Expression system utilizing GPI anchor protein containing selenocysteine and cell for highly expressing recombinant protein
A selenocysteine and anchored protein technology, which is applied in the field of cells using a GPI-anchored protein expression system containing selenocysteine and cells with high expression of recombinant proteins, can solve hair loss, nail and skin darkening and other problems to achieve the effect of simplifying difficulty and convenient screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
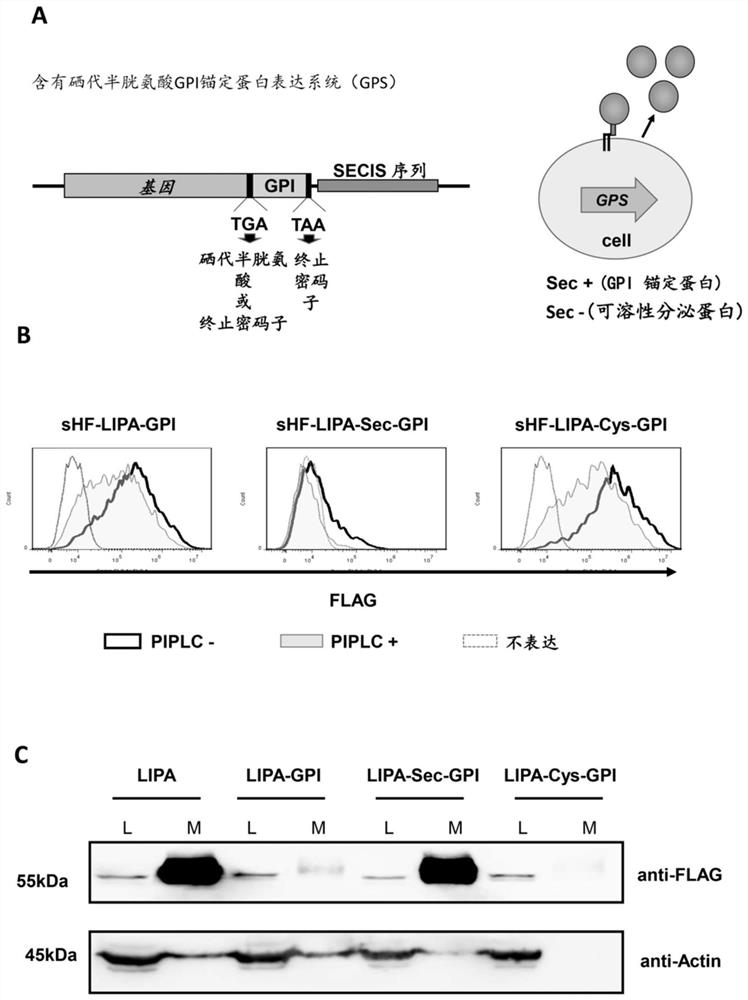
[0033] Construction of a GPI-anchored protein expression system containing selenocysteine (taking recombinant lysosomal acid lipase (LIPA) as an example) by combining the oxidoreductase protein family selenocysteine and GPI Ankyrin synthesis features are constructed.
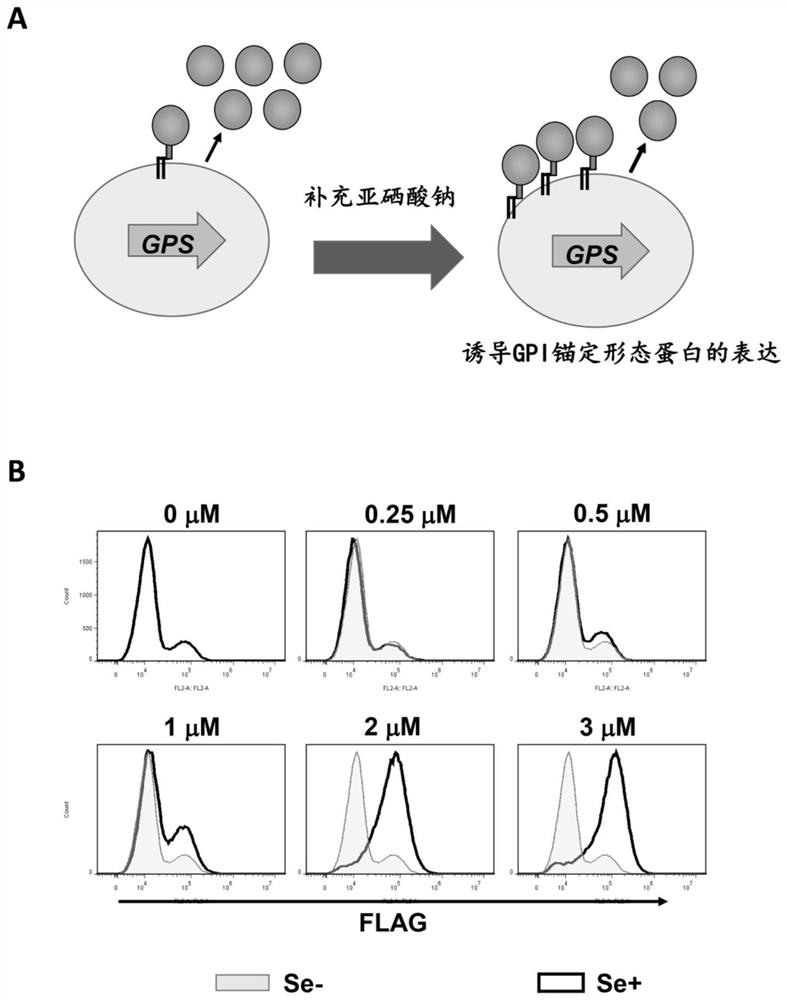
[0034] To express LIPA with GPI-anchored and soluble forms, the stop codon UGA was inserted before the GPI attachment signal sequence of pME-Puro-sHF-LIPA-GPI (sHF stands for endoplasmic reticulum signal sequence plus His6-FLAG-tag ) by site-directed mutagenesis of CTAATGAGGAAATATCAGTGACTCGAGAATGGTGGGACA and TGTCCCACCATTCTCGAGTCACTGATATTTCCTCATTAG with primers to generate pME-Puro-sHF-LIPA-TGA-GPI. The SECIS sequence of the human SELT gene was amplified using the primer set TCATCCCTAAGCGGCCGCCACCCTATCAGCACTGAAAAC and GACTAGTCTAGCGGCCGCGCCAGCACTGCATGCACTGAAACACTATCTTG, and the stop codon (UAA) of the LIPA-TGA-GPI sequence was inserted after the NotI site by infusion cloning. The sHF-LIPA-GPI and sHF-LIPA-Sec...
Embodiment 2
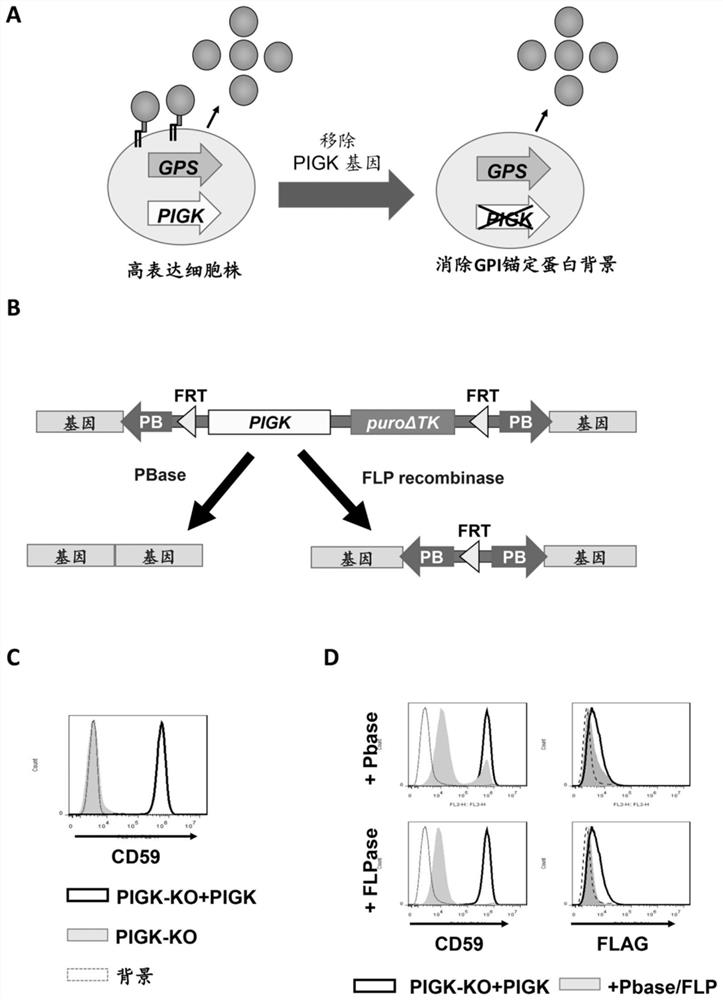
[0041] Construction of a system for removing the PIGK gene: First, the PIGK gene was knocked into HEK293 cells using the CRISPR / Cas9 system. BbsI cuts the vector pX330-EGFP(25). The PIGK-KO target sequence set caccGCTCTTGTCCTTCGGCAGCGTGG and aaacCCACGCTGCCGAAGGACAAGAGC were ligated into digested pX330-EGFP to generate pX330-EGFP-PIGK-KO. After transfection, cells with EGFP were sorted with a cell sorter S3 (Bio-Rad Laboratories). The collected cells were cultured for 7 days or more and subjected to limiting dilution to obtain clonal KO cells. The clone without WT allele was selected, and the DNA sequence was analyzed by sequencing. Then, the PIGK expression construct was inserted into the genome of PIGK-KO cells. The vector was pPB-FRT-PGKp-PurodTK, which contained a PGK promoter, a poly Cloning site, a bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal, an SV40 promoter and puroΔTK flanked by PB terminal repeats and Flippase recognition target (FRT) ends. PIGK was amplified and ...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Validation of elimination of GPI-form recombinant proteins by knocking out the PIGK gene: Even though we obtained cell lines highly expressing recombinant proteins using the GPS system, some recombinant proteins were expressed on the cell surface in the form of GPI-AP. When administered as a drug, the small fraction of GPI-anchored forms may affect protein properties such as activity and immunogenicity. We therefore next attempted to eliminate the GPI-anchored form from cells.
[0050] For this purpose, we established cell lines that can regulate the expression of the GPI biosynthesis gene PIGK. Deletion of endogenous PIGK from HEK293 cells resulted in loss of GPI-AP expression (attached image 3 A). Then, a cassette containing the PIGK gene fragment and the puroΔTK gene flanked by FRT sites and PB transposon recognition sites was reinserted into the genome to restore GPI-AP expression in the rescued cells. In this system, PIGK can be excluded by FLP recombinase or P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com