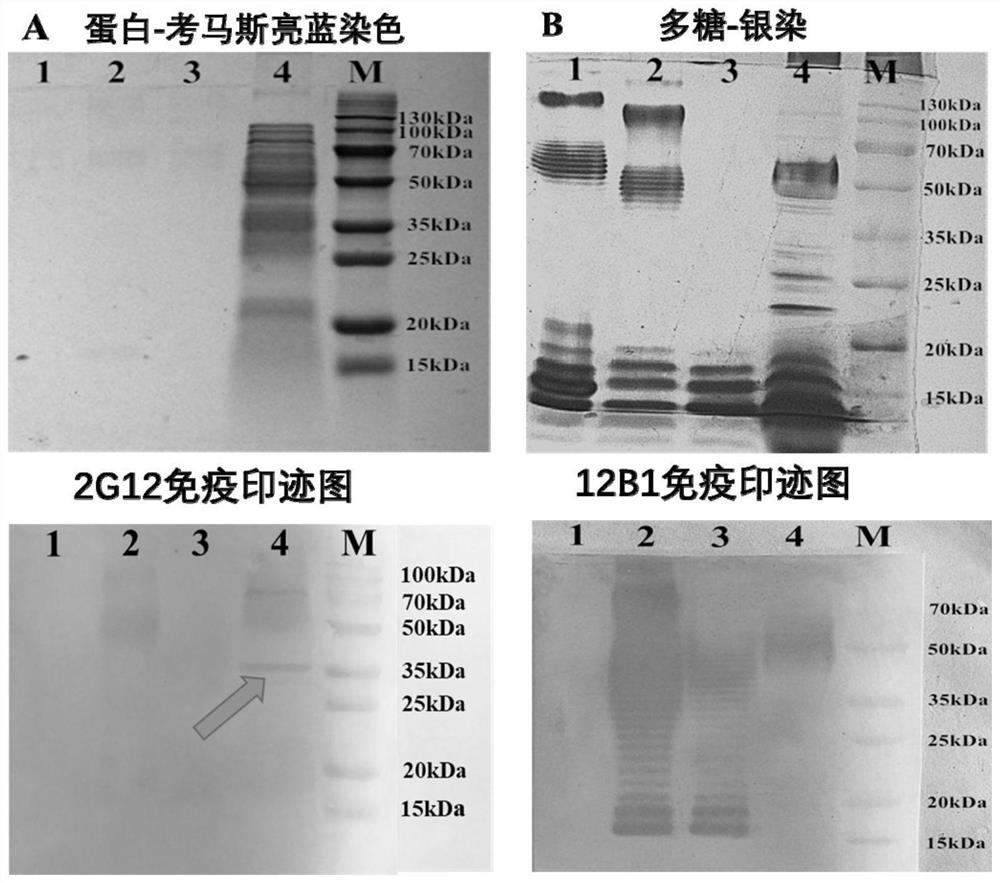
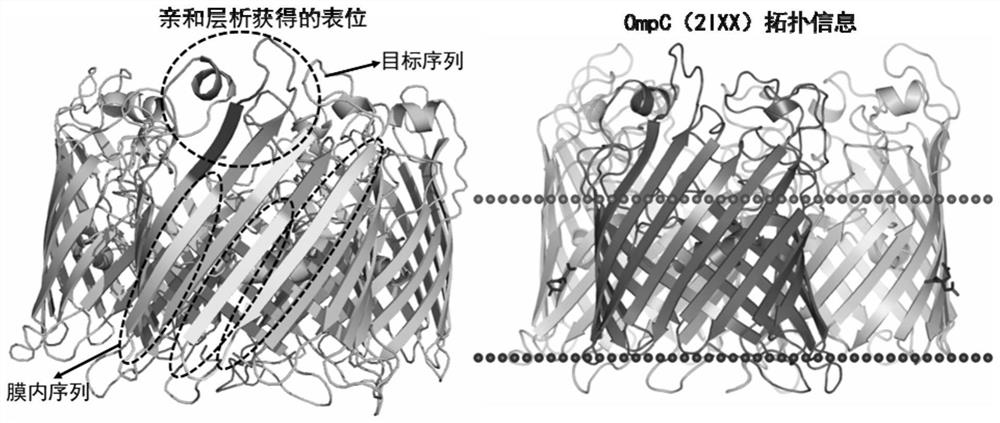
[0033] The recognition epitope identification of implementation example 1 monoclonal antibody 2G12
[0034] (1) Identification of the type of antigen recognized by monoclonal antibody 2G12
[0035] Bacterial whole bacterial protein was prepared by ultrasonic crushing method. The ultrasonic conditions were fully mixed in an ice bath, ultrasonic crushed in an ice bath at 4°C, and the intensity was 50%. Centrifuge the sonicated bacterial solution at 12,000 g at 4°C for 10 min, and collect the supernatant. The whole bacterial protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE protein gel electrophoresis, and the protein was transferred to PVDF membrane by electroporation and semi-dry method (current was 40mA / cm, electroporation was 30min), and immunoblotting was performed (primary antibody and secondary antibody Concentrations were 0.5 μg / mL and 0.2 μg / mL).
[0036] Bacterial lipopolysaccharide was extracted by the hot phenol method, and E.coli O157:H7 was cultured at 37°C for 24 hours,...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Cross-reactivity test of embodiment 2 monoclonal antibody 2G12
[0060] The cross-reaction of monoclonal antibody 2G12 to 68 strains of bacteria was detected by indirect ELISA coated with bacteria. ① Packing plate: Take the boiled and inactivated E.coli O157:H7 bacteria and dilute it with CBS carbonate buffer to a concentration of 108 CFU / ml, add 100uL / well to the microtiter plate. Afterwards, the plate was sealed and placed in a constant temperature incubator, and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. ②Washing: shake off the liquid and pat dry, add washing solution at 230uL / well, oscillate on a shaker at a constant speed for 3min, spin dry, repeat the steps of washing 3 times, and pat dry. ③Sealing: Add 200uL / well of blocking solution, seal the plate and put it into a constant temperature incubator to seal for 2h. ④ Add serum: After washing according to step (2), dilute the monoclonal antibody (2G12, 12B1 in this article) with antibody diluent (take it out of the refrigerat...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Example 3 Affinity Determination of Monoclonal Antibody 2G12
[0062] The bacteria liquid to be tested was from 10 8 / mL began to coat with six different concentrations of 3-fold dilution of the coating solution, and each well was made in triplicate. Starting from 4 μg / mL, monoclonal antibody was diluted 8 times by 3 times, and the titer of monoclonal antibody (mAb) was determined by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent method. Then, with the logarithmic value of mAb concentration (μg / mL) as the abscissa and the absorbance value Abs (450nm) as the ordinate, four S-shaped curves (R 2 ≥0.99), calculate the corresponding antibody concentration when Abs (450nm) is 50% of the highest absorbance value according to the curve equation, convert the unit mol / L of the antibody concentration, and then calculate the affinity constant (Ka ):
[0063] Ka=(n-1) / 2{n[Ab']t-[Ab]t}
[0064] Among them, n is the ratio of the two coating concentrations (greater than 1); [Ab']t is the cor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com